Scelta del materiale migliore e configurazione per Coltelli Circolari Industriali Le lame sono progettate per lavorare al meglio in qualsiasi fabbrica. Il materiale della lama, il tipo di filo e i rivestimenti speciali devono essere adatti al materiale da tagliare e alle esigenze di ogni settore. Acciaio rapido, carburo di tungsteno, ceramica e rivestimenti speciali hanno tutti i loro vantaggi. Scegliere la soluzione giusta garantisce tagli più netti, prolunga la durata delle lame e velocizza il lavoro.
Punti chiave
- Scegliere il materiale giusto per la lama, come acciaio rapido, carburo di tungsteno, ceramica o acciaio inossidabile, aiuta le lame a tagliare meglio e a durare più a lungo.
- Le tipologie di taglio della lama, come smusso singolo, doppio o seghettato, devono adattarsi al materiale. Questo aiuta a ottenere tagli puliti e meno sprechi.
- Rivestimenti come TiN, DLC e TiCN rendono le lame più resistenti. Riducono inoltre l'attrito, prevengono la ruggine e ne prolungano la durata.
- Le lame rotanti tagliano più velocemente e si consumano in modo uniforme. Sono ideali per materiali sottili e lavori rapidi.
- Le lame personalizzate, realizzate per materiali e lavorazioni speciali, possono ridurre i tempi di fermo macchina fino a 75%. Riducono anche notevolmente il tasso di scarto.
- Prendersi cura delle lame pulendole, affilandole e riponendole ne garantisce il corretto funzionamento e consente di risparmiare denaro.
- L'abbinamento del materiale della lama, del tipo di bordo e del rivestimento al lavoro rende il lavoro più veloce e meno costoso.
- Parlare con esperti o aziende come Nanjing Metal può aiutarti a scegliere o progettare la lama più adatta alle tue esigenze.
Risultati chiave
I migliori materiali
La scelta del materiale giusto per la lama è molto importante per ogni lavoro. Acciaio rapido (HSS) è molto duro e mantiene il filo affilato anche con movimenti rapidi. Il carburo di tungsteno è molto resistente e dura a lungo, quindi è ideale per i luoghi in cui le lame vengono utilizzate molto. Le lame in ceramica rimangono affilate a lungo e non arrugginiscono, il che è ottimo per tagli precisi in ambienti puliti o medici. L'acciaio per utensili D2 e gli acciai ad alto tenore di carbonio come il 1095 e il 52100 sono resistenti e durano a lungo, quindi sono adatti per il taglio di gomma e plastica. L'acciaio inossidabile è ideale per lavori alimentari, medici e su tessuti non tessuti perché non arrugginisce ed è facile da pulire.
Realizzazione di lame con elevata concentricità Aiuta a tagliare meglio e a durare più a lungo. Le lame che non oscillano molto vibrano meno, durano più a lungo e sprecano meno materiale. Questo è molto utile nel settore dell'imballaggio e della produzione alimentare.
Configurazioni principali
Come il Coltelli Circolari Industriali Vengono apportate modifiche che influenzano la loro efficacia e la frequenza con cui è necessario ripararle. Le lame sottili e affilate con un solo bisello sono ottime per tagliare la pellicola. Eseguono tagli netti e non sprecano molto materiale. I bordi a doppio bisello o smussati sono resistenti e adatti a gomma e plastica. Possono assorbire gli urti e non si scheggiano facilmente. I bordi seghettati o ondulati sono adatti per materiali resistenti o elastici. Aiutano la macchina a lavorare più facilmente e rendono i tagli più uniformi. Le lame con punta in metallo duro e rivestimento ceramico durano più a lungo e devono essere sostituite meno spesso nelle fabbriche più trafficate.
- I tipi di lama più adatti sono:
- Lame da taglio per pellicole e lamine sottili
- Lame per taglio a punti per gomma e schiuma
- Lame da taglio per carta e cartone
- Lame perforatrici per imballaggio
- Lame dentate per materiali spessi o fibrosi
Pulire, affilare e conservare le lame nel modo giusto aiuta a farle durare più a lungo e a farle funzionare al meglio.
Matrice applicativa
La tabella seguente mostra i migliori materiali per lame e tipi di taglienti per diversi lavori:
| Area di applicazione | Materiali comuni delle lame | Tipi e configurazioni di bordi tipici | Considerazioni sulle prestazioni |
|---|---|---|---|
| Film | HSS, Carburo di tungsteno | Bordo sottile e affilato, smusso singolo | Tagli molto precisi, lavoro veloce, poco spreco |
| Gomma e plastica | Acciaio per utensili D2, HSS, Carburo | Doppio bisello, bordo smussato | Molto resistente, dura a lungo, può sopportare colpi |
| Non tessuti (igiene) | Acciaio inossidabile, ceramica | Bordo affilato e pulito, smusso singolo | Tagli puliti, non arrugginisce, sicuro per l'igiene |
| Carta e lamina | HSS, Acciaio per utensili, Carburo | Bordo tagliente, smusso singolo o doppio | Tagli uniformi, meno polvere, le lame durano più a lungo |
| Lavorazione alimentare | Acciaio inossidabile, ceramica | Bordo affilato, smusso singolo | Sicuro per gli alimenti, non arrugginisce, facile da pulire |
Nota: i rivestimenti come TiN, CrN e DLC rendono le lame più resistenti e le aiutano a tagliare meglio in tutti i lavori.
Domande frequenti
Quale materiale per la lama circolare è migliore per tagliare pellicole multistrato?
Carburo di tungsteno o HSS Le lame con un bordo sottile e affilato sono le più adatte per le pellicole multistrato. Garantiscono tagli netti e non sprecano molto materiale.
Il rivestimento TiCN può superare le prestazioni del TiN nel taglio ad alta velocità?
I rivestimenti TiCN sono più duri e durano più a lungo di quelli TiN. Sono ideali per tagli rapidi quando si desidera che le lame durino più a lungo.
Panoramica dei coltelli circolari industriali
Definizione
I coltelli circolari industriali sono utensili rotondi con bordi affilati. Ruotano per tagliare, fendere o incidere molti materiali in fabbrica. La loro rotazione li rende adatti per lavori rapidi sulle linee di produzione. La forma del bordo contribuisce a realizzare tagli netti e precisi. I produttori utilizzano acciaio al carbonio, acciaio rapido, acciaio legato per utensili, carburo di tungsteno, ceramica e acciaio inossidabile per diversi lavori. Rivestimenti come il nitruro di titanio (TiN) e il nitruro di cromo (CrN) rendono i coltelli più duri e ne aumentano la durata. Questi rivestimenti prevengono anche la ruggine e riducono l'attrito. Esistono molti tipi di coltelli circolari. Alcuni sono dischi pieni, altri hanno lame inserite e altri ancora sono incisi, tagliati a cesoia, perforati, tagliati a fessura, concavi o dentati. Ogni tipo è realizzato per un tipo specifico di taglio o materiale.
Il movimento rotatorio, i design speciali e le forme dei bordi rendono i coltelli circolari industriali diversi dagli altri utensili da taglio. Sono adatti alle fabbriche veloci e sono importanti per la produzione moderna.
Stili di bordo
Lo stile del bordo influenza la qualità del taglio di un coltello circolare. Determina anche quali materiali può tagliare. Scegliere la forma giusta del bordo aiuta a ottenere tagli netti e meno sprechi. La tabella seguente mostra gli stili di bordo più comuni e le loro funzioni:
| Stile del bordo | Descrizione e impatto sulle prestazioni di taglio | Idoneità dell'applicazione |
|---|---|---|
| Stile V | La forma a V standard fornisce una forza uniforme. Alcune forme a V distribuiscono la forza e controllano la pressione. | Adatto per tagli generali con forza uniforme |
| Smerlato | Ha denti arrotondati come una sega. Taglia senza problemi oggetti morbidi o spessi. | Utilizzato per schiume, alcuni alimenti e materiali morbidi |
| Stile L | Non spiegato | Non spiegato |
| Stile piolo | Non spiegato | Non spiegato |
| dente obliquo | Non spiegato | Non spiegato |
È necessario scegliere il tipo di bordo più adatto alla durezza e allo spessore del materiale. Ad esempio, il taglio a V è adatto alla maggior parte dei lavori. I bordi smerlati sono più adatti a materiali morbidi o spessi.
Lame rotanti vs. lame dritte
Le lame rotanti e dritte svolgono funzioni diverse in fabbrica. Le lame rotanti sono rotonde e ruotano quando vengono utilizzate. Questo consente loro di tagliare rapidamente e ripetutamente. Sono ideali per lamiere sottili, bobine e materiali che necessitano di tagli frequenti. Le lame dritte hanno un bordo piatto che non si muove. Vengono utilizzate in macchine come le ghigliottine per tagliare materiali spessi come lamiere o barre d'armatura in un'unica passata.
