クラッシュカットナイフ 重工業機械向けに設計された特殊なブレードです。これらのクラッシュカットナイフは、材料をスライスするのではなく、押し付けて破砕することで切断するため、標準的なブレードでは切断が難しい、硬くて繊維質な材料に最適です。ブレードが硬い表面に接触することで、きれいで効率的な切断を実現します。
重要なポイント
- クラッシュカットナイフは、硬い素材を切るのではなく、強い力で砕きます。そのため、繊維、ゴム、プラスチックの切断に適しています。
- これらのナイフは、刃先が丸みを帯びているため、力が分散されます。これにより、刃の寿命が長くなり、よりきれいに切ることができます。
- 空気圧システムは、刃の動きの強さと速度を制御します。これにより、機械は迅速かつ安全に、そして正確に切断することができます。
- クラッシュカッティングはセットアップが簡単なので、時間とコストを節約できます。メンテナンスもほとんど必要なく、多くの材料や業界で使用できます。
- 南京Metalのカスタムクラッシュカットナイフは、刃の寿命を延ばし、機械の停止回数を減らします。また、特殊な切断作業にも適しており、工場の生産性向上にも貢献します。
クラッシュカットナイフの概要
クラッシュカットナイフとは
クラッシュカットナイフは多くの工場で重要な役割を果たしています。これらの刃は通常のナイフのように切るのではなく、力を使って材料を砕き、破砕します。この方法は、硬いものや繊維質のものに適しています。鋭利な刃では切りにくいものにも適しています。工場では、繊維、ゴム、一部のプラスチックなどにクラッシュカットが使用されています。
これらのナイフは、湾曲した刃先を持つ丸い刃を備えています。刃先はカミソリのように鋭くはなく、強く押し付けるように作られています。刃は回転し、丈夫な金属の金床と連動して動作します。以下の表は、これらのナイフの主な特徴を示しています。
| 特徴/測定 | 説明/価値 |
|---|---|
| ブレードタイプ | 丸みを帯びた刃先を持つ回転円形刃 |
| ブレードのベベル角度 | 30°、45°、または60°(45°が一般的) |
| エッジ半径 | 0.05 mm~0.30 mm(ユニバーサル:0.10~0.15 mm) |
| ブレード材質 | D2工具鋼、HSS-M2 |
| アンビルロール硬度 | 63-65 HRC(刃よりも硬い) |
| ナイフの装填 | 強力なシリンダーで空気圧で負荷をかける |
| カット圧力 | プログラム可能で調整可能 |
| 最大切断速度 | 1分間に最大60カット |
| 切断長さの精度 | +/- 0.1 mm |
クラッシュカットナイフの仕組み
クラッシュカットは特殊な方法で行われます。刃が上下に動き、材料を金床に押し付けます。これにより、接触部分に大きな圧力がかかります。材料はスライスされるのではなく、その力によって砕かれます。 プラスチックと金属のテストではこれが示されています。 物質は圧縮されると壊れる切るのではなく、切るのです。例えば、プラスチックを切るとき、刃が押し下げられます。すると、隙間ができ、ひび割れが生じ、プラスチックが割れてしまいます。
空気圧システムがブレードの圧力と動きを制御します。作業者は様々な材料に合わせて圧力を調整できます。金床はブレードよりも硬いため、ブレードが先に摩耗します。これにより、切断面がきれいになり、両方の部品の寿命が長くなります。ブレード、金床、材料の速度を一致させることで、すべてがスムーズに進み、良好な結果が得られます。
ヒント:クラッシュカットは、刃がスライスするのではなく押し付けるため、粉塵が非常に少なくなります。これにより、多くの工場作業において作業場を清潔に保つことができます。
クラッシュカットプロセス

ナイフとアンビルの機構
接触原理と力の適用
