Kundenspezifische Kreismesser are very important in industries needing high accuracy and trust. Regular blades do not work well with tough materials like laminates or composites. Manufacturers pick custom circular knives because of their special shape, strong materials, and special coatings. These things help fix certain problems and give steady results. Real-life examples show that smart design and good material choices make cutting better.
Die wichtigsten Erkenntnisse
- Custom circular knives cut better and last longer. They use special shapes, strong materials, and coatings for hard jobs.
- Picking the right blade size, edge, material, and coating helps save materials. It also lowers costs and makes machines work better.
- Real stories show custom knives make work faster. They waste less material and stop machines less in packaging, printing, and metalworking.
- Buyers should choose suppliers with quality certificates. Good communication and custom order experience help get the best blades.
- Talking clearly about cutting needs and testing blades first helps avoid mistakes. This makes sure the knives fit and work well.
Custom Circular Knives Overview
Custom circular knives are very important in many factories. These knives are round and help cut things over and over with care. They do jobs like slitting, scoring, perforating, and trimming many materials. Some industries that use these knives are food processing, plastics, tire and rubber, textiles, packaging, and metalworking.
Standard Blade Limits
Standard industrial circular knives have trouble with hard or tricky materials. For example, when cutting composites, laminates, or films with layers, regular blades get dull fast or make rough cuts. This means workers must change blades more often. It also costs more to fix and wastes more material. In food processing, packaging, and metalworking, these problems can slow down work and make products worse.
Note: Many companies say regular cutting tools are not fast or accurate enough for today’s factories.
Customization Value
Kundenspezifische Kreismesser help by giving special shapes, strong materials, and special coatings. Makers can choose the right size, thickness, edge, and coating for their needs. This means blades last longer, cuts are cleaner, and machines stop less.
- Key benefits of custom blades:
- Less material waste
- Lower repair costs
- Better product quality
- Machines last longer
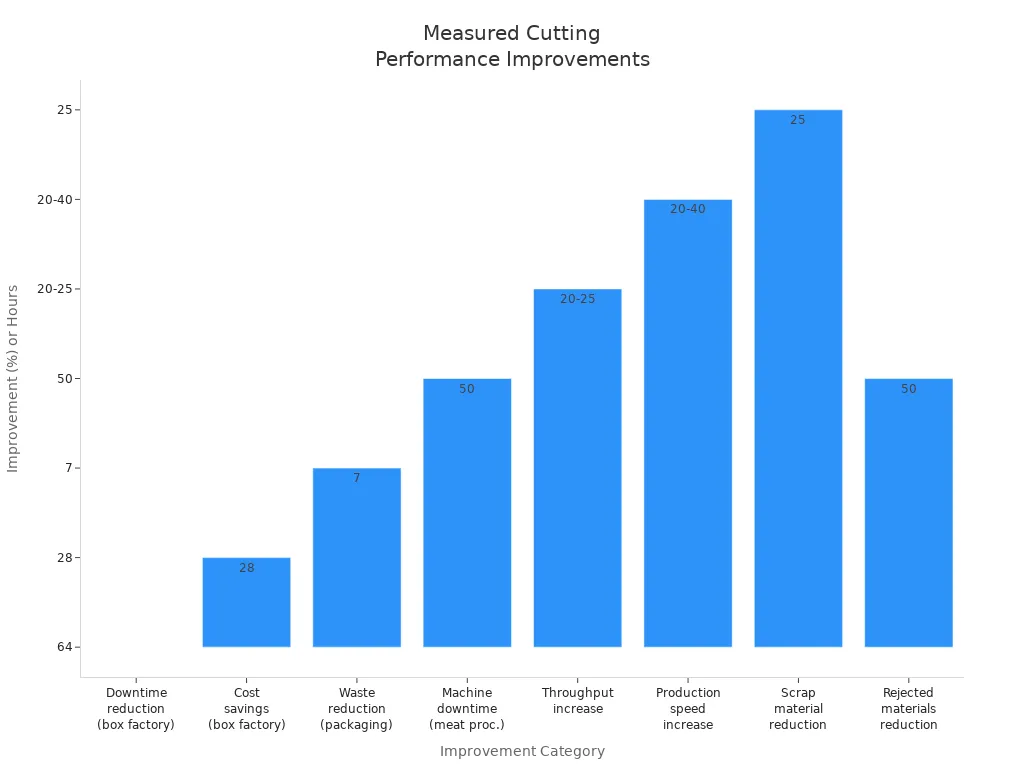
A battery company saw a 20% faster cycle time and made 15-25% more products after using custom blades. Material waste went down from 5% to 2%, saving $150,000 each year. Blades lasted three times longer, and repair time was cut in half.