Le lame rotanti vengono sottoposte a trattamenti termici speciali per renderle più resistenti e durature. Questi trattamenti includono tempra, cementazione e nitrurazione. Ciò significa che le lame rotanti si usurano più lentamente e richiedono meno riparazioni. Ad esempio, le lame rotanti trattate termicamente possono durare fino a 40% più lungo rispetto a quelle non trattate. Le lame dritte possono usurarsi in modo non uniforme e necessitano di essere affilate o sostituite più spesso.
| Caratteristica | Lame dritte | Lame rotanti |
|---|---|---|
| Progettazione della lama | Bordo piatto; utilizzato per cose spesse | Rotondo, gira; taglia cose sottili più e più volte |
| Meccanismo di taglio | Tagli in una mossa dritta | Rotazioni per tagli rapidi e ripetuti |
| Velocità ed efficienza di taglio | Più lento, ideale per lavori spessi o piccoli | Più veloce, adatto a lavori grandi e impegnativi |
| Applicazione | Lamiere Metal, barre d'armatura, piastre spesse | Metalli sottili, lamine, strisce, pellicole, carta |
| Usura e manutenzione | Si consuma in modo non uniforme; necessita di essere affilato spesso | Si consuma in modo uniforme; necessita di meno riparazioni |
| Durata e longevità | Dipende da cosa taglia | Dura più a lungo con uno speciale trattamento termico |
| Costo e complessità | Semplice, solitamente più economico | Più parti, più costa perché gira |
Le lame rotanti si consumano in modo uniforme e durano più a lungo, soprattutto nelle fabbriche più dinamiche e trafficate. Le lame dritte sono più adatte per oggetti spessi che necessitano di un taglio netto e deciso.
Nanjing Metal è un produttore leader di coltelli circolari industriali. Produce lame da oltre 20 anni. L'azienda è in grado di realizzare lame speciali per diverse esigenze produttive. Il suo team controlla ogni lama per garantirne l'alta qualità. Se un'azienda ha bisogno di una lama speciale, Nanjing Metal offre servizi di lame personalizzate per aiutare.
Impatto del materiale e del rivestimento della lama su costi ed efficienza
Il materiale e il rivestimento della lama che scegli possono influire sui costi e sul tempo investiti da una fabbrica. Ogni materiale è più adatto a determinati lavori. I rivestimenti migliorano la resa delle lame, prolungandone la durata e rendendole più lisce.
Come il materiale della lama influisce su costi ed efficienza
Scegliere il materiale giusto per la lama fa risparmiare denaro e migliora il taglio. Materiali più duri come il carburo di tungsteno e la ceramica durano più a lungo. Non devono essere sostituiti così spesso. Acciaio inossidabile e HSS Non sono così resistenti, ma costano meno e durano comunque a lungo. La tabella seguente mostra come i diversi materiali delle lame influiscono sul costo e sulla loro efficacia:
| Materiale della lama | Durezza (HRC) | Applicazioni ideali | Impatto su costi ed efficienza |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acciaio inossidabile | 55–60 | Alimentare, medico, leggero | Durata media, resistenza alla corrosione, durata media |
| Acciaio ad alta velocità | 60–64 | Carta, legno, plastica | Supporta vari spessori dei bordi, costi e durata bilanciati |
| Carburo di tungsteno | 75–85 | Metal, gomma, compositi | Elevata durezza, maggiore durata, riduce i cambi di lama e i tempi di fermo macchina |
| Ceramica | 80–90 | Lamine, microfilm, ottica | Bordi ultrasottili ma fragili, rischio di rottura se usati in modo improprio |
Le lame in carburo di tungsteno e ceramica possono tagliare materiali resistenti per lungo tempo. Ciò significa che non è necessario fermarsi e sostituire le lame così spesso. Ad esempio, HSS Le lame per il taglio delle pellicole rimangono affilate e durano a lungo. Ecco perché molte fabbriche le utilizzano per il confezionamento.
Il ruolo dei rivestimenti nelle prestazioni delle pale
Rivestimenti come il nitruro di titanio (Stagno), carbonio simile al diamante (Contenuti scaricabili), e carbonitruro di titanio (TiCN) migliorano la funzionalità delle lame. Questi rivestimenti rendono le lame più dure e lisce. Impediscono inoltre che i residui si attacchino alla lama. La tabella seguente mostra le proprietà di ciascun rivestimento:
| Tipo di rivestimento | Vantaggio chiave | Aree di applicazione | Effetto sui costi di proprietà e sull'efficienza |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiN (nitruro di titanio) | Riduce l'attrito, aumenta la durezza | Alimenti, imballaggi, tessili | Prolunga la durata della lama, riduce l'usura dovuta all'attrito |
| DLC (carbonio simile al diamante) | Previene l'incollamento, dissipa il calore | Pellicola, plastica, gomma | Aumenta gli intervalli di cambio lama di 53%, eliminando l'accumulo di adesivo |
| TiCN (carbonitruro di titanio) | Migliora la resistenza all'usura in condizioni difficili | Metal, compositi | Migliora la durata in condizioni difficili, riduce gli scarti e i tempi di fermo |
Coltelli rotanti in carburo di tungsteno con Contenuti scaricabili Il rivestimento può tagliare materiali appiccicosi o ruvidi senza dover essere pulito o sostituito spesso. Le lame in ceramica per tessuti non tessuti rimangono affilate e non arrugginiscono, quindi sono ideali per lavori medici e di pulizia.
Impatto nel mondo reale: guadagni in termini di costi ed efficienza
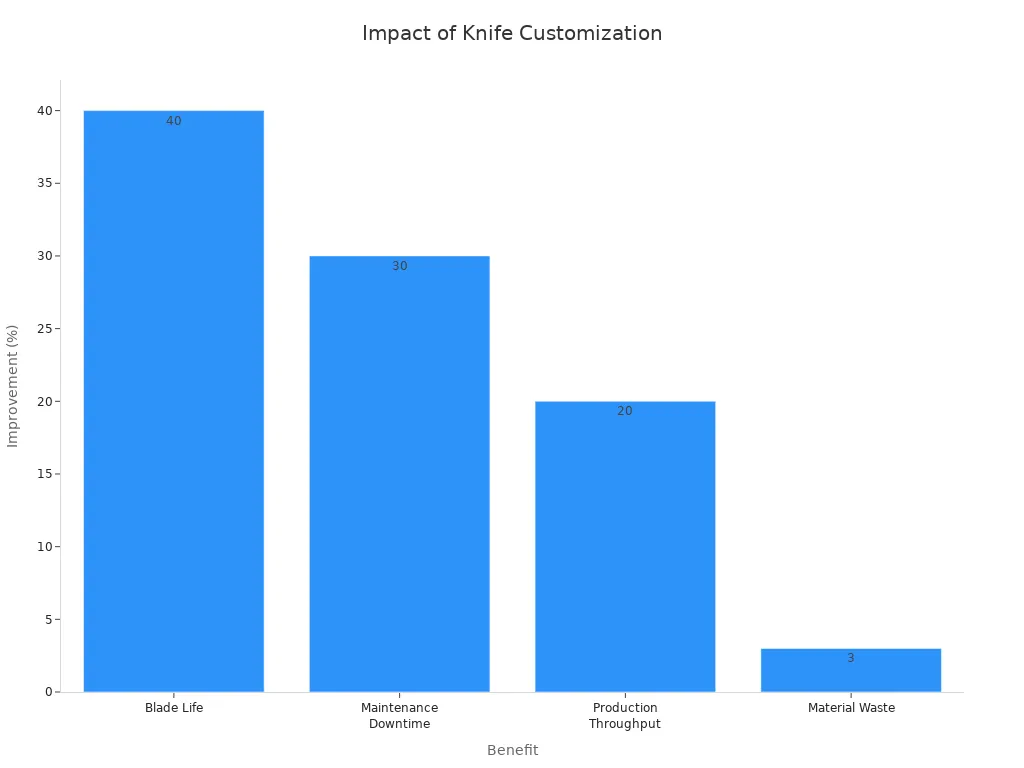
Quando le fabbriche utilizzano i migliori materiali e rivestimenti per le lame, queste funzionano meglio. Il grafico seguente mostra come le lame personalizzate aiutano le fabbriche:
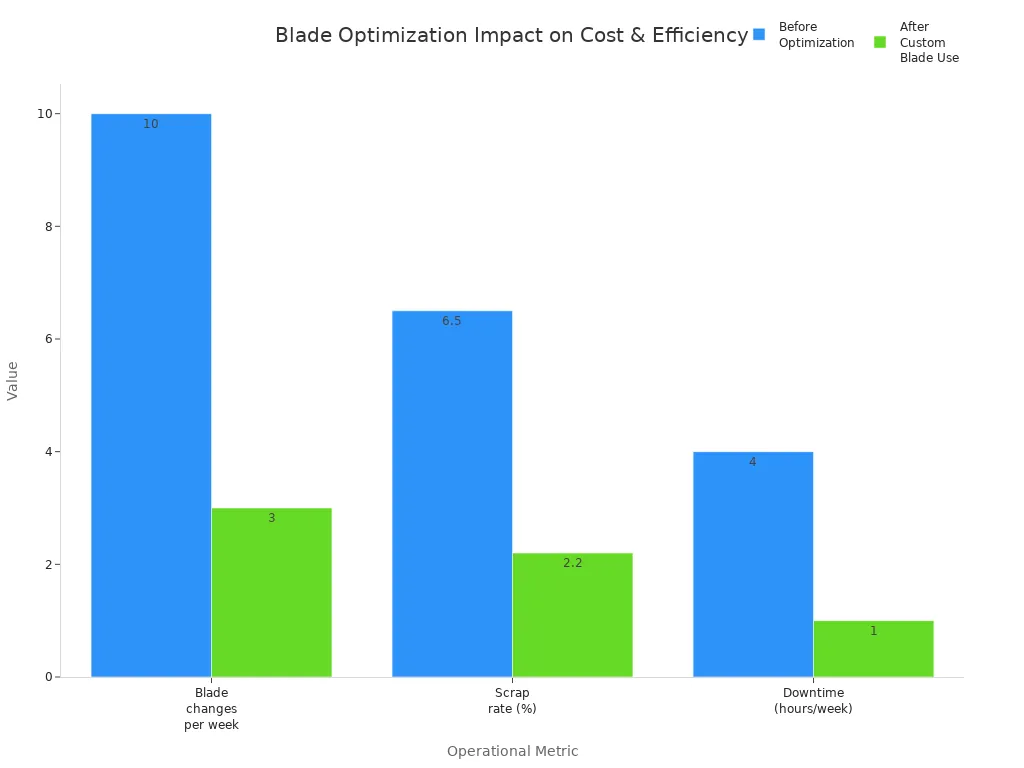
- I cambi di lama settimanali sono diminuiti del 70%.