クラッシュカットは、強力でありながらシンプルな切断方法です。クラッシュカットナイフを硬い金床またはローラーに押し付けます。これにより、刃が材料に接触する部分に高圧の線が作られます。この圧力は材料を切断するのではなく、圧縮して砕きます。この方法は、通常の刃では切断しにくいものに適しています。
機械試験では、力が非線形に増加することが示されています。刃の下には「先端破砕帯」と呼ばれる特殊な部分が形成されます。この部分で、材料は小さな破片や粉末に変化します。科学者たちは次のようなアイデアを用いています。 最小限の仕事とエネルギーのバランス これを説明するには、これらの考え方が、材料が切れるのではなく折れる理由を説明しています。ナイフと金床は正確に一直線上になければなりません。これにより、きれいな切り口が得られ、材料が過度に曲がるのを防ぐことができます。
切削品質に対するR刃先の影響
クラッシュカットナイフにとって、R刃は非常に重要です。この刃は丸みを帯びており、他の刃のように鋭くはありません。丸みを帯びた形状により、力が小さな点に分散されます。これにより、刃とアンビルの損傷を防ぎ、刃の寿命も長くなります。R刃はカットをよりきれいにし、工程を安定させます。工場では、それぞれの材料と切断品質に合わせて適切な刃のRを選択します。
産業機械統合
空気圧作動ワークフロー
多くの機械は、クラッシュカットナイフを動かすために空気圧を利用しています。空気圧シリンダーが空気で刃を上下に動かします。作業者は材料の種類に合わせて空気圧を調整できます。これにより、切断は高速で、再現性が高く、正確になります。空気圧を使用することで、手作業の負担が軽減され、安全性も向上します。
産業機械における統合手順
工場ではクラッシュカットナイフを追加するためにいくつかの手順に従います。
- ナイフとアンビルを機械のフレームに置きます。
- シリンダーにエアラインを取り付けます。
- 適切な圧力を設定し、部品を並べます。
- テスト材料で切断してみてください。
以下の表に、マシンの重要な機能を示します。
| 機能/パラメータ | 振動ナイフ切断機(クラッシュカットナイフ付き) |
|---|---|
| 切断方法 | 高周波のブレード上下運動 |
| 材料の適合性 | 軟質から半硬質の材料 |
| 切削精度 | 高い |
| エッジ品質 | きれいで、焼け跡はありません |
| スピード | 速い |
| 材料の歪み | 最小限 |
| 騒音レベル | 適度 |
| 粉塵と煙の発生 | 低い |
| ツールのメンテナンス | ブレード交換のみ |
| 自動化の互換性 | 高性能CNC制御 |
| 切断厚さ | 厚い素材もうまく扱えます |
| 多層切断 | はい |
| 切断パスの複雑さ | 複雑で鋭角な角度に最適 |
| 安全性 | より安全(高熱や裸火は使用不可) |
| 運用コスト | 低い |
空気圧システムの利点と欠点
空気圧システムには多くの利点があります。反応が速く、圧力の変更も簡単です。メンテナンスも簡単で、通常は刃を交換するだけです。これらのシステムは消費電力が少なく、切断速度も速いです。しかし、空気漏れがないか確認し、圧力を一定に保つ必要があります。そうすることで、システムを良好な状態に保つことができます。空気圧駆動は工場内の機械に最適です。手工具や工場以外の作業には適していません。
クラッシュカットと他の方法の比較
せん断切断の比較
操作の違い
せん断切断では、2枚の刃が互いにすれ違うように動きます。はさみのように機能し、材料をきれいに切り分けます。一方、クラッシュ切断は異なります。丸い刃を硬い金床に押し付けます。材料はスライスするのではなく、圧力によって砕けます。いくつかの研究によると、クラッシュ切断は高価な工具よりも材料と費用を節約できるとされています。せん断切断はより滑らかで正確な切れ味を実現します。クラッシュ切断は、硬い材料や繊維質の材料に適しています。
セットアップとメンテナンスの要件