Real stories and examples in this article will show how custom circular knives help many industries do better.
Market Drivers for Industrial Circular Knives
OEM Replacement Needs
Many companies need new industrial circular knives. They use these knives to replace old or rare OEM parts. Factory machines often need special blades. These blades are not easy to find in stores. When a machine breaks, workers look for custom blades. They want blades that fit their machines just right. Custom industrial circular knives help with this problem. They match the size and shape of the old part. They also use the same blade material. This keeps machines working and stops long breaks.
Note: Factories always need new blades because old ones wear out. They need good places to buy industrial circular knives.
Special Material Demands
Industrial circular knives cut many different materials. Some jobs need blades for tough or sticky things. For example, cutting metal, rubber, or food packaging is hard. These jobs need special blade material. Wolframkarbid and ceramic blades are good for this. They last longer and stay sharp with hard jobs. Many factories pick tungsten carbide for its strength. It does not wear out fast. Ceramic blades work well too, especially for clean or food-safe jobs. The right blade material helps cut faster and makes better products.
- Key reasons for more demand:
- Factories use better blade material like tungsten carbide and ceramic blades
- They want industrial circular knives that last longer
- Packaging, metalworking, and food industries are growing
- Companies want to make things in better and greener ways
Community Insights
People talk about custom industrial circular knives online. They share stories about making fruit peeler blades or using drawings to make new blades. Many want to turn their ideas into real products. They look for suppliers who can use special blade material. Some want tungsten carbide or ceramic blades. People also talk about how hard it is to find the right maker. More machines and new tech mean more need for good industrial circular knives. More companies now want blades made just for them.
Tip: Sharing stories online helps people find the best blade material and suppliers for industrial circular knives.
Custom Blades Design Factors
Kundenspezifische Klingen are very important in factories today. How well they work depends on many things. These things are geometry, edge type, blade material, and blade coatings. Each one changes how the blade works in different jobs.
Geometry Parameters
The shape of a blade changes how it cuts. There are five main things to look at:
- Outer Diameter (OD): This tells how big the blade is. Bigger OD means deeper cuts and fits large machines. In packaging, big OD cuts thick film rolls at once.
- Inner Diameter (ID): This helps the blade fit on the machine. A good ID keeps the blade steady, even when cutting fast labels.
- Dicke: Thick blades do hard jobs like cutting metal coils. Thin blades are better for soft things like foil or paper. Thin blades help stop bending.
- Edge Angle: The angle makes the blade sharp or strong. Small angles cut cleaner but get dull fast. Big angles last longer, even with rough stuff.
- Radius: The edge radius stops stress and chipping. Small radius keeps blades from breaking in food jobs. The right radius makes cuts better and blades last longer.
