
You must know how to プレスブレーキの曲げ力とトン数を計算 to ensure safe and effective metal bending. The formulas below are commonly used in metalworking:
| Formula | 説明 |
|---|---|
| P (lbs.) = 2 × b × t² × Fy/W | This is the basic method to calculate press brake bending force. |
| P (tons/foot) = 0.012 × t² × Fy/W | This is a straightforward way to calculate press brake bending tonnage. |
Obtaining the correct calculations prevents issues. If you do not apply enough force, the bends will not be accurate. Conversely, using too much force can damage your material or machine.
| Impact of Miscalculations | 結果 |
|---|---|
| Insufficient Force | Bends are not accurate |
| Excessive Force | Material and machine can be damaged |
High-quality press brake tooling, like what Nanjing Metal offers, ensures consistent results every time. To calculate press brake bending force and tonnage, you need to consider the type of material, the thickness of the sheet, the length of the bend, the die width, and the method of forming.
重要なポイント
- Knowing press brake bending force is very important. It helps you shape metal the right way. Use the right formulas for good results.
- Figure out press brake tonnage before you bend metal. This stops damage and keeps everyone safe. It also keeps your work strong.
- Each material needs a different amount of force. Always look at the material type and its features. Change your math to fit the material.
- Thicker sheets need more force to bend. Measure the thickness carefully. This helps you pick the right tonnage.
- The die opening width changes the force needed. Make sure the die width matches the sheet thickness. This gives you the best results.
- Pick the best forming method for your project. Air bending, bottom bending, and coining all need different forces.
- Always add a safety margin to your math. This keeps your press brake and tools safe from problems.
- Use online calculators for fast checks. They save time and help you make sure your math is right before you bend.
Press Brake Bending Force Basics

What Is Press Brake Bending Force
It is important to know about press brake bending force before working with metal. Press brake bending force is how much force you use to bend a metal plate. This force changes the shape of the metal. It also helps make sure the final product is correct. In factories, people measure this force to make sure the metal bends the right way. They want the metal to match what they need. If you use good press brake tooling you get the same results each time. This helps stop problems like bent metal that is not right or bends that are not correct.
Why Calculate Press Brake Tonnage
You should always figure out press brake tonnage before you start bending. This keeps your work safe and stops damage. Here are some main reasons to do this:
- Avoiding Material Damage: If you do not use enough force, the metal might crack or bend the wrong way. If you use too much force, the metal can bend too far or get damaged.
- Ensuring Accuracy: The right tonnage lets you bend metal to the exact shape you want. This is very important in jobs like making cars or planes, where every part must fit.
- Enhance Tooling Life: Using the right tonnage keeps your press brake tooling from wearing out too fast. This makes your tools last longer and saves money on fixing them.
- Picking the best press brake and tooling is not just about using enough force. If you make a mistake in your math, you can break your tools or even hurt the press brake machine.
When you figure out press brake tonnage, your work is safer and faster. You also keep your machines safe and make better products.
よくある間違い
Many people get press brake bending force wrong. These mistakes can cause big problems. The table below shows some mistakes and what can happen:
| 間違い | 結果 |
|---|---|
| Misinterpreting material properties | Wrong tonnage means the bends are not good. |
| Incorrect machine setup | Machines can break and people can get hurt. |
| Overloading the machine | The machine can break and accidents can happen. |
| Neglecting maintenance | Bends are not even and the machine may not work right. |
Tip: Always check your math and machine setup before you bend metal. Take care of your press brake and tooling often. This helps you get even bends and keeps your work going well.
You can stop these mistakes by learning the basics, using good press brake tooling, and following the right steps. This helps you make safe, correct, and good bends every time.
Bending Force Variables

When you calculate the force for your press brake, you need to look at several important variables. Each one affects how much force you need during the bending process. If you understand these variables, you can make better decisions and get more accurate bends.
材質タイプ
The type of metal you use changes the force needed in the bending process. Some metals are soft and easy to bend. Others are strong and need more pressure from the press brake. You must always check the material before you start.