シャースリッター機では、両方の刃を正確に揃える必要があります。作業者は刃の角度と間隔を調整する必要があります。これには時間がかかりますが、切れ味は良好です。シャースリッター機では、両方の刃を研磨し、損傷がないか確認する必要があります。一方、クラッシュカットのセットアップは簡単です。作業者は刃とアンビルを揃えるだけです。メンテナンスは、刃が鈍くなったときに交換するだけです。これにより、忙しい工場でもクラッシュカットが容易になります。
適切な材料と用途
せん断は、薄い、弱い、または壊れやすい素材に最適です。工場では、フィルム、箔、薄い紙などに使用されます。一方、クラッシュカットは、厚い、強い、または粘着性のある素材に適しています。繊維、ゴム、不織布工場の多くのスリッター機では、クラッシュカットが使用されています。どちらを選ぶかは、何を切断するか、そしてどのような端面を希望するかによって異なります。
| パフォーマンスメトリック | せん断切断 | クラッシュカッティング |
|---|---|---|
| エッジの滑らかさ | とても滑らか | ざらざらした、ギザギザした |
| エッジの直角度 | 正方形、正確 | 変形、巻き |
| 粉塵発生 | 最小限 | さらにほこり |
| ナイフライフ | より長い | 短い |
| 材料の適合性 | 薄くて脆い | 丈夫で繊維質 |
カミソリによるスリットの比較
操作の違い
カミソリカットは、鋭く薄い刃を使って材料を切断します。材料が刃の前を通過する間、刃は静止しています。そのため、非常にきれいな切断面が得られます。一方、クラッシュカットは、力を使って材料を破断します。カミソリカットは軽い材料に最適です。クラッシュカットは、重い製品や層状の製品に適しています。
セットアップとメンテナンスの要件
カミソリ式スリッターは刃がすぐに鈍くなるため、頻繁に交換する必要があります。セットアップは簡単ですが、作業者は刃の状態を注意深く確認する必要があります。メンテナンスとは、刃の交換と機械の清潔さの維持です。クラッシュカット用のセットアップは、新しい刃が必要になるまでの寿命が長くなります。ただし、非常に硬いものを切断する場合は、刃の摩耗が早くなることがあります。
適切な材料と用途
レーザースリッターは、薄いフィルム、ラップフィルム、軽い紙などに最適です。厚手のものや粘着性のあるものにはあまり適していません。クラッシュカットは、粘着テープ、繊維、不織布に適しています。工場では、切断対象に応じて適切なスリッターを選択します。
エッジ品質とメンテナンス
エッジ品質の比較
エッジの品質は、使用する切断方法によって異なります。シアースリッターは最も滑らかで正確なエッジを作ります。レザースリッターもきれいなエッジを作りますが、刃が鈍い場合は小さなバリが残ることがあります。クラッシュカットは、凹凸のある粗いエッジになることが多いです。試験では、クラッシュカットはバリが多くなり、エッジの曲がりが少なくなることが示されています。完璧なエッジを求める工場では、通常、シアースリッターまたはレザースリッターが選択されます。
メンテナンスの要求
メンテナンスの必要性は、それぞれの方法によって異なります。シャースリッターは、頻繁に研磨と慎重なセットアップが必要です。レザースリッターは、頻繁に新しい刃が必要です。クラッシュカッティングシステムは、セットアップはそれほど必要ありませんが、特に硬い材料の場合は、より頻繁に新しい刃が必要になる場合があります。テストでは、良質の刃は長持ちすることが示されていますが、すべてのスリッターは、切断を安全かつ清潔に保つために定期的な点検が必要です。
注: 適切なスリッターと切断方法を選択すると、工場はエッジの品質、速度、メンテナンス コストのバランスをとることができます。
クラッシュカットスリッティングアプリケーション

クラッシュカットスリッティングを使用する業界
多くの工場では、毎日クラッシュカットスリットを使用しています。この方法は多くの大規模産業で役立っています。業界によって材料やニーズは異なります。スリッター機はこれらの作業に役立ちます。クラッシュカットスリットを使用している主な業界は以下のとおりです。