The table shows how edge radius helps with different materials:
| Materialtyp | Empfohlener Kantenradius (µm) | Impact on Performance and Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Dünne Kunststofffolien | 5–10 | Sharp edge radius prevents stretching and ensures clean cuts |
| Papier & Karton | 10–20 | Medium radius reduces dust and improves edge smoothness |
| Dicke Gummiplatten | 20–30 | Larger radius prevents blade sticking and reduces friction |
| Folie & Aluminium | 5–15 | Sharp to medium radius avoids edge curling and material deformation |
| Blech | 30–50 | Large radius enhances durability and prevents blade chipping |
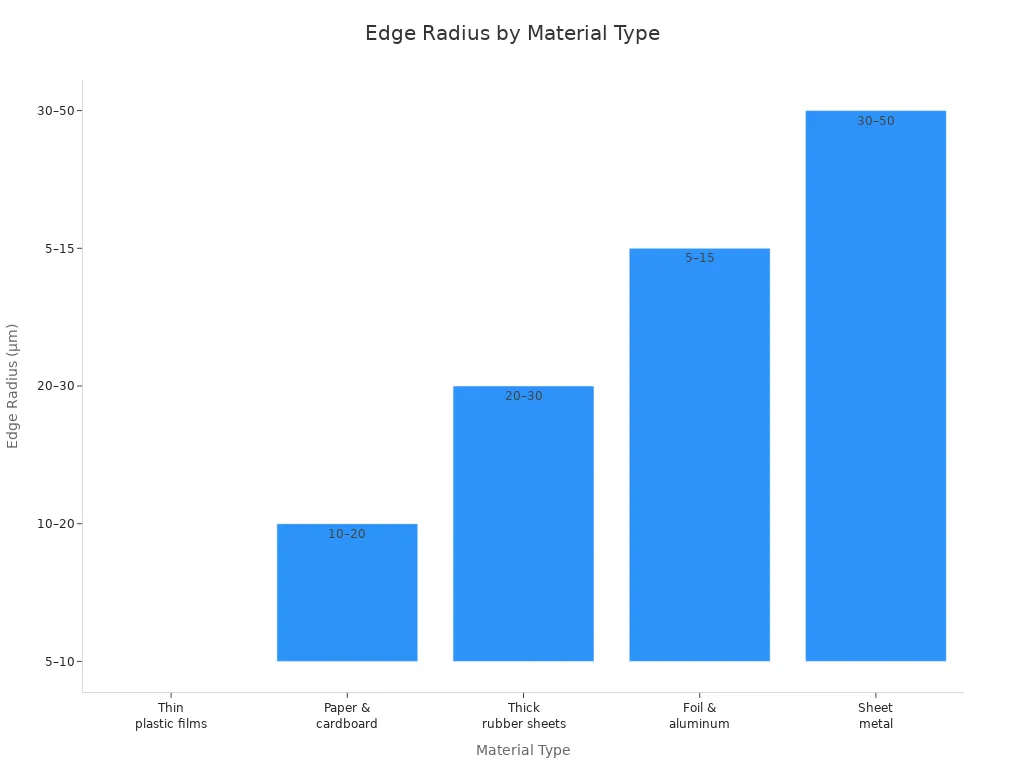
Picking the right shape helps blades cut better and last longer. Makers change these things to match the blade and the job.
Edge Types
Edge type is also very important for custom blades. The right edge makes cutting faster and better. Here are some common edge types:
- Einzelne Abschrägung: Only one side is angled. This edge is sharp and cuts well. It is good for film and foil.
- Doppelte Abschrägung: Both sides are angled. This edge is sharp and strong. It works for many jobs.
- Scalloped Edge: This edge is wavy or has bumps. It cuts tough things like textiles or rubber. It helps stop sticking.
- Perforated Edge: This edge has notches or holes. It is best for packaging films or labels that need to tear easily.
The edge type depends on the blade and what you cut. Scalloped edges help in food jobs by stopping squishing. Perforated edges make it easy to open packages.
Material Choices
Blade material is very important for custom blades. The kind you pick changes how long it lasts and how safe it is. The table below shows some popular materials:
| Material | Härte und Verschleißfestigkeit | Toughness & Impact Resistance | Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Application Suitability for Circular Knives |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolframkarbid | Extremely hard (800-2100 HV), very wear-resistant | Very brittle, chips easily, low toughness | Contains cobalt (toxic), not stainless | Used in industrial cutting tools with wide edge angles; unsuitable for knives needing toughness or food/medical use |
| High-Speed Steel (T1, M2) | Good hardness and wear resistance | Good toughness and impact resistance | Not stainless | Suitable for metal cutting and planar knives in wood processing |
| D2 Stahl | Good hardness | Moderate toughness, prone to rust | Semi-stainless, rusts easily | Less favored for knives due to rust issues |
| Stainless Steel (VG10, N690Co) | Moderate hardness and wear resistance | Balanced toughness | Good corrosion resistance | Preferred for circular knives offering balanced wear and corrosion resistance |
Tungsten carbide is very hard and lasts a long time. It is best for cutting rough things. High-speed steel is tough and lasts well, so it is used for metal and wood. D2 steel is hard but rusts, so it is not used much for food or medical jobs. Stainless steel is balanced and does not rust, so it is good for food and packaging. Ceramic blades are used when cuts must be clean and safe.