軟鋼
Mild steel is common in many shops. It bends well and does not need extra force. When you use mild steel, you can use the standard formula for the press brake. The adjustment factor for mild steel is 1.0.
ステンレス鋼
Stainless steel is much stronger than mild steel. It needs more force in the bending process. If you use stainless steel, you must increase the tonnage on your press brake. The adjustment factor for stainless steel is 1.5. This means you need 50% more force than mild steel.
アルミニウム
Aluminum is softer than steel. It bends with less force. The adjustment factor for aluminum ranges from 0.5 to 1.0. You should check the exact type of aluminum before you set up your press brake.
Here is a table that shows the adjustment factors for different materials:
| 材質タイプ | Adjustment Factor |
|---|---|
| 軟鋼 | 1.0 |
| ステンレス鋼 | 1.5 |
| アルミニウム | 0.5 to 1.0 |
| Bronze (Soft) | 0.5 |
| Chrome-Molybdenum Steel | 2.0 |
You can also see these differences in the chart below:
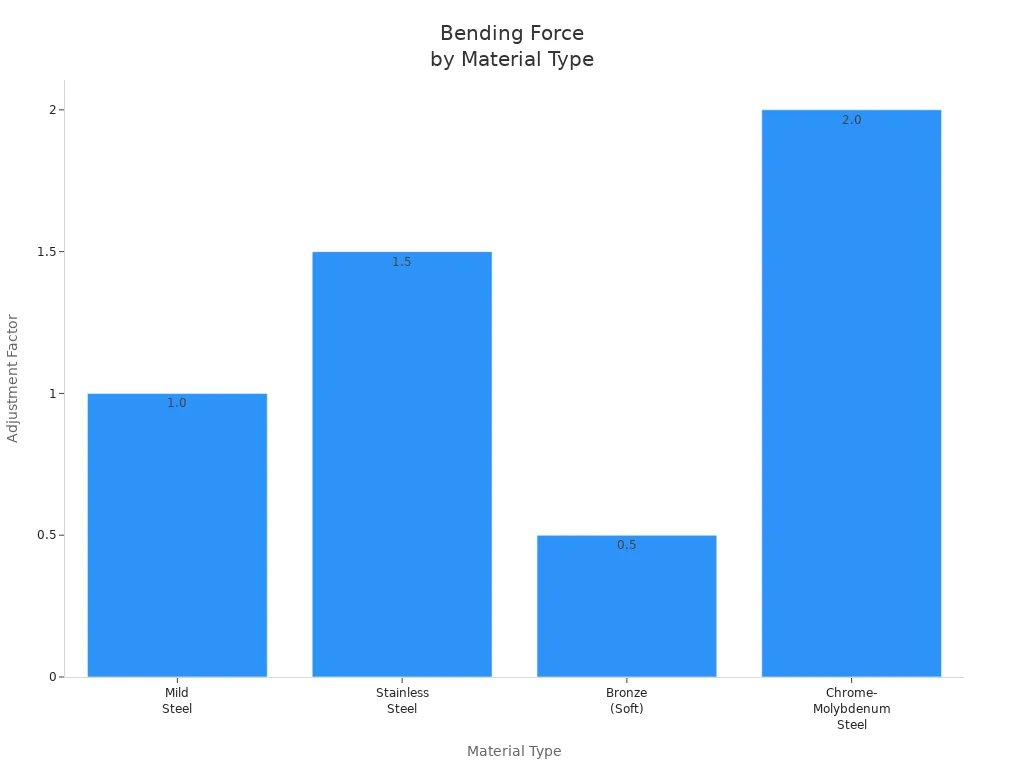
Tip: Always use the correct adjustment factor for your material. This helps you avoid mistakes in the bending process.
Sheet Thickness
Sheet thickness is another key variable. Thicker sheets need more force from the press brake. If you try to bend a thick sheet with too little force, the bend will not form. If you use too much force, you can damage your tooling or the press brake.
- Thicker sheet metal needs higher tonnage.
- You must select the right tonnage based on the bending sheet thickness.