- I tassi di rottamazione sono diminuiti di 66%.
- I tempi di inattività sono stati ridotti di 75%.
Un'azienda alimentare ha utilizzato lame seghettate personalizzate e ha tagliato più velocemente con 22%. Le loro lame sono durate da 2 a 6 settimane. I loro tagli erano anche più precisi, con una differenza inferiore a 0,5 mm.
Influenza del materiale e del rivestimento sulla stabilità e sulla durata della lama
I test dimostrano che acciaio inossidabile martensitico, come X39Cr13, è molto duro e resistente. Questo aiuta le lame a durare più a lungo e a tagliare meglio. I rivestimenti applicati tramite PVD, come AlCrN e Contenuti scaricabili, fanno sì che le lame durino ancora più a lungo. Tuttavia, se nel materiale sono presenti elementi duri come la sabbia, le lame possono usurarsi più velocemente. Scegliere la lama e il rivestimento giusti mantiene il taglio costante ed evita che le macchine si rompano.
Perché la personalizzazione è importante
Ogni fabbrica ha i suoi problemi di taglio. Le lame personalizzate realizzate per lavori specifici aiutano a risparmiare tempo e denaro. Nanjing Metal è un produttore leader di coltelli circolari industriali. Produce lame personalizzate da oltre 20 anni. Il suo team offre servizi di lame personalizzate per soddisfare le esigenze di ogni cliente.
Suggerimento: scegli sempre il materiale e il rivestimento della lama adatti al tipo di taglio che intendi effettuare. Questo ti aiuterà a risparmiare denaro, a lavorare più velocemente e a far durare le lame più a lungo.
Domande frequenti
In che modo rivestimenti come DLC e TiN influiscono sulla frequenza di sostituzione delle pale?
Contenuti scaricabili E Stagno I rivestimenti rendono le lame più dure e lisce. Questo significa che durano più a lungo e devono essere sostituite meno spesso.
Qual è la lama migliore per tagliare la gomma abrasiva?
Coltelli rotanti in carburo di tungsteno con un Contenuti scaricabili I rivestimenti sono più adatti per tagliare la gomma ruvida. Durano più a lungo e si consumano più lentamente.
Le lame personalizzate possono davvero ridurre i tempi di inattività?
Sì. Le lame personalizzate realizzate per lavori speciali possono ridurre i tempi di fermo fino al 75% e abbassare i tassi di scarto.
Vuoi migliorare il tuo taglio? Contatta i tecnici commerciali di Nanjing Metal per aiuto e consigli.
Confronto completo dei materiali dei coltelli circolari industriali e delle loro prestazioni
Acciaio per utensili
Caratteristiche del materiale
L'acciaio per utensili è molto utilizzato perché è duro, tenace e non troppo costoso. È realizzato in acciaio al carbonio e legato. Queste lame sono adatte a lavori in cui l'usura non è troppo rapida. Le lame in acciaio per utensili sono facili da modellare e affilare. Non durano quanto altri materiali per lame. Tuttavia, sono una scelta intelligente quando si vuole risparmiare denaro e non si ha bisogno che la lama duri per sempre.
La tabella sottostante mostra il principali tipi di acciaio per utensili, in cosa sono bravi e dove vengono utilizzati:
| Tipo di acciaio per utensili | Caratteristiche principali delle prestazioni | Applicazioni comuni |
|---|---|---|
| Acciai temprati in acqua | Si indurisce in acqua, resiste allo stress e all'usura | Utilizzato per il taglio del legno e della carta |
| Acciai resistenti agli urti | Non si crepa o si rompe se colpito duramente | Utilizzato per scalpelli, punzoni e utensili che vengono colpiti |
| Acciai rapidi | Rimane duro e forte anche quando è caldo | Utilizzato per tagli e forature veloci |
| Acciai per lavorazioni a freddo | Resistente e non si consuma rapidamente a temperatura ambiente | Utilizzato per utensili che tagliano o modellano oggetti per lungo tempo |
| Acciai per lavorazioni a caldo | Rimane duro e resistente quando è caldo | Utilizzato per forgiatura, pressofusione e utensili a caldo |
L'acciaio D2 è un tipo di acciaio per utensili con un elevato contenuto di carbonio e cromo. È molto duro e mantiene bene il filo dopo il trattamento termico. Può raggiungere i 60-62 HRC. I coltelli in acciaio per utensili vengono utilizzati nella lavorazione della carta, degli imballaggi, degli alimenti, della plastica e dei metalli. La scelta del tipo di acciaio dipende da quanto duro, resistente o facile da affilare si desidera e da quanto si è disposti a spendere.
Le lame in acciaio per utensili sono la scelta migliore quando si ha più a cuore il risparmio che la durata della lama.
Lame HSS
Caratteristiche del materiale
Acciaio rapido (HSS) le lame funzionano meglio del normale acciaio per utensili. HSS Le lame rimangono dure e affilate anche quando si surriscaldano. Questo le rende ideali per lavori di taglio rapidi e impegnativi. Durano più a lungo e non necessitano di essere sostituite spesso. Questo aiuta gli operatori a ottenere di più.