- 製紙業界
製紙工場では、大きなロール紙をクラッシュスリットで切断します。これにより、ノートや包装用の小さなロール紙が作られます。機械は高速で動作し、大きなロール紙を扱える必要があります。 - 不織布産業
おしりふきやおむつを製造する工場では、クラッシュスリット加工が用いられています。不織布は柔らかく、粘着性がある場合もあります。スリッターは、粉塵を出さずにきれいに切断する必要があります。 - 繊維産業
繊維工場では、生地やフェルトの裁断にクラッシュスリットを使用しています。この機械は太くて丈夫な繊維を裁断するため、端面がきれいに仕上がり、材料を節約できます。 - ゴム産業
ゴムシートやテープは丁寧に切断する必要があります。クラッシュスリットは、硬くて伸縮性のあるゴムに最適です。スリッターは天然ゴムと合成ゴムの両方を切断できます。 - プラスチックフィルム産業
プラスチックラップや袋を製造する工場では、クラッシュスリット加工が用いられています。スリッターは薄いフィルムを破ることなく切断する必要があります。これにより、包装用の滑らかなロールが製造されます。
注:テープ、断熱材、自動車などの他の業界でもクラッシュスリット加工が使用されています。この方法は、強度の高い素材や層状の素材を迅速かつきれいに切断する必要がある場合に適しています。
素材とブレードの選択
クラッシュカットスリッティングでは、適切なブレードを選ぶことが重要です。素材によって必要なブレードと硬度は異なります。以下の表は、それぞれの素材に最適なブレードを示しています。
| 業界 | 一般的な材料 | ブレード材質 | 刃先タイプ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 紙 | クラフト、コーティング、リサイクル | D2工具鋼 | 半径45° |
| 不織布 | ポリプロピレン、ポリエステル | HSS-M2、超硬 | 半径60° |
| 繊維 | 綿、フェルト、混紡 | HSS-M2、D2 | 半径45° |
| ゴム産業 | 天然、合成 | D2、炭化物 | 半径30° |
| プラスチックフィルム | PE、PET、PVC | HSS-M2、超硬 | 半径60° |
工場では、材料の硬さや粘着性に基づいて刃の材質を選択します。D2工具鋼は耐久性が高いため、紙やゴムに適しています。HSS-M2刃は、硬い繊維や粘着性のある不織布に適しています。超硬刃は、粗い材料や厚い材料に適しています。丸みを帯びた刃先は、刃とアンビルを保護します。
スリッター機は、刃の圧力を制御するために空気圧を使用することが多いです。作業者は材料ごとに圧力を調整できます。適切な刃、刃先、そして圧力を使用することで、きれいな切断が可能になり、刃の寿命も長くなります。
ヒント:刃の点検と交換を頻繁に行うことで、機械の稼働状態を良好に保つことができます。作業ごとに適切な刃を使用することで、機械の停止回数が減り、より良い製品が生まれます。
カスタムクラッシュカットナイフ
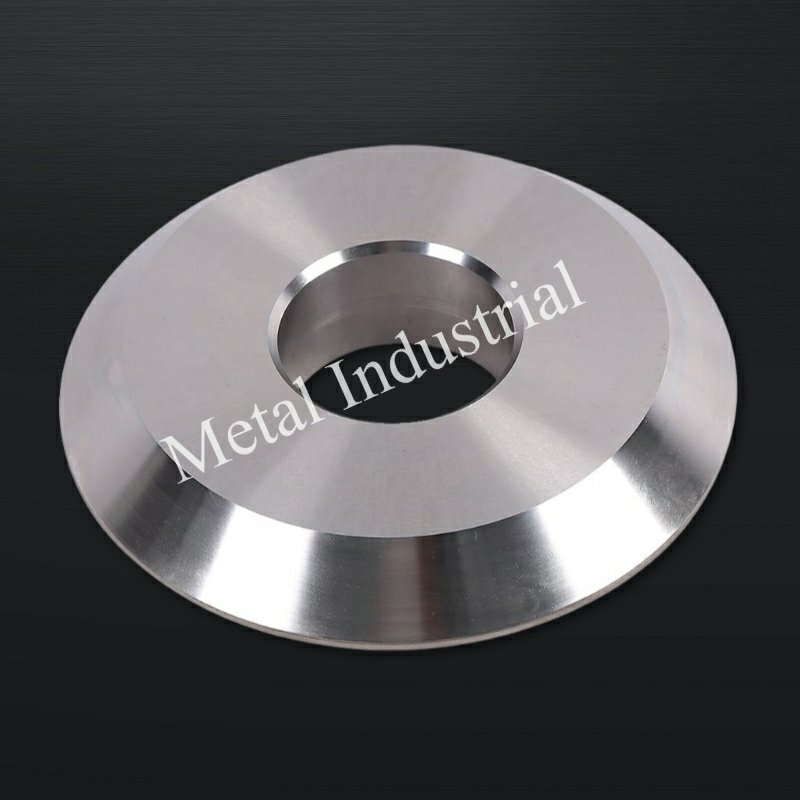

カスタマイズのメリット
工場では、材料を切断する際に様々な問題を抱えています。カスタムメイドのクラッシュカットナイフは、それぞれの作業のニーズに合わせてカスタマイズできるため、作業効率が向上します。Fasco MachineやMuraplastといった企業が、この事例を共有しています。これらの事例では、カスタムメイドのブレードが特殊な形状や高速切断に適していることが示されています。標準ブレードでは、必ずしもこれらの作業に対応できるとは限りません。