- For example, bending a 1/2-inch sheet takes much more force than a 1/8-inch sheet.
Bend Length
Bend length is the distance along the sheet where you want the bend. Longer bends need more force in the bending process. If you double the bend length, you double the force needed from the press brake.
- Measure the bend length before you start.
- Use the correct value in your calculations.
- Always check your press brake’s maximum capacity for long bends.
Note: Using quality press brake tooling helps you get even results, no matter the material or thickness.
Die Opening Width
Die opening width, also called the V-die opening, plays a big role in how much force you need when using a press brake. You must match the die opening width to your material thickness for the best results. If you use the wrong size, you can damage your press brake machine or get poor bends.
Here is how die opening width affects the force needed:
- A narrower die opening increases the required tonnage. The force gets concentrated in a smaller area, so your press brake must work harder.
- A wider die opening reduces the tonnage needed. The force spreads out, making it easier for the press brake machine to bend the metal.
- A smaller V-opening creates a tighter bend radius but needs more force. A larger V-opening gives a bigger inside bend radius and uses less force.
- The type of tooling you use also affects the performance and tonnage capacity of your press brake machine.
Tip: Always check that your die opening width matches your material thickness. This helps you get accurate bends and protects your press brake tooling.
You can measure the die opening width by looking at the V-shaped groove in your lower die. Most shops use a die opening that is 8 times the thickness of the sheet metal. For example, if you have a 2 mm thick sheet, you should use a 16 mm die opening.
Forming Method
The forming method you choose changes how much force your press brake needs. There are three main methods: air bending, bottom bending, and coining. Each method uses the press brake machine in a different way.
| 曲げ方法 | Required Force (Relative) |
|---|---|
| エアベンディング | 1.0 |
| Bottom Bending | 5.0+ |
| 鋳造 | 10.0+ |
- Air bending uses the least force. The punch does not press the sheet all the way into the die. This method allows for some springback, so you can adjust the angle after bending.
- Bottom bending needs more force than air bending. The punch pushes the sheet to the bottom of the die, making the bend more accurate and reducing springback.
- Coining uses the most force. The punch presses the sheet fully into the die, creating a very sharp and precise bend with almost no springback.
Note: Always set your press brake machine to match the forming method you plan to use. Using the wrong force can damage your tooling or the press brake.
Choosing the right forming method and die opening width helps you get the best results from your press brake. You will make accurate bends, protect your press brake machine, and extend the life of your tooling.
How to Calculate Press Brake Bending Force and Tonnage

Main Formula
Formula and Variable Breakdown
When you want to know how to calculate press brake bending force and tonnage, you need to start with the main formula. This formula helps you calculate bending force for any job. You use it to make sure your press brake can handle the work and to protect your tooling.
Here is the standard formula for press brake bending force:
F = (k × L × T²) / (8 × V)
Let’s break down each part of the formula so you can understand how to calculate press brake bending force and tonnage:
| 変数 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| F (Tonnage Force) | The total force required for bending (tons) |
| k (Material Factor) | A factor based on the tensile strength of the material |
| L (Length of Bend) | The total length of the bend being performed (mm or in) |
| T (Material Thickness) | The thickness of the material being bent (mm or in) |
| V (Die Width Opening) | The width of the die used in the bending process (mm or in) |
- F tells you the tonnage force your press brake must deliver.
- k changes based on the material you use.
- L is the length of the bend line.
- T is the thickness of your sheet metal.
- V is the width of the die opening.
You must use the same units for all measurements. If you use millimeters for one, use millimeters for all.
Tip: Always check your press brake tooling and blade size. If you need custom blades, you can find more information on custom blades here.
Example Calculation
Let’s walk through an example so you can see how to calculate press brake bending force and tonnage step by step.
Suppose you want to bend a piece of mild steel. Here are your values:
- Material: Mild Steel (k = 1)
- Length of Bend (L): 1000 mm
- Material Thickness (T): 2 mm
- Die Width Opening (V): 16 mm
Plug these numbers into the formula:
F = (1 × 1000 × 2²) / (8 × 16)
F = (1 × 1000 × 4) / 128
F = 4000 / 128
F ≈ 31.25 tons
You need about 31.25 tons of force to make this bend. This is how you calculate bending force for your press brake. If you use a different material or thickness, you must change the values in the formula.