Makers pick blade material for the job. Tungsten carbide is for rough jobs. Stainless steel is for food safety. High-speed steel is for metal. Ceramic is for clean rooms or medical places.
Beschichtungsoptionen
Blade coatings help custom blades work better and last longer. Two common coatings are Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC).
| Beschichtungstyp | Key Properties | Typische Anwendungen | Blade Lifespan Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titannitrid (TiN) | Increases surface hardness and wear resistance | High-speed cutting, metal slitting | Approximately 2.5 times longer |
| Diamantähnlicher Kohlenstoff (DLC) | Ultra-low friction, prevents material adhesion | Precision cutting in aerospace and automotive | Approximately 3 times longer |
TiN makes the blade harder and stops it from wearing out. It is good for fast cutting and metal jobs. DLC makes the blade slippery and stops things from sticking. It is best for careful cutting in planes and cars. Both coatings can make blades last up to three times longer. They also help save money and time.
Blade coatings keep blades sharp longer. They stop friction, keep blades cool, and waste less material. Many makers use coatings to save money and help the planet. These coatings mean you do not have to change blades as often.
Tip: The right blade coating can make custom blades last longer and help factories work without stopping.
Customization Process
Consultation & Requirements
Making custom blades starts with a meeting. Customers talk to sales engineers about what they need. They share what material they will cut and how fast. They also talk about where the blade will be used. This helps everyone know what kind of circular knife is needed. Customers might give CAD drawings, real samples, or hand sketches. The supplier checks these to make sure the blade fits the machine. They also want to be sure the blade cuts the right way.
Tip: Talking clearly now stops mistakes later. Giving lots of details about the job and material helps get better blades.
Suppliers let customers order different amounts. Some let you buy just one blade to test. Others want you to order more for big jobs. This helps both small and big companies get the blades they need.
Design & Prototyping
After learning what is needed, the design team makes a plan. They use CAD software to draw the blade’s shape and edge. CAD helps them see the blade and change it fast. Designers can test how the blade will work before making it. This helps stop mistakes.
CNC machines and 3D printers help make test blades quickly. These tools let engineers check if the blade fits and is sharp. If something is wrong, they can fix the CAD drawing and make a new test blade. This makes the process faster and helps the final blade work well.
A good test phase has these steps:
- Use CAD to find and fix mistakes.
- Make test blades with CNC or 3D printing.
- Let the customer try the blade and give feedback.
- Change the design if needed after testing.
This way, the final blade matches what the customer wants and works well.
Production & Quality
When the test blade is approved, full production starts. Factories use laser cutting and grinding to make each blade match the plan. Quality checks are very important during this time.
Many factories follow strict rules for quality. Some have ISO 9001:2015 certification. This shows they care about making good products and checking every step. The rules cover everything from picking materials to the last check before shipping.
The steps in making blades are:
- Use special machines to make the blades.
- Check the size and hardness during the process.
- Look at each blade by hand before sending it out.
Note: ISO 9001:2015 means every batch of blades is checked for quality and works well.
Making custom blades is not easy. Heat treatment must be done at the right temperature. If it is too hot or cold, the blade can bend or break. Surface treatments like hardening or coating need careful work. This stops rust and keeps the edge sharp. Keeping the right size is very important, especially for fast machines.
Some common problems are:
- Keeping the same temperature during heat treatment.
- Stopping rust and loss of carbon.
- Making sure the blade fits and works right.
- Keeping the edge hard and sharp every time.
Suppliers fix these problems by using special ovens and skilled workers. Sometimes they send blades to experts for heat treatment. But they always check the work to make sure the blades are made right.