La tabella sottostante confronta HSS lame e lame in carburo di tungsteno:
| Parametro | Lame in acciaio rapido (HSS) | Lame in Carburo di Tungsteno |
|---|---|---|
| Durezza (Vickers) | 700 – 900 HV | 1600 – 2200 HV |
| Velocità di taglio | Circa 70 m/min (acciaio) | Circa 160 m/min (acciaio legato) |
| Durata dell'utensile | Bene, ma non così a lungo | Dura 5-10 volte di più |
| Resistenza al calore | Fino a 500°C | Fino a 1000°C |
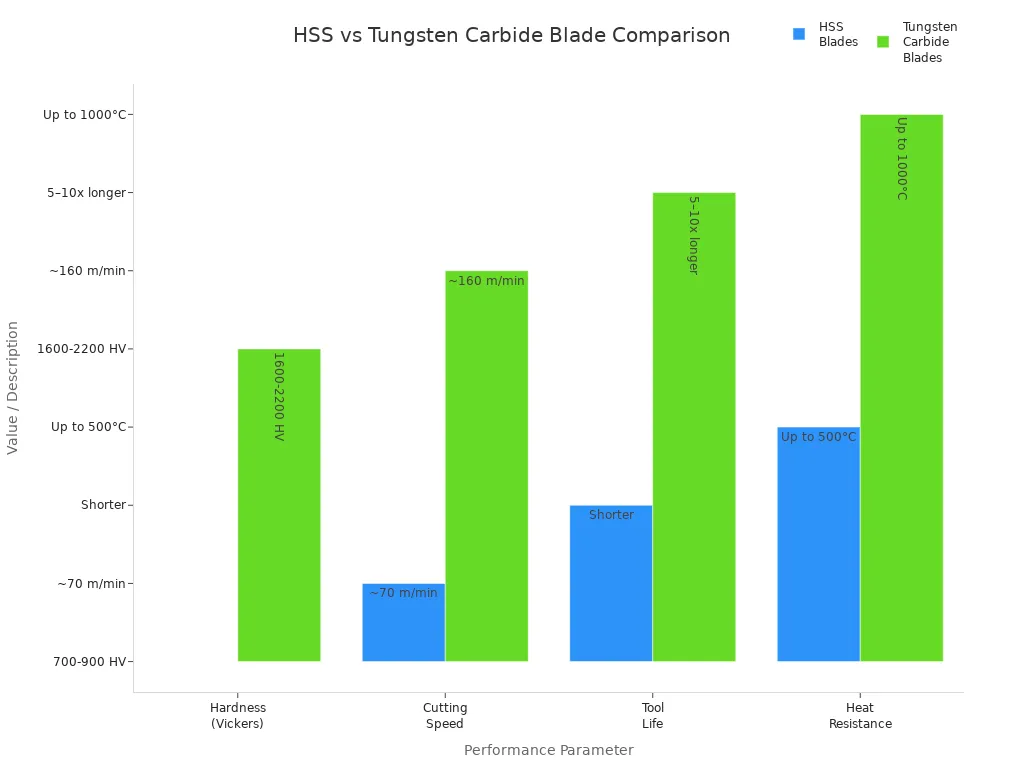
HSS Le lame sono resistenti e possono assorbire gli urti senza rompersi. Sono più facili da affilare e costano meno delle lame in carburo di tungsteno. Questo le rende adatte per materiali più morbidi e lavori non troppo ruvidi. Nelle cartiere, HSS Le lame sono molto utilizzate per tagliare e fendere. Devono essere affilate più spesso rispetto alle lame in metallo duro.
HSS Le lame offrono un buon mix di durata, costi contenuti e facilità di riparazione. Ecco perché molti le usano per i coltelli circolari industriali.
Lame in Carburo di Tungsteno
Caratteristiche del materiale
Le lame in carburo di tungsteno sono le più dure e durano più a lungo. Mantengono il filo affilato molto più a lungo dell'acciaio per utensili o HSSQuesto è vero quando si tagliano oggetti duri o ruvidi. Essendo così duri, possono tagliare più velocemente e durare più a lungo. Questo è molto utile in luoghi affollati che necessitano di tagli precisi.
La tabella seguente mostra come le lame in carburo di tungsteno differiscono da HSS e lame in acciaio per utensili:
| Attributo | Lame in Carburo di Tungsteno | Lame in acciaio HSS e per utensili |
|---|---|---|
| Durezza | Molto più difficile, il più difficile | Non duro come il carburo |
| Mantenimento del bordo | Rimane affilato molto più a lungo, anche con materiali ruvidi | Necessita di essere affilato più spesso |
| Resistenza all'usura abrasiva | Ideale per non consumarsi, ottimo per le situazioni difficili | Si consuma più velocemente, diventa opaco più velocemente |
| Robustezza | Più probabilità di scheggiarsi se colpito | Più resistente, può sopportare colpi e scosse |
| Resistenza al calore | Gestisce più calore, può tagliare più velocemente | Non sopporta molto calore, diventa morbido sopra i 600°C |
| Costo | Costa di più all'inizio ma fa risparmiare denaro in seguito | Più economico all'inizio, più facile ed economico da affilare |
| Applicazioni adatte | Ideale per molti tagli e lavori difficili | Adatto per lavori normali e cose più morbide |
- Le punte in carburo di tungsteno mantengono il filo e durano più a lungo, anche con oggetti duri o spessi.
- Le lame in carburo rimangono dure anche a temperature molto elevate (oltre 1100 °C), quindi possono tagliare più velocemente e durare più a lungo.
- Il carburo è più duro ma può rompersi più facilmente del HSS se colpito o scosso.
- Le lame in carburo sono ideali per tagli rapidi, precisi e grossolani. HSS le lame sono più adatte per lavori normali e quando la lama potrebbe essere urtata.
Le lame in carburo di tungsteno devono essere maneggiate con cura perché possono scheggiarsi. Ma sono così efficaci nei lavori più impegnativi che molti pensano che ne valga la pena. Le fabbriche che tagliano gomma, materiali compositi o pellicole stratificate spesso scelgono il carburo di tungsteno per la sua affilatura e la sua lunga durata.
Se vuoi che le tue lame durino il più a lungo possibile e si interrompano meno spesso, le lame in carburo di tungsteno sono le migliori.
Nanjing Metal è un produttore leader di coltelli circolari industriali. Produce lame personalizzate da oltre 20 anni. Il suo team è in grado di realizzare lame speciali per molteplici applicazioni. Se avete bisogno di una lama speciale, potete consultare servizi di lame personalizzate per aiutarti nel tuo lavoro.
Domande frequenti
Quale materiale per lame circolari è migliore per tagliare materiali compositi abrasivi?
Le lame in carburo di tungsteno sono ideali per tagliare materiali compositi grezzi perché sono molto dure e non si usurano rapidamente.
Le lame HSS sono adatte al taglio ad alta velocità di carta e pellicola?
SÌ, HSS Le lame rimangono affilate anche ad alte velocità e sono adatte al taglio di carta e pellicola. Tuttavia, devono essere affilate più spesso rispetto alle lame in metallo duro.
Vuoi migliorare il tuo taglio? Puoi chiedere Ingegneri commerciali di Nanjing Metal per chiedere aiuto.
Lame in Ceramica
Caratteristiche del materiale
Le lame in ceramica sono molto resistenti e mantengono l'affilatura a lungo. Sono realizzate con materiali ceramici speciali come lo zirconio o l'allumina. Queste lame hanno una durezza Mohs di 8,2, molto più dura dell'acciaio. Per questo motivo, le lame in ceramica possono rimanere affilate fino a dieci volte più a lungo delle lame in acciaio. Gli operatori apprezzano il fatto che le lame in ceramica non arrugginiscano né si corrodano. Questo le rende ideali per ambienti puliti come industrie alimentari, stabilimenti medicali e linee di produzione di prodotti per l'igiene.
Le lame in ceramica sono leggere, quindi gli operatori non si stancano facilmente. Non essendo metalliche, non reagiscono a contatto con oggetti sensibili. Tuttavia, data la loro elevata durezza, le lame in ceramica possono rompersi o scheggiarsi se colpite lateralmente. Ecco perché le fabbriche utilizzano lame in ceramica principalmente per il taglio accurato di materiali morbidi o delicati come pellicole, tessuti non tessuti e carte speciali.
| Proprietà | Lame in Ceramica | Lame in acciaio |
|---|---|---|
| Durezza (Mohs) | 8.2 (molto difficile) | 5–6 |
| Mantenimento del bordo | Rimane affilato fino a 10 volte più a lungo | Necessita di essere affilato spesso |
| Fragilità | Alto (può scheggiarsi o rompersi facilmente) | Basso (più flessibile e resistente) |
| Durata | Difficile ma può rompersi | Resistente e si piega di più |
Nota: per affilare le lame in ceramica sono necessari utensili diamantati. Inizialmente costano di più, ma non è necessario sostituirli o ripararli con altrettanta frequenza.
Riepilogo comparativo: durata e resistenza all'usura
Le lame in ceramica sono le migliori per quanto riguarda la durata e la resistenza all'usura. La loro durezza consente loro di mantenere un filo affilato a lungo, anche tagliando materiali morbidi o ruvidi. Rispetto all'acciaio per utensili, all'HSS e al carburo di tungsteno, le lame in ceramica non arrugginiscono e non vengono danneggiate dagli agenti chimici.