Material Factor
Common Material Factors Table
The material factor (k) is very important when you calculate tonnage force. Different metals need different amounts of force. The k-factor tells you how strong the material is and how much force you need.
Here is a table with common material factors for press brake work:
| 材質タイプ | K-factor Range |
|---|---|
| 軟鋼 | 1.0 |
| ステンレス鋼 | 1.5 |
| アルミニウム | 0.5~1.0 |
| Bronze (Soft) | 0.5 |
| Chrome-Moly Steel | 2.0 |
| Common Metals | 0.3 – 0.5 |
| Default Value | 0.446 |
- Use the right k-factor for your material. If you use the wrong one, your calculation will not be correct.
- For most jobs, mild steel uses a k-factor of 1. Stainless steel needs more force, so use 1.5. Aluminum is softer, so use a lower k-factor.
You must always check the material before you calculate bending force. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your press brake safe.
Method Factor
Influence of Forming Method
The forming method you choose also changes how to calculate press brake bending force and tonnage. The method factor tells you how much extra force you need for different bending styles.
- Air bending uses the standard formula for press brake tonnage. You do not need to change the k-factor.
- Bottoming needs about 1.5 times the force of air bending. You must multiply your answer by 1.5.
- Coining needs about 5 times the force of air bending. You must multiply your answer by 5.
The k-factor also changes with the forming method. The position of the neutral axis in the metal moves depending on the method you use. This affects how you calculate bending force and how the metal bends.
- The k-factor is a multiplier that shows where the neutral axis moves after bending.
- It is different for each material and forming method.
- The neutral axis never goes past 50% of the material thickness.
Note: Always adjust your calculation based on the forming method. This keeps your press brake and tooling safe and gives you the best results.
Units and Conversion
Common Unit Conversions
When you use a press brake, you need to know the units for force. In the United States, most shops use short tons to measure press brake tonnage. Other countries use metric tons, which are also called tonnes. Sometimes, you will see force in Newtons per square millimeter or kilograms per square millimeter.
You can change between these units by following some easy rules:
| Unit | Conversion Method |
|---|---|
| Short Ton (US) | 1 short ton = 2,000 pounds |
| Metric Ton (Tonne) | 1 metric ton = 2,204.62 pounds |
| Newton (N) | 1 N = 0.10197 kg |
| N/mm² to kg/mm² | Divide value by 10 |
If you have Newtons per square millimeter, divide by 10 to get kilograms per square millimeter. This makes it easy to switch units when you figure out press brake tonnage.
Tip: Always look at what units your press brake uses before you start. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your answers right.
注記
You must use the same units for every part of your math. If you mix up units, you can get the wrong answer. For example, do not use millimeters for thickness and inches for die opening width in the same formula. Pick one system and use it for everything.
Check your conversions before you bend any metal. If you make a mistake, you might get the wrong press brake tonnage. This can mess up your bends or even break your machine.
You should also know how much force your press brake can handle. Every machine has a maximum force it can give. If your math shows a force higher than your machine’s limit, you need to change your setup or use a different press brake.
Note: Always check your answer against your press brake’s tonnage limit. This keeps your machine safe and helps you avoid expensive repairs.
Using Online Calculators
You can use a bending calculator to help you. Many websites have free tools that tell you the force you need for your press brake. These calculators let you type in your material, thickness, bend length, and die opening width. The calculator then tells you the press brake tonnage you need.
Here are some popular online calculators:
- American Machine Tools Press Brake Bending Force Calculator
- Engineers Edge Press Brake Tonnage Calculator
- MachineMfg Press Brake Tonnage Calculator
When you use a calculator, always check that the units match what your shop uses. Make sure you put in the right numbers for material and thickness. If you use the wrong units, the calculator might give you an answer that does not work for your press brake.