Cutting Performance in Real Applications
Verpackungsindustrie
Food Film Cutting
Factories that pack food often cut thin films. These films can be sticky or easy to tear. Regular blades do not work well for this. Custom circular knives use special blade material like tungsten carbide or high-speed steel. These blades stay sharp longer and cut better. Tungsten carbide blades do not wear out fast, even at high speeds. High-speed steel blades are tough and sharp. They work for both soft and harder films.
Workers pick single bevel or thin blades for straight cuts. Coatings like TiN or DLC help the blade slide and stop film from sticking. This makes cutting easier and means blades last longer.
Case Example: High-Speed Snack Packaging
A snack company wanted to pack snacks faster. Their old blades wore out and stopped the line a lot. They changed to custom tungsten carbide blades with a TiN coating. The new blades made cutting 30% faster. Blade changes went from twice a shift to once every three days. The new blades and coating also cut film waste by 40%. The line ran better and snacks looked nicer.
Key Performance Factors
- Blade material (tungsten carbide or high-speed steel) for less wear
- Thin, sharp edges for clean cuts
- Coatings (TiN, DLC) to stop sticking and help blades last
- Steady cutting speed and less stopping
Note: The right blade material and shape help lines go faster and waste less.
Printing & Label
Label Slitting with Custom Geometry
Printing and label factories need very neat cuts. They cut paper, films, and coated labels. Custom circular knives with thin, straight edges and small bevel angles (20–25°) cut cleaner. Micro-serrated blades with a 0.5–1 mm pitch stop fibers from pulling out. Thin blades (0.5 mm or less) work well for films and save material.
Blade material is important. Tungsten carbide and high-speed steel are used a lot. Tungsten carbide lasts a long time for big jobs. High-speed steel is sharp and tough for jobs with many blade changes.
Case Example: Perforated Blades for Easy-Open Labels
A label maker wanted labels that tear open easily. They used custom micro-serrated blades made from high-speed steel with a DLC coating. The new blades stopped fraying and made tears more even. Blade changes dropped from three times a day to once every two days. Bad products dropped from 7% to less than 1%. Downtime went from two hours a week to under 30 minutes. These changes came from better blade thickness and edge angle, not new machines.
Key Performance Factors
- Blade material (tungsten carbide, high-speed steel) for sharpness and strength
- Custom edge shapes (micro-serrated, thin) for neat cuts
- Coatings (DLC, TiN) to lower friction and help blades last
- Better cutting, less waste, and more machine time
Tip: Changing blade shape and material can make labels better and save money.
Metal-Verarbeitung
D2 Blades for Metal Coil Slitting
Metal plants use D2 steel blades to cut metal coils. D2 steel has lots of carbon and chromium. This makes it hard and helps it last longer. Molybdenum and vanadium in D2 steel make it strong for tough jobs. Tungsten carbide blades are also used for jobs that wear blades out fast.
Case Example: Reducing Downtime in Steel Plants
A steel shop changed from regular blades to custom D2 steel blades. The new blades stayed sharp longer and did not bend. Work speed went up by 30% because blades needed fewer changes. In a recycling plant, blade changes dropped by 67%. Machines ran longer and cut mixed metals better. The right blade material and setup made cuts tighter and smoother, with less waste.
Key Performance Factors
- Blade material (D2 steel, tungsten carbide) for sharpness and strength
- Good blade setup and pressure for longer blade life
- Steady cutting even with hard jobs
- Fewer blade changes, less stopping, and better products
Note: D2 steel and tungsten carbide blades help metal plants cut faster, stop less, and save money.
Material-Application Table
The table below matches blade material, coatings, and edge types to common jobs. This helps factories pick the best setup for their work.