IL la tabella seguente mostra come si confrontano i materiali delle pale principali:
| Materiale | Durezza (HRC) | Resistenza all'usura | Resistenza alla corrosione | Stabilità termica | Applicazioni tipiche |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acciaio ad alto tenore di carbonio | 55–62 | Moderare | Basso | Moderare | Taglio generale, risparmio di denaro |
| Acciaio per utensili D2 | 58–62 | Alto | Moderare | Alto | Taglio preciso, lavori difficili |
| Acciaio rapido M2 | 60–65 | Molto alto | Moderare | Molto alto | Lavoro di taglio rapido e a caldo |
| Carburo di tungsteno | 75–80 | Estremamente alto | Alto | Molto alto | Lavori duri, durano a lungo |
| Ceramica | 85+ | Alto | Molto alto | Basso | Lavori super precisi e non metallici |
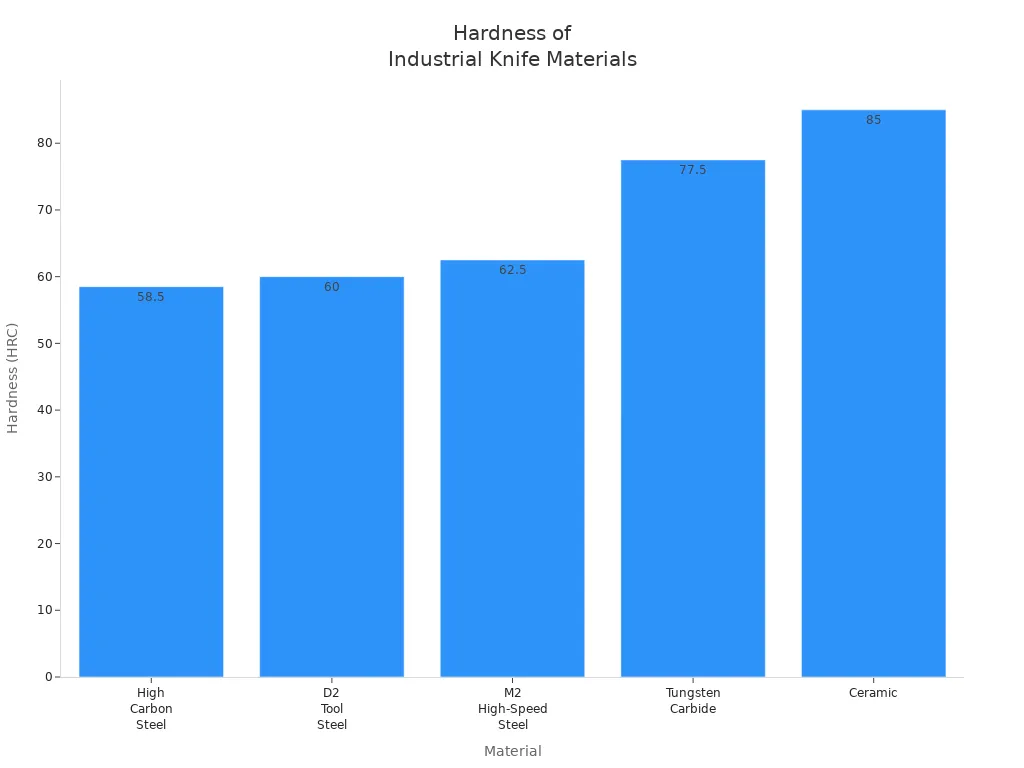
- Le lame in ceramica restano affilate molto più a lungo delle lame in acciaio o in carburo.
- Sono adatti per lavori in cui non si desidera cambiare spesso le lame.
- Tuttavia, non sopportano bene il calore, quindi non sono adatti al taglio a caldo.
- Poiché possono rompersi, non vengono utilizzati per lavori pesanti o ruvidi.
Riepilogo: Le lame in ceramica sono ideali per tagli precisi e duraturi su superfici morbide o ruvide, ma bisogna fare attenzione a non scheggiarle.
Domande frequenti
Le lame in ceramica sono adatte al taglio di tessuti non tessuti abrasivi o prodotti per l'igiene?
Sì. Le lame in ceramica rimangono affilate e garantiscono tagli netti su tessuti non tessuti e materiali igienici. Questo significa che non è necessario sostituire le lame così spesso.
Le lame in ceramica possono essere utilizzate per il taglio ad alta velocità delle pellicole?
Le lame in ceramica possono tagliare rapidamente le pellicole sottili, ma bisogna fare attenzione a non colpirle lateralmente altrimenti potrebbero scheggiarsi.
Qual è il limite principale delle lame in ceramica nell'uso industriale?
Il problema più grande è che possono scheggiarsi o rompersi se vengono colpiti lateralmente o se cadono.
Analisi completa dei rivestimenti delle lame e del loro impatto sulle prestazioni dei coltelli circolari industriali
Tipi di rivestimento comuni
I rivestimenti delle lame aiutano gli utensili da taglio a funzionare meglio e a durare più a lungo. I produttori utilizzano rivestimenti speciali per risolvere problemi come usura, attrito e ruggine. Ecco alcuni rivestimenti comuni:
- Rivestimento diamantato: Mantiene le lame affilate più a lungo e ne previene l'usura. Ciò significa meno tempo speso per la sostituzione delle lame.
- Nitruro di cromo (CrN): Aderisce bene alle lame, combatte la ruggine e riduce l'attrito. Questo mantiene le lame fresche.
- Nitruro di zirconio (ZrN): Rende le lame molto dure e previene la ruggine. Aiuta le lame a effettuare tagli più netti.
- Rivestimento cromato: Rende le lame più dure e ne aumenta la durata. Protegge dalla ruggine e dall'usura.
- Rivestimento in Teflon (PTFE): Impedisce che gli oggetti si attacchino alle lame. Aiuta anche a ridurre il calore e l'attrito.
- Nitruro di titanio (TiN): Questo rivestimento ceramico duro è realizzato tramite PVD. Rende le lame più dure, resistenti e lisce.
- Teflon nero antiaderente: Questo rivestimento approvato dalla FDA impedisce l'accumulo di sostanze appiccicose. Combatte anche la ruggine e l'usura, il che è ottimo per le applicazioni alimentari.
- Nitruro di carbonio di titanio (TiCN): Contiene titanio, carbonio e azoto. Rende le lame più dure e previene la ruggine. È ottimo per tagli rapidi.
- Cromo duro: Aiuta le lame in acciaio a combattere la ruggine e l'usura. Inoltre, le fa durare più a lungo.
- Carbonio simile al diamante (DLC): Rende le lame molto dure e lisce. Aiuta anche le lame a sopportare il calore e i lavori più impegnativi.
- Politetrafluoroetilene (PTFE): Questo rivestimento si piega facilmente, non reagisce con le sostanze chimiche e ha un punto di fusione elevato.
- Nichelatura chimica: Rende le lame più lisce e combatte la ruggine e l'usura. Ma non le rende più dure.
I rivestimenti rendono le lame più dure, riducono l'attrito, prevengono la ruggine e contribuiscono a farle durare più a lungo.
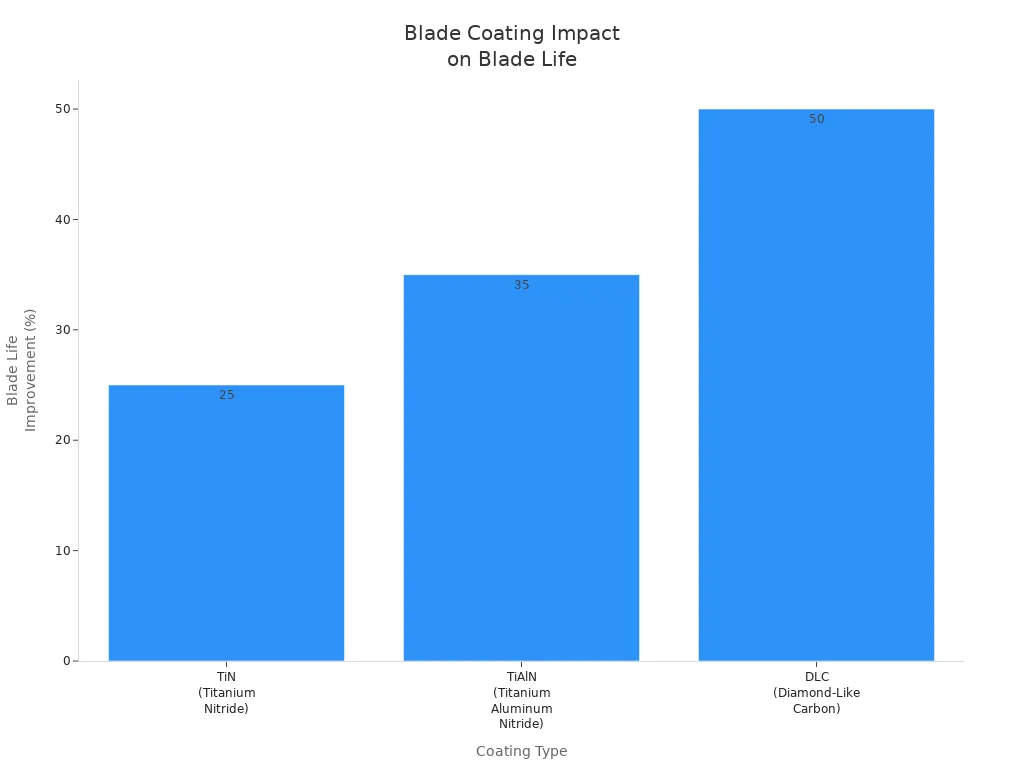
Rivestimento TiN (nitruro di titanio)
Il rivestimento in TiN è dorato e molto duro. I produttori lo applicano alle lame tramite PVD. Il TiN rende le lame più dure di circa 25%. Riduce inoltre l'attrito e ne prolunga la durata. Il TiN impedisce alle lame di arrugginirsi. Viene utilizzato per tagliare metalli teneri come alluminio e rame. Le lame con TiN durano 20-30% in più rispetto alle lame senza.