Tip: Online calculators save time and help you make fewer mistakes. Use them for quick checks, but always double-check the answer before you start bending.
Calculate Bending Force Step-by-Step

To figure out press brake tonnage, you need good data. You must follow each step to get the right force for bending. This helps you avoid errors and keeps your bends safe.
Gather Data
Before you start, collect all the details you need. Every variable changes how much force you need.
Identify Material Type
You should know what metal you want to bend. Each metal needs a different amount of force. Mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum are all different. Look at your tonnage chart to match the metal.
Measure Sheet Thickness
Use a caliper or micrometer to check sheet thickness. Write down the number in millimeters or inches. Thicker sheets need more force, so measure carefully.
Determine Bend Length
Find the length of the bend line. This is how far you want to bend the sheet. Longer bends need more force.
Select Die Opening Width
Check your tooling for the die opening width. Most shops use a die opening eight times the sheet thickness. For example, a 3 mm sheet needs a 24 mm die opening.
Choose Forming Method
Pick the forming method you will use. You can choose air bending, bottom bending, or coining. Air bending needs less force. Coining needs much more force. The method changes the force you need.
Tip: Always add a safety margin when you gather data. This keeps your machine and tooling safe.
Plug Values Into Formula
After you have your measurements, you can start your calculation. Put your numbers into the standard formula.
Standard Formula
The most used formula for press brake tonnage is:
F = (650 × S × t² × L) / V
- F is the force you need in tons.
- S is the yield strength in N/mm².
- t is the sheet thickness in mm.
- L is the bend length in mm.
- V is the die opening width in mm.
Substitute Collected Data
Let’s say you have mild steel with these numbers:
- Yield strength (S): 240 N/mm²
- Thickness (t): 3 mm
- Bend length (L): 1000 mm
- Die opening width (V): 20 mm
Put these numbers into the formula:
F = (650 × 240 × 3² × 1000) / 20
F = (650 × 240 × 9 × 1000) / 20
F = (650 × 2160 × 1000) / 20
F = (1,404,000,000) / 20
F = 70,200,000
Divide by 1,000,000 to get tons:
F = 70.2 tons
Note: Always check your equipment before you bend. Make sure your press brake can handle the force.
Calculate Result
Now you know the force you need for your job. You can check your answer by thinking about friction and plastic deformation. Watch the bending process to make changes for better results.
Example Calculation for Mild Steel
Here is a table with a sample calculation for mild steel:
| 変数 | 説明 | 価値 |
|---|---|---|
| P | Pressure in kN | 975 kN |
| S | Thickness in mm | 6 mm |
| L | Length in meters | 2 m |
| V | Die opening width in mm | 48 mm |
Use the formula to find the force for these numbers. Always check your units before you do the math.
Adjusting for Stainless Steel and Aluminum
Different metals need different force. Stainless steel is stronger, so you need more force. Aluminum is softer and needs less force. Use the right material factor in your formula.
| 要素 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 材料の厚さ | Thicker metal needs more force and changes the bend formula. |
| Bend Radius | A smaller radius makes a sharper bend and needs more force. |
| 曲げ角度 | Bigger angles use more metal, so you need careful math. |
| Grain Direction | Bending against the grain can cause cracks, so change your calculation. |
Tip: Always check the grain direction before you bend. This helps stop cracks and weak bends.
Adjusting for Different Thicknesses
If you change the sheet thickness, you must recalculate the force. Thicker sheets need much more force. If you double the thickness, the force goes up four times because thickness is squared in the formula.
- Thin sheets need less force.
- Thick sheets need much more force.
- Always use the right thickness in your formula.
Note: Using correct data for press brake tonnage helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your machine safe. Use these steps for every job.
Calculating Press Brake Tonnage: Practical Examples

Mild Steel Example
You can figure out press brake bending force and tonnage for mild steel by following a few easy steps. First, pick your material. In this example, use low-carbon mild steel with a material constant K of 1.45. Next, measure how long the bend will be. Imagine you need to bend a sheet that is 1000 mm long. Then, check how thick the sheet is. Let’s say it is 4 mm thick. After that, find the V-die opening width. Use a die that has a 32 mm opening. Also, use the constant C for metric units, which is 2.5. When you put these numbers into the formula, you get a needed tonnage of 290 tons. This helps you set up your press brake the right way and avoid mistakes. You can see how each part changes the final answer. Always check your measurements before you start bending.