| Anwendungsbereich | Empfohlene Klingenmaterialien | Typical Edge Types & Configurations | Key Coating Types and Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Film Slitting | tungsten carbide, high-speed steel, hardened steel | Thin, sharp edge, single bevel | TiN (less wear up to 45%), TiAlN (handles heat), DLC (cuts force by 50%) |
| Rubber & Plastics | tungsten carbide, high-speed steel, D2 tool steel | Double bevel, blunt edge | DLC (stops sticking, lasts longer), TiAlN (handles heat), TiN (saves money) |
| Nonwovens/Textiles | D2 tool steel, M2 high-speed steel, tungsten carbide, ceramic | Sharp, clean edge, single bevel | TiN, TiCN, TiAlN, DLC (lasts longer, smooth cuts) |
| Paper & Foil | D2 steel, M2 steel, CPM 10V steel, carbide inlay | Sharp edge, single or double bevel | TiN, DLC (hard, smooth) |
| Lebensmittelverarbeitung | stainless steel, ceramic | Sharp edge, single bevel | CrN, PTFE/Teflon (stops rust, non-stick) |
| Beschichtungstyp | Hauptvorteile | Quantified Improvements |
|---|---|---|
| Titannitrid (TiN) | Makes blades harder, lowers friction | Up to 45% less wear |
| Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiAlN) | Handles heat, stops rust | Funktioniert gut bei hohen Geschwindigkeiten |
| Diamantähnlicher Kohlenstoff (DLC) | Lasts long, stops sticking | Can cut force by over 50% |
| Chromnitrid (CrN) | Stops rust | Good for wet or chemical jobs |
| PTFE/Teflon | Non-stick, stops rust | 10-20% longer blade life |
| Kantentyp | Beschreibung | Am besten für |
|---|---|---|
| Square Edge | Flat and sharp | Slitting, paper, film |
| Einseitig abgeschrägt | One side slanted, one side flat | Thin things, careful cuts |
| Double Bevel | Both sides slanted | Tough things like rubber, foam |
| Serrated/Toothed | Saw-like teeth | Textiles, nonwovens, hard jobs |
| Überbacken | Rounded teeth, smooth cut | Soft things, food, foam |
| Schrägzahn | Angled teeth for tough jobs | Thick or stringy things |
Summary: Factories cut better and save money by matching blade material, edge type, and coating to each job. For example, film slitting works best with tungsten carbide or high-speed steel blades, thin edges, and TiN or DLC coatings. Rubber and plastics need stronger blades and double bevel edges. Nonwovens and textiles do well with hard steels or ceramics and tough coatings. Paper and foil cutting uses tool steels with sharp edges and smooth coatings. Food jobs need stainless steel or ceramic blades with coatings that stop rust.
Community & Industry Challenges

Sourcing Issues
Many people online talk about how hard it is to find good Lieferanten for industrial circular knives. They often need custom blades for special machines or materials. Some want to go from one drawing to making many blades. It is hard to find suppliers who take small orders or special requests. More people want custom blanks made from tungsten carbide or ceramic blades. But not many companies can make these products. Users say they have to wait a long time and buy a lot at once. Some suppliers do not have the right blade material, like tungsten carbide or ceramic blades, for what users need.
Many companies want tungsten carbide or ceramic blades because they last longer and cut better, but it is not easy to find a supplier who can help.
Manufacturer Limitations
Manufacturers have problems when making industrial circular knives for special jobs. One big problem is these knives only cut straight at a 90-degree angle. This makes it hard to use them for jobs that need other angles. Manufacturers can change the edge style, tooth shape, or blade material. But the cutting angle always stays the same. This makes it hard to use tungsten carbide and ceramic blades for some jobs. Some factories do not have the right tools or skills to work with tough materials like tungsten carbide or to shape ceramic blades for custom orders. These problems slow things down and make it hard for users to get the blade they want.
Gelernte Lektionen
Users and companies learned some things from these problems:
- Always check if a supplier can make custom orders for tungsten carbide or ceramic blades before sending drawings.
- Ask about the smallest order you can make and how long it will take for industrial circular knives.
- Make sure the supplier knows how to work with both tungsten carbide and ceramic blades.
- Try a small batch before buying a lot.
- Give clear details about the material and cutting job.
Tip: Talking clearly with suppliers helps stop mistakes and saves time.