Rivestimento TiAlN (nitruro di titanio e alluminio)
Il TiAlN è ancora più duro del TiN e può sopportare più calore. Questo lo rende ideale per lavori di taglio rapidi e a caldo, come il taglio di metalli duri. Il TiAlN può aumentare la durata delle lame fino a 35%. Ha un aspetto grigio scuro o nero e protegge le lame dal calore e dall'usura.
Rivestimento DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon)
Il rivestimento DLC è molto duro e super liscio. Impedisce che i materiali si attacchino alle lame. Aiuta le lame a lavorare meglio, soprattutto quando si tagliano velocemente o materiali appiccicosi. Le lame rivestite in DLC sono ideali per metalli morbidi e lavori appiccicosi. Possono durare fino a 50% in più, quindi sono adatte anche per i punti più difficili.
Miglioramenti delle prestazioni grazie ai rivestimenti
Resistenza all'usura e riduzione dell'attrito
I rivestimenti delle pale aiutano a contrastare l'usura e a ridurre l'attrito. TiN, TiAlN e DLC presentano punti di forza specifici:
| Tipo di rivestimento | Durezza (HV) | Vantaggi principali | Applicazioni tipiche | Miglioramento della durata della lama |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiN (nitruro di titanio) | ~2200-2400 HV | Rende le lame più dure, riduce l'attrito, previene la ruggine | Metalli teneri come alluminio e rame | 20-30% più lungo |
| TiAlN (nitruro di titanio e alluminio) | Fino a 3200 HV | Ancora più duro, assorbe più calore, ottimo per tagli rapidi | Metalli duri, taglio di bobine di metallo | Fino a 35% più lungo |
| DLC (carbonio simile al diamante) | 1000-2400 HV | Molto duro, super liscio, non si attacca più | Metalli teneri, taglio veloce | Fino a 50% più lungo |
Questi rivestimenti aiutano le lame a rimanere affilate, a mantenersi fredde e a tagliare in modo fluido. Ad esempio, il DLC rende le lame meno appiccicose e garantisce tagli più netti. Il TiAlN può sopportare più calore, quindi è ideale per lavori rapidi e a temperature elevate.
Le lame rivestite durano più a lungo, tagliano meglio e devono essere sostituite meno spesso.
Protezione dalla corrosione
Molti rivestimenti impediscono inoltre la formazione di ruggine sulle lame. Il nitruro di cromo (CrN), il cromo duro e il PTFE proteggono le lame dall'acqua e dalle sostanze chimiche. Questo è importante nei settori alimentare, igienico e medico, dove le lame devono rimanere pulite. Il Teflon e il Teflon Black Nonstick impediscono inoltre l'accumulo di sostanze appiccicose e facilitano la pulizia.
Tabella comparativa: resistenza all'usura e costo
Le lame rivestite costano di più all'inizio, ma consentono di risparmiare denaro in seguito. Richiedono meno riparazioni e durano più a lungo. Ecco una tabella che confronta i diversi rivestimenti:
| Tipo di rivestimento | Resistenza all'usura | Protezione dalla corrosione | Riduzione dell'attrito | Costo iniziale | Estensione della durata della lama |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stagno | Alto | Moderare | Moderare | Moderare | 20-30% |
| TiAlN | Molto alto | Moderare | Moderare | Alto | Fino a 35% |
| Contenuti scaricabili | Eccezionale | Alto | Molto alto | Alto | Fino a 50% |
| CrN | Alto | Alto | Alto | Moderare | 20-30% |
| PTFE/Teflon | Moderare | Alto | Molto alto | Moderare | 10-20% |
I rivestimenti di finitura come TiN e TiCN possono aumentare la durata delle lame fino a 40%. Riducono anche i tempi di fissaggio di 30%. I rivestimenti DLC offrono la migliore resistenza all'usura e scorrevolezza. Sono ideali per lavori difficili o appiccicosi. Sebbene le lame rivestite costino di più all'inizio, consentono di risparmiare denaro nel tempo, durando più a lungo e funzionando meglio.
Rivestimenti migliori aiutano le lame a durare più a lungo e rendono i prodotti migliori, tagliando più velocemente e commettendo meno errori.
Una fabbrica tessile è passata dalle lame in acciaio al carbonio a quelle in acciaio inossidabile con rivestimento. Le lame in 30% sono state sostituite meno frequentemente e quelle in 12% sono state prodotte in quantità maggiori. Le lame rivestite hanno inoltre ridotto lo spreco di tessuto e hanno tagliato più velocemente.
Domande frequenti
Quale rivestimento è migliore per tagliare materiali adesivi o appiccicosi?
I rivestimenti DLC e PTFE sono ideali per le superfici appiccicose. Impediscono che i residui si attacchino e mantengono le lame pulite.
Come si confrontano i rivestimenti TiN e TiAlN per il taglio ad alta velocità dei metalli?
Il TiAlN è più duro e assorbe più calore del TiN. È più indicato per il taglio rapido e a caldo di metalli duri.
Le lame rivestite fanno davvero risparmiare denaro nel lungo periodo?
Sì. Le lame rivestite durano più a lungo, richiedono meno riparazioni e tagliano meglio. Questo fa risparmiare denaro nel tempo.
Applicazioni di coltelli circolari industriali nei settori chiave
Taglio della pellicola
Il taglio di pellicole richiede lame che eseguano tagli rapidi, lisci e puliti. Le fabbriche tagliano pellicole e imballaggi in plastica sottile. La lama deve rimanere affilata e non usurarsi rapidamente. Inoltre, non deve accumulare elettricità statica. Scegliere il materiale e il rivestimento giusti è molto importante.
Combinazioni consigliate di materiali e rivestimenti
I materiali migliori per il taglio di pellicole sono il carburo di tungsteno, l'acciaio rapido e l'acciaio temprato. Questi materiali sono duri e resistenti. Non si usurano rapidamente. Le fabbriche utilizzano rivestimenti come il nitruro di titanio (TiN), il nitruro di titanio e alluminio (TiAlN) e il carbonio simile al diamante (DLC). Questi rivestimenti contribuiscono a prolungare la durata delle lame e a ottenere un taglio più fluido.
| Requisito di prestazione | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| Durezza | Mantiene la lama affilata per tagli di pellicola puliti |
| Robustezza | Impedisce alla lama di scheggiarsi o rompersi |
| Resistenza all'usura | Fa sì che la lama duri più a lungo nei lavori più impegnativi |
| Duttilità | Lascia che la lama si pieghi un po' senza rompersi |
| Purezza | Assicura che la lama funzioni sempre allo stesso modo |
| Materiale | Applicazione e vantaggi |
|---|---|
| Carburo di tungsteno | Molto forte, taglia pellicole resistenti, dura a lungo |
| Acciaio ad alta velocità | Buon mix di duro e resistente, funziona bene |
| Acciaio temprato | Trattato termicamente per essere resistente e durare più a lungo |
| Tipo di rivestimento | Vantaggi principali | Miglioramento quantificato |
|---|---|---|
| Nitruro di titanio (TiN) | Rende le lame più dure, riduce l'attrito | Fino a 45% in meno di usura |
| Nitruro di titanio e alluminio (TiAlN) | Gestisce il calore, combatte la ruggine, dura più a lungo | Funziona bene ad alte velocità |
| Carbonio simile al diamante (DLC) | Taglia più uniformemente, non si attacca più | Può ridurre la forza di oltre 50% |
| Rivestimenti ceramici | Duro, non metallico, combatte la ruggine e l'usura | Adatto per lavori bagnati o difficili |
| Rivestimenti nano multistrato | Molti strati sottili, meno attrito | Fa sì che le lame durino più a lungo e taglino meglio |
Cambiare la forma e il bordo della lama può farla durare più a lungo fino a 40% più lungoPuò anche ridurre i tempi di manutenzione di 30%. Le fabbriche possono produrre 15-25% in più e sprecare meno materiale, riducendo gli sprechi da 5% a 2%.
Consigli principali:
- HSS con rivestimento TiN: ottimo per il taglio rapido delle pellicole, con minore attrito e incollaggio.
- Carburo di tungsteno con rivestimento DLC: ideale per pellicole resistenti o stratificate, dura più a lungo.