製紙業界では、切れ味が良く長持ちする刃が求められています。カスタムメイドの工業用ナイフには、高速度鋼や超硬合金などの高強度素材が使用されています。そのため、丈夫で信頼性が高くなっています。各刃は機械にぴったり合うように作られています。つまり、廃棄物が減り、より多くの製品を生産できるということです。カスタムメイドの刃を使用する企業は、ダウンタイムと修理の回数を減らすことができます。下の表は、カスタムメイドの刃が標準の刃よりも優れている点を示しています。
| メトリック | 標準ブレード | カスタムブレード |
|---|---|---|
| ブレードの寿命 | 約10日間 | 40日以上 |
| ダウンタイムの削減 | ベースライン | 65% ダウンタイム短縮 |
| 緊急修理 | ベースライン | 70% 修理回数が減る |
| 年間交換コスト | $25,000 | $9,500 |
カスタムメイドの工業用ナイフは、企業のコスト削減と安全性確保に役立ちます。例えば、ドイツのリサイクル会社は保管コストを40%削減しました。中国の家具メーカーは、カスタムメイドの刃を使用することで、$120万の増益を達成しました。
南京Metalソリューション
南京Metalは信頼できる 工業用ナイフメーカー20年以上の経験を持つ同社は、熟練した設計・製造チームで知られています。南京Metalは、様々な工場の作業向けにカスタムメイドの工業用ナイフを製造しています。同社のエンジニアは、顧客と協力して、特定のニーズに合わせた刃を設計します。
多くの工場が、迅速なサービスと高い品質を理由にNanjing Metalを選んでいます。同社は高度なCNC工作機械と最高品質の素材を使用し、すべての刃が厳格な基準を満たしていることを保証しています。Nanjing Metalのカスタム刃は、工場の切断面の美しさと刃の寿命の延長に貢献します。また、工場の作業効率と生産性の向上にも貢献しています。
興味のある読者は お問い合わせ 南京 Metal のセールス エンジニアが、自社のマシン向けのカスタム ブレード ソリューションについて話し合いました。
利点と限界

主なメリット
クラッシュカットナイフは、工場の機械にとって多くの利点があります。簡単で安価、そして多くの作業に対応できるため、多くの工場でこの方法が好まれています。作業員は様々な材料にこのナイフを使用しています。そのため、多くの場所でこのナイフが選ばれています。
- コスト削減クラッシュカットナイフは刃先が硬いので、頻繁に交換する必要がありません。そのため、長期的に見てコストを節約できます。
- シンプルさ設計はシンプルです。作業員は簡単にブレードの設置と固定ができます。特別な訓練は必要ありません。
- 汎用性これらの刃は様々な用途に使用できます。繊維、ゴム、紙、不織布などを切断します。
- 耐久性刃先はそれほど鋭くはありませんが、強度はあります。高い圧力にも耐え、折れることはありません。刃先を研ぐことで、刃持ちが良くなり、切れ味も均一になります。
- 精度: 工場では正確なカットが可能です。複雑な形状や狭いスペースでも対応可能です。
- 適応性: 作業者は圧力と設定を変更できます。これにより、さまざまな作業や変化するニーズに対応できます。
以下の表は、これらのナイフがどれだけ効果的か、また工場でどのような役に立つかを示しています。
| 有効性指標 | 説明 | 実証された主な利点 |
|---|---|---|
| 優れた硬度と耐摩耗性 | 超硬ナイフは鋼鉄よりも硬いため、切れ味が長持ちします。 | ブレードの寿命が長くなり、交換の必要性が少なくなり、コストも節約できます。 |
| 優れた切断性能 | ほとんど手間をかけずに、さまざまな素材をきれいにカットできます。 | カットはいつも良好で、プロセスも信頼できます。 |
| 耐久性と寿命の向上 | 厳しい作業や高温下でも、すぐに摩耗したり曲がったりしません。 | ダウンタイムが短縮され、修正が減り、作業速度が向上します。 |
| 精密切断能力 | 硬い形状や狭いスペースも非常にうまく切断できます。 | ミスが減り、製品はより良くなり、毎回同じ結果が得られます。 |