A table can help users remember what to check:
| Was zu überprüfen ist | Warum es wichtig ist |
|---|---|
| Supplier’s material options | Not all offer tungsten carbide or ceramic blades |
| Minimum order quantity | Some only accept large orders |
| Experience with custom jobs | Reduces risk of errors |
| Cutting angle limitations | Affects suitability for your job |
Selection Guide for Custom Circular Knives

Supplier Checklist
Picking the right supplier for custom circular knives is important. It helps the knives work well and last longer. Buyers should look for suppliers with good certifications and lots of experience. They should also have helpful support. Most buyers, about 72%, say certifications like ISO 9001 are very important. A good supplier should offer custom choices and help after you buy, like sharpening and technical support.
Key things to look for:
- Certifications (ISO 9001 or similar)
- Ability to make custom knives
- Help after buying (sharpening, fixing)
- Good machines and enough workers
- Clear and quick communication
| Kriterien | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| Quality standards | Can meet or beat quality needs; has certifications like ISO 9001 |
| Delivery capabilities | Sends orders on time and can be flexible |
| Technical expertise | Has skills for special blade designs |
| Financial stability | Has enough money to stay in business |
| Communication | Gives clear updates and answers questions fast |
Note: Check your supplier’s skills often to keep quality high.
Cost-Benefit Tips
Getting the best price, quality, and delivery time takes planning. Buyers should pick the features that matter most for their job. Fancy blade shapes, special materials, and shiny finishes cost more and take longer to make. But these extras can help the blade last longer and cut better.
| Faktor | Impact on Cost and Value | Impact on Lead Time and Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Fancy shapes and features cost more | Takes more time for setup and checks |
| Materialien | Better steels cost more but last longer | Finding them can take longer |
| Finish | Shiny finishes cost extra | Some finishes help blades last |
| Accessories | Special holders or stands cost more | May take more time to make |
Tip: Buyers should choose blade features that fit their budget and schedule.
Mistakes to Avoid
Many buyers make mistakes when ordering custom circular knives. Avoiding these mistakes helps get better results.
- Always pick trusted and skilled suppliers to lower risk.
- Do not trust only photos; ask for clear pictures or check samples if you can.
- Think about the whole blade, not just the steel—edge shape and heat treatment are important.
- Tell the supplier clearly how you will use the blade and what you want.
Blades can chip or break if the edge shape or steel is wrong. Picking the right steel, edge, and heat treatment stops these problems. For wet or harsh places, pick materials and finishes that do not rust.
Tip: Talking clearly and giving details helps stop mistakes and makes sure the knife works as needed.
Making custom circular knives work well needs good design and the right materials. Companies do better when they follow simple steps:
- Think about what you need to cut and how your machines work.
- Look at different blade types and materials for your job.
- Talk to a few suppliers about testing and getting help.
- Try out the blades in real work before picking one.
- Be careful not to forget if the blade fits your machine or if the place is too hot or wet.
- Use online tools to find good companies to work with.
Experts and people in the industry give advice that helps everyone choose better. For the best results, ask a specialist or talk to others who use these knives.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
What is the minimum order quantity for custom circular knives?
Most suppliers want you to buy a certain number of knives. This number is usually between 10 and 100 pieces. Some companies let you buy just one knife to test. Always ask about the minimum order before you start your project.
How long does it take to receive custom circular knives?
It usually takes four to six weeks to get your knives. This time covers design, making samples, and checking quality. If your knife is special or uses rare materials, it might take longer.
Can customers provide their own drawings or samples for customization?
Yes. Most companies let you send in CAD files, hand drawings, or real samples. Clear drawings help make sure your custom circular knives are made the way you want.
What materials are available for custom circular knives?
Manufacturers have many materials to pick from. Some common ones are tungsten carbide, high-speed steel, D2 tool steel, and stainless steel. The best material depends on what you are cutting and where you use the knife.
Are special coatings available for custom circular knives?
Yes. Suppliers can add coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC). These coatings help blades last longer, lower friction, and work better with sticky or rough materials.
Siehe auch
Industrielle Kreismesser: Leistungs- und Materialvergleich
So wählen Sie das beste Kreismesser für Ihre Schneidanforderungen
Top 10 Tipps, wie Sie die Lebensdauer Ihrer Kreisrasierklingen verlängern
So wählen Sie die richtigen Kreisschneiderklingen für lang anhaltende Leistung
So halten Sie die Klinge Ihres Rundmessers scharf und langlebig