Tip: The right press brake tooling, like V-punches or custom dies, helps you make good bends and keeps your equipment safe.
Stainless Steel Example
Stainless steel needs more force than mild steel because it is harder to bend. You must think about the material type and thickness when you figure out press brake bending force and tonnage. The table below shows how mild steel and stainless steel are different:
| 材質タイプ | 降伏強度 | Required Tonnage | Resistance to Bending |
|---|---|---|---|
| ステンレス鋼 | より高い | より高い | More resistant |
| 軟鋼 | より低い | より低い | Less resistant |
Many things change the tonnage needed for stainless steel. Thicker sheets need more force. Stainless steel’s higher strength means you need more tonnage. The right die shape and angle help you bend stainless steel without damage. You must use a higher material factor for stainless steel. This makes sure your press brake gives enough force for a clean bend. Always check your tooling and machine strength before working with tough materials.
Adjusting for Tooling
The tooling you pick is very important for press brake bending force and tonnage. You must match your tooling to the material and bend you want. Think about these things when you choose press brake tooling: Tooling choice changes the force needed for each material. Different materials need special die shapes and angles for good bends. The V opening of the die changes the bend radius and the tonnage needed. If the inside bend radius is smaller than the material thickness, you might see problems like side bulges. You can find many types of press brake tooling, like V-punches, gooseneck punches, and custom dies. Nanjing Metal has strong tooling for many jobs, helping you get the same results every time. Always pick tooling that matches your material and bend needs. This helps you get the best quality and avoid trouble during bending.
Tip: Check your tooling before every job. The right tooling helps you control press brake bending force and tonnage, so your bends are safer and more accurate.
Press Brake Tooling and Safety

Tooling Selection
Picking the right press brake tooling is very important for safe bending. You must choose tooling that matches your material type, thickness, and the shape you want. If you use the wrong tool, your bend might not turn out right. You could also hurt your press brake.
Here is a table to help you choose the best tool:
| ツールタイプ | 材料の厚さ | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| V-Die (narrow V) | Thin materials | General bending |
| V-Die (wide V) | Thick materials | Heavy-duty bending |
| Gooseneck Dies | Complex shapes | Intricate bends |
| Acute Angle Dies | Thin materials | Sharp bends |
| Radius Tools | Various | Special bending needs |
| ヘミングツール | Various | Edge folding |
When you pick tooling, think about these things: What material are you bending? How thick is it? Is the tool hard enough? What bending method will you use? Does your material need something special?
Good tooling gives you the same results every time. It also keeps your equipment safe. Good tools help you control press brake bending force and tonnage.
Safety Margins
You should always add a safety margin when you figure out press brake bending force and tonnage. This extra bit helps keep your machine safe if something changes, like the material or if your tool gets worn out.
Here is a table with safety margin tips:
| ソース | Safety Margin Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Durmark Machinery | Add a margin for material changes, tool wear, and surprises |
| SSHL Machinery | Add about 20% more tonnage for machine longevity |
| The Fabricator | Consider tonnage per meter or foot for real-world applications |
A safety margin means you do not push your press brake to its highest force. This helps your machine last longer. It also lowers the chance of accidents. Always check your math and add a little more tonnage to be safe.
Tip: Adding a safety margin is smart. It helps you avoid big mistakes and keeps your shop working well.
Machine Limits
Every press brake has a top tonnage it can use. You must know your machine’s limit before you start bending. If you use too much force, you can break your press brake or make things unsafe.
Remember these points: Tonnage is the force your press brake uses to bend metal. Different materials and thicknesses need different force. Use a press brake tonnage calculator to find the right force. Too much tonnage wastes money and wears out your machine. Not enough tonnage makes bad bends or can break your tools.