| アプリケーションをまたぐ汎用性 | 彼らは多くの業界で、多くの材料を扱っています。 | 柔軟性が高まり、切断性能が向上し、刃の交換回数が少なくなります。 |
ヒント: 工場では、材質に合わせてより良いカットを得るために、半径付きや鋸歯状などのさまざまなエッジ タイプを選択できます。
主な制限事項
クラッシュカットナイフには多くの利点がありますが、問題点もいくつかあります。これらの問題点によって、ナイフの性能や仕上がりの見た目が変わってしまう可能性があります。
- エッジ品質: 切り口には繊維や毛羽立ち、あるいは少し潰れたように見える場合があります。また、刃先はシャーやカミソリで切った場合ほど滑らかではありません。
- 粉塵発生紙などを切ると粉塵が発生します。清掃を怠ると粉塵が蓄積し、機械が停止する可能性があります。
- メンテナンスの必要性作業者はナイフと金床を注意深く監視する必要があります。圧力や硬さが適切でないと、刃に欠けや溝が入ることがあります。
- 材料の適合性: この方法は、硬いもの、糸状のもの、または層になっているものに最適です。非常に薄いものや壊れやすいものにはあまり適していません。
- 速度制限ほとんどの空気圧式ホルダーは最大300 m/分で動作します。それ以上の速度で動作させると、ブレードが摩耗し、粉塵が増え、オイルの必要量も増える可能性があります。
- 運用管理圧力は適度にかけなければなりません。圧力が強すぎると刃や金床が壊れる可能性があり、圧力が弱すぎると切れ味が悪くなります。
注:ナイフの形状、空気圧、ホルダーの設計はすべて、良好な結果を得るために重要です。自動化により、特に大量の製品を製造する際に、カットの均一性を保つことができます。
クラッシュカットナイフの長所と短所の両方を知ることは、工場が材料を切断する最良の方法を選択するのに役立ちます。
クラッシュカットナイフは多くの工場で重要なツールです。強力な力と特殊な形状により、硬いものを素早く粉砕します。優れた性能と困難な作業への対応力から、多くの業界でこの刃が採用されています。
- ブレードの半径と角度を 30°、45°、60° などにすると、より良いカットが可能になります。
- 工場では、刃の寿命を延ばすために、D2、HSS-M2、または超硬合金を選択します。
- カスタムコーティングとデザインにより、各ナイフの機能が向上します。
適切な切削工具を選び、作業ごとに交換することで、工場はより多くの製品を生産できるようになります。カスタムソリューションをご希望の場合は、Nanjing Metalのセールスエンジニアまでお問い合わせください。
よくある質問
どのような材料を粉砕切断ナイフで加工できますか?
クラッシュカットナイフは様々な用途に使用できます。繊維、ゴム、紙、不織布、プラスチックフィルムなどを切断できます。工場では、硬いもの、糸を引くもの、粘着性のあるものを切断する際にこの刃を使用します。標準的な刃ではこれらの素材はうまく機能しません。
工場ではクラッシュカットブレードをどのくらいの頻度で交換する必要がありますか?
刃の寿命は、何を切るか、そしてどれくらい使用するかによって異なります。ほとんどの工場では、刃を毎日点検しています。切れ味が悪くなったり、均一でなくなったりした場合は、刃を交換します。適切な刃の素材を選ぶことで、刃の寿命を延ばすことができます。
工場ではなぜクラッシュカットナイフに空気圧システムを使用するのでしょうか?
空気圧システムは安定した圧力を供給し、高速で作業します。これにより、常に均一な切断が可能になります。作業者は作業ごとに空気圧を調整できるため、より安全かつ簡単に切断できます。
Nanjing Metal は、特殊な機械用のカスタムクラッシュカットナイフを製造できますか?
はい。Nanjing Metalは工業用ナイフを製造する信頼できる会社です。同社のチームは、様々な機械に合わせてカスタムブレードを製造しています。工場では、特殊な形状、サイズ、素材のご要望にも対応可能です。



1件のフィードバック