- Rivestimenti nano multistrato: aiutano con pellicole speciali, rendono le lame più precise e durano più a lungo.
Suggerimento: le fabbriche dovrebbero adattare l'altezza della lama e la velocità alla pellicola. Un'altezza della lama di 5 mm e una velocità di 370 giri al minuto sono spesso le soluzioni migliori.
Taglio della gomma
Il taglio con la gomma è un problema per le lame. La gomma è spessa ed elastica. Può attaccarsi alla lama e causare problemi. Le lame non devono incollarsi, devono rimanere affilate e resistere a sfregamenti intensi. Il materiale e il rivestimento giusti contribuiscono a far durare le lame e a tagliarle meglio.
Combinazioni consigliate di materiali e rivestimenti
Il carburo di tungsteno e l'acciaio rapido sono i materiali migliori per il taglio della gomma. Questi materiali sono resistenti e mantengono il filo. Rivestimenti come DLC e TiAlN impediscono alle lame di incollarsi e durano più a lungo.
| Materiale | Vantaggi del taglio della gomma |
|---|---|
| Carburo di tungsteno | Taglia la gomma ruvida, rimane affilato, non si consuma velocemente |
| Acciaio rapido (HSS) | Resistente e non troppo costoso, adatto alla maggior parte dei lavori in gomma |
| Acciaio per utensili D2 | Molto duro, ottimo per la gomma meno ruvida |
| Rivestimento | Vantaggio chiave |
|---|---|
| Contenuti scaricabili | Evita l'inceppamento, riduce l'attrito, fa durare più a lungo le lame |
| TiAlN | Gestisce il calore, aiuta le lame a durare nei lavori più difficili |
| Stagno | Adatto per lavori normali in gomma, bilancia costi e lavoro |
Consigli principali:
- Carburo di tungsteno con rivestimento TiAlN: ideale per tagliare gomma ruvida e resistente.
- HSS con rivestimento TiN: adatto alla maggior parte dei lavori con la gomma, fa risparmiare denaro ed è durevole.
- Carburo di tungsteno con rivestimento DLC: ideale per gomma appiccicosa o ad alto attrito.
Nota: la lama e il rivestimento giusti comportano meno cambi di lama e un lavoro più fluido.
Tessuti non tessuti e tessili
Per tagliare tessuti e tessuti non tessuti sono necessarie lame che impediscano lo sfilacciamento e garantiscano tagli netti. Questi materiali possono essere morbidi, sintetici o stratificati. La lama deve rimanere affilata e non tirare le fibre.
Combinazioni consigliate di materiali e rivestimenti
Per queste lavorazioni, le fabbriche utilizzano acciaio per utensili D2, acciaio rapido M2, carburo di tungsteno e ceramica. Questi materiali sono molto duri e mantengono il filo. Rivestimenti come TiN, TiCN, TiAlN e DLC contribuiscono a una maggiore durata delle lame e a un taglio migliore.
| Materiale / Rivestimento | Proprietà chiave | Vantaggi del taglio di tessuti non tessuti/tessuti |
|---|---|---|
| Acciaio per utensili D2 | Molto duro, i combattimenti si consumano | Le lame durano a lungo e rimangono affilate |
| Acciaio rapido M2 (HSS) | Duro e tenace | Adatto per lavori tessili difficili |
| Carburo di tungsteno | Super duro, i combattimenti si consumano | Dura più a lungo, taglia i materiali ruvidi in modo pulito |
| Ceramica | Molto duro, basso attrito | Effettua tagli netti, meno calore e usura |
| Nitruro di titanio (TiN) | Più duramente, i combattimenti si consumano | Le lame durano più a lungo, i tagli rimangono puliti |
| Carbonitruro di titanio (TiCN) | I combattimenti si indossano molto bene | Le lame durano più a lungo nei lavori più difficili |
| Nitruro di titanio e alluminio (TiAlN) | Gestisce bene il calore | Rimane duro nel taglio veloce |
| Carbonio simile al diamante (DLC) | Molto duro, basso attrito | Minore attrito e usura, le lame durano più a lungo |
| cromatura | Combatte la ruggine, finitura liscia | Protegge la lama, riduce l'attrito |
- Per lame che durano nel tempo, utilizzare acciaio resistente e carburo.
- Le lame sono affilate e lisce per evitare che si sfilaccino.
- Le fabbriche possono acquistare lame personalizzate per lavori speciali.
- La realizzazione accurata delle lame garantisce tagli netti e uniformi.
- Per tessuti e tessuti non tessuti vengono realizzati coltelli speciali, come quelli dalle forme dritte, rotonde o dentate.
- La forma del filo della lama e le guide strette impediscono che si sfilacci e consentono di effettuare tagli di buona qualità.
Consigli principali:
- Lame in ceramica: restano affilate e garantiscono tagli netti, ideali per fibre morbide o sintetiche.
- HSS con rivestimento TiN: dura più a lungo e impedisce lo strappo delle fibre, ideale per lavori tessili rapidi.
- Carburo di tungsteno con rivestimento DLC: ideale per tessuti non tessuti ruvidi e lavori lunghi.
Domande frequenti
Quale materiale per la lama circolare è migliore per tagliare pellicole multistrato?
Le lame in carburo di tungsteno o HSS con un bordo sottile e affilato sono le migliori per le pellicole multistrato. Effettuano tagli netti e riducono gli sprechi.
Il rivestimento TiCN può superare le prestazioni del TiN nel taglio ad alta velocità?
I rivestimenti TiCN sono più duri e durano più a lungo del TiN. Sono ideali per tagli rapidi e resistenti.
In che modo le lame personalizzate aiutano nel taglio di tessuti e tessuti non tessuti?
Le lame personalizzate garantiscono tagli migliori, evitano sfilacciamenti e riducono i tempi di fermo. Le fabbriche ottengono risultati migliori e risparmiano sui costi di riparazione.
Carta e lamina
Combinazioni consigliate di materiali e rivestimenti
Tagliare carta e fogli di alluminio è complicato. Gli operatori devono bloccare la polvere, mantenere le lame affilate ed effettuare tagli puliti e duraturi. Scegliere il materiale e il rivestimento giusti per le lame aiuta a migliorarne la resa e a risparmiare denaro.
- Le lame in acciaio D2 sono adatte a molti lavori e non costano molto. Sono facili da affilare e durano a lungo quando si taglia carta o plastica.
- Le lame in acciaio M2 sono ancora più resistenti. Sono adatte anche alla carta ruvida e durano più a lungo, così gli operatori devono fermarsi meno spesso.
- L'acciaio CPM 10V è estremamente resistente e non si usura rapidamente. È ideale per il taglio di materiali multistrato o ruvidi e può essere utilizzato a lungo.
- Le lame con inserti in carburo rimangono affilate giorno e notte. Sono ideali per carta ruvida e fogli di alluminio e aiutano gli operatori a sostituire le lame meno spesso.
- I coltelli con fondo diviso consentono agli operatori di sostituire rapidamente le lame. Ciò significa che non devono estrarre l'intero set, quindi il lavoro non si ferma a lungo.
- Con uno spessore del filo compreso tra 10 e 20 micrometri, la lama rimane affilata e resistente. Questo contribuisce a ridurre la formazione di polvere e a prolungare la durata delle lame.
- Rivestimenti come il nitruro di titanio (TiN) e il carbonio simile al diamante (DLC) rendono le lame più dure e lisce. Questi rivestimenti contribuiscono a farle durare più a lungo e a tagliare meglio.
- È importante impostare correttamente il punto di serraggio e utilizzare portalame resistenti. Questo impedisce alle lame di usurarsi troppo rapidamente e le mantiene affilate.
Un'azienda cartaria ha utilizzato una lama con un filo da 20 micrometri e le lame durano 25% in più. I loro tagli sono migliorati di 15%. Altri report mostrano 20% in meno di cambi di lama e 18% in meno di polvere con un filo da 15-20 micrometri.
Buone pratiche per il taglio di carta e fogli:
- Per la maggior parte dei lavori su carta e fogli di alluminio, scegli l'acciaio D2 o M2.
- Per materiali ruvidi o stratificati, utilizzare lame CPM 10V o lame con inserti in carburo.
- Applicare rivestimenti TiN o DLC alle lame per aumentarne la durata e migliorare il taglio.
- Mantenere le lame affilate per fermare la polvere ed evitare di perdere i prodotti.