Always look in your machine’s manual for its tonnage rating. Never go over this limit. If you need more force than your machine can give, use another press brake or change your setup.
If you follow these steps, you can safely control press brake bending force and tonnage. You will protect your equipment and make good bends every time.
Quick Tips for Beginners

Reference Tables
Reference tables help you find the right press brake force fast. You do not have to do hard math each time you bend metal. These tables show how much pressure you need for different sheet sizes. You can look up your material type and use the right number for your math. For example, stainless steel uses 1.5, and mild steel uses 1.0. You match your material and thickness to the chart to see the force you need.
- Bending force charts give quick answers for many jobs.
- You can find tables for mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
- The answer depends on the material’s strength and the number you use.
- Example problems in these tables show how to change for different materials.
Tip: Always use the right number for your material. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your bends correct.
Online Calculators
Online calculators help you figure out press brake force and tonnage fast. You type in your material, thickness, bend length, and die opening width. The calculator tells you the force you need in just a few seconds. Many press brake machines have charts or calculators built in. You can check your answer by doing the math yourself with tonnage charts.
- Use online calculators for quick checks before bending.
- Type in all your numbers carefully to get the right answer.
- Compare the calculator’s answer with your machine’s force reading.
- Look at tonnage charts from your press brake maker for more accuracy.
Note: Online calculators save time and help you avoid mistakes. Always check your numbers before you bend metal.
Consulting Experts
You can learn a lot by talking to people who know press brakes well. They know how to pick the right force for each job. They can help you avoid mistakes and keep your machine safe. You should ask about material thickness, bend angle, and your press brake’s tonnage.
| 重要な考慮事項 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| Material Thickness and Type | Needed to find the right tonnage and bending force |
| Bending Angle and Radius | Changes the force needed for a good bend |
| Tonnage Capacity of the Machine | Must match the force needed so you do not break the machine |
- Experts can show you how to use calculators and built-in charts.
- They can help you check your math with tonnage charts.
- You can ask for help with special materials or tricky bends.
Tip: If you have questions, ask experienced operators or trusted suppliers. They can help you get the best results with press brake bending force and tonnage.
You can figure out press brake bending force and tonnage by doing these steps:
- Find out what kind of metal you have, how thick it is, and how strong it is.
- Use the right formula to get the material factor.
- Pick the method factor that matches how you want to bend the metal.
- Put all your numbers into the formula to get the forming tonnage.
Always check your force settings twice and keep a chart of K-factors for different metals. Practice doing the math and take care of your press brake so it works safely and gives good results. If you need help, you can ask our sales engineers ここ.
よくある質問
What is the difference between air bending and bottom bending?
Air bending uses less force and gives you more flexibility with angles. Bottom bending needs more force and creates a sharper bend. You should choose the method based on your project needs.
How do you choose the right die opening width?
You should match the die opening width to your material thickness. A common rule is to use a die opening about eight times the thickness of your sheet metal.
Why does material type affect bending force?
Different metals have different strengths. Harder metals like stainless steel need more force to bend. Softer metals like aluminum need less force. Always check your material before you start.
Can you use the same tooling for all materials?
No. You need to pick tooling that matches your material type and thickness. Using the wrong tooling can damage your press brake or give you poor results.
How do you calculate press brake tonnage safely?
First, gather your material type, thickness, bend length, and die width. Use the standard formula. Always add a safety margin to protect your machine and tooling.
What happens if you use too much force?
Too much force can damage your press brake, tooling, or the metal itself. Always check your calculations and never exceed your machine’s maximum tonnage.
Do you need to adjust for different bend lengths?
Yes. Longer bends need more force. Always measure your bend length and use it in your calculations for accurate results.
参照
ヨーロッパ式 vs. アメリカ式プレスブレーキ金型:あなたの工場に最適なのはどちらか?
エアベンディング vs. ボトミング:あなたのプロジェクトに最適なプレスブレーキ金型を選ぶ
プレスブレーキ工具の習得: パンチとダイの摩耗を特定して修復する方法



1件のフィードバック
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.