- Insegnare ai lavoratori come installare e manutenere le lame per ottenere i migliori risultati.
| Materiale della lama | Vantaggio chiave | Caso d'uso tipico |
|---|---|---|
| Acciaio D2 | Adatto a molti lavori, facile da affilare | Taglio di carta o plastica |
| Acciaio M2 | Resistente, dura più a lungo | Carta ruvida, carta patinata |
| CPM 10V | Super resistente, dura più a lungo | Molti strati, materiali grezzi |
| Intarsio in carburo | Rimane affilato, funziona tutto il giorno | Carta ruvida o stagnola |
| Rivestimento | Beneficio |
|---|---|
| Stagno | Rende le lame più dure, riduce l'attrito |
| Contenuti scaricabili | Le lame durano più a lungo, tagli più puliti |
Suggerimento: controlla sempre che i portalame siano ben serrati e posizionati correttamente. In questo modo le lame rimangono affilate e si produce meno polvere.
Domande frequenti
- Quale materiale di lama è più adatto per lunghe tirature di taglio della carta?
Le lame con inserti in carburo o CPM 10V durano più a lungo e sono più adatte per lavori lunghi. - Come possono gli operatori ridurre la polvere durante il taglio della lamina?
Utilizzare lame con un bordo da 15-20 micrometri e applicare rivestimenti TiN o DLC per produrre meno polvere e ottenere tagli migliori.
Altri settori
Combinazioni consigliate di materiali e rivestimenti
Molti lavori richiedono lame e rivestimenti speciali. Scegliere quello giusto aiuta le macchine a funzionare meglio, a garantire la sicurezza delle persone e a realizzare prodotti di qualità.
- Lame in acciaio inossidabile sono ideali per lavori alimentari. Non arrugginiscono e sono sicuri da usare con gli alimenti.
- Le lame in acciaio per utensili sono robuste e resistenti. Sono ideali per le auto e per la lavorazione dei metalli perché rimangono affilate anche dopo un uso intenso.
- Le lame in acciaio al carbonio sono dure e mantengono il filo. Sono utilizzate per tagliare metallo, carta e plastica.
- Materiali speciali come il metallo duro integrale, la ceramica, gli acciai CPM 10V, 52100, M-2 e D-2 sono molto duri e possono sopportare il calore. Sono adatti per lavori impegnativi come il taglio di fibra di vetro, materiali compositi o materiali medicali.
- Rivestimenti come TiN, DLC e PTFE aiutano le lame a rimanere affilate e a durare più a lungo. Questi rivestimenti sono ideali per materiali appiccicosi o ruvidi.
- Diverse forme di bordo, come Standard V, Vari-Depth V, Hi/Low V, Scalloped, Peg Style e Slant Tooth, aiutano le lame a tagliare meglio e a rendere più semplice il lavoro delle macchine.
- Le lame personalizzate e la scelta del materiale giusto sono utili per lavori speciali e tagli difficili.
| Industria | Materiale/rivestimento della lama consigliato | Vantaggio chiave |
|---|---|---|
| Lavorazione alimentare | Acciaio inossidabile, rivestimento in PTFE | Non arrugginisce, sicuro per gli alimenti |
| Automobilistico/Metal | Acciaio per utensili, rivestimento DLC/TiN | Resistente, non si consuma velocemente |
| Plastica/Compositi | Carburo solido, ceramica, rivestimento DLC | Molto duro, fa tagli netti |
| Medicina/Igiene | Ceramica, acciaio inossidabile | Sicuro, non reagisce con le sostanze chimiche |
| Fibra di vetro/Avanzata | CPM 10V, Carburo, Rivestimento protettivo | Dura a lungo, rimane affilato, assorbe il calore |
Nota: le lame personalizzate aiutano le fabbriche a svolgere meglio il loro lavoro, a risparmiare tempo e a impedire che i macchinari si rompano.
Nanjing Metal è un produttore leader di lame circolari industriali con oltre 20 anni di esperienza. L'azienda è nota per il suo team qualificato e l'eccellente design. Nanjing Metal realizza lame personalizzate per molteplici applicazioni. Consultate la nostra selezione di lame personalizzate qui. servizi di lame personalizzate collegamento.
Domande frequenti
- Quale materiale per lame è più adatto alla lavorazione degli alimenti?
L'acciaio inossidabile con rivestimento in PTFE è la scelta migliore perché è sicuro e non arrugginisce. - Qual è l'opzione migliore per tagliare la fibra di vetro o i materiali compositi?
Le lame CPM 10V o in metallo duro integrale con rivestimento durano a lungo e restano affilate. - In che modo le lame personalizzate possono essere utili nei settori specializzati?
Le lame personalizzate si adattano a ogni lavoro, realizzano tagli migliori e aiutano le macchine a funzionare più a lungo.
Guida alla selezione
Abbinamento dei materiali
Per scegliere il materiale giusto per la lama, è necessario innanzitutto sapere cosa si sta tagliando. Ogni materiale è diverso e modifica il funzionamento della lama. Ecco un modo semplice per scegliere la lama più adatta al lavoro:
- Valutare il materiale da tagliare
Scopri cosa stai tagliando. Controlla se è spesso, sottile, morbido o duro. Plastiche morbide, compositi ruvidi e gomma appiccicosa richiedono tutti lame diverse. - Definire i requisiti dell'applicazione
Decidi a cosa servirà la lama. Fetterà, inciderà, taglierà o farà dei buchi? Ogni lavoro richiede un tipo di lama diverso. - Seleziona il materiale della lama
- Scegli l'acciaio ad alto tenore di carbonio se hai bisogno di una lama resistente per un uso frequente.
- Se la lama si bagna o entra in contatto con il cibo, utilizzare acciaio inossidabile, perché non arrugginisce.
- Per lavori molto difficili, come il taglio di pellicole ruvide o stratificate, si consiglia di utilizzare il carburo solido.
- Scegli la ceramica se desideri una lama che non debba essere cambiata spesso o se tagli oggetti per scopi medici o di pulizia.
- Scegli la geometria del bordo e del dente
Adatta la forma del bordo a ciò che stai tagliando. Un bordo squadrato è adatto alla maggior parte dei lavori. I bordi dentellati o obliqui sono più adatti per oggetti morbidi o fibrosi. - Consultare esperti o produttori
In caso di dubbi, parla con gli ingegneri o con il produttore della lama. Possono aiutarti a scegliere o progettare una lama speciale. - Eseguire il reverse engineering durante la sostituzione delle lame
Se stai sostituendo una vecchia lama, osserva come si è usurata. Questo ti aiuterà a scegliere una lama migliore la prossima volta.
Suggerimento: pensa sempre a dove verrà utilizzata la lama. Calore, acqua e sostanze chimiche possono alterarne la durata.
Scelta del tipo di bordo
Il tipo di filo determina il modo in cui la lama taglierà. Scegliere il filo giusto rende i tagli più puliti, riduce gli sprechi e contribuisce a una maggiore durata della lama. Ecco alcuni tipi di filo comuni e le loro applicazioni più adatte:
| Tipo di bordo | Descrizione | Il migliore per |
|---|---|---|
| Bordo squadrato | Piatto e tagliente | Taglio, carta, pellicola |
| Singolo smusso | Un lato inclinato, un lato piatto | Tagli attenti, cose sottili |
| Doppio smusso | Entrambi i lati inclinati | Materiale resistente, gomma, schiuma |
| Dentellato/Seghettato | Denti a forma di sega | Tessili, non tessuti, lavori pesanti |
| Smerlato | Denti arrotondati, taglio liscio | Cose morbide, cibo, schiuma |
| Dente obliquo | Denti angolati per lavori difficili | Cose spesse o filamentose |
- Utilizzare bordi squadrati o con un solo bisello per tagli netti e dritti su pellicole e fogli.
- Per oggetti spessi o ruvidi, scegli bordi con doppia smussatura o dentellati.
- Per alimenti morbidi, elastici o fibrosi, scegli bordi dentellati o obliqui.
Nota: un bordo sbagliato può rendere il taglio poco preciso o causare polvere. Scegli sempre il bordo giusto per il pezzo che stai tagliando.
Selezione del rivestimento
I rivestimenti delle lame contribuiscono a farle durare più a lungo e a tagliare meglio. Il rivestimento giusto rende le lame più lisce, più resistenti e le protegge dalla ruggine. Ecco come scegliere il rivestimento migliore:
- Identificare la sfida principale del taglio
Scopri cosa rende il lavoro più difficile. È l'usura, l'inceppamento, il calore o la ruggine? - Selezionare un rivestimento in base alle esigenze
- Utilizzare il nitruro di titanio (TiN) per far durare più a lungo le lame e tagliare in modo più fluido, soprattutto per lavori rapidi o difficili.
- Scegli il carbonio simile al diamante (DLC) per una maggiore durezza e per impedire l'accumulo di sostanze appiccicose.
- Se la lama si scalda e si raffredda molto, provate i nanorivestimenti, perché questi rivestimenti proteggono dagli sbalzi di calore.
- Abbinare il rivestimento al materiale della lama
Per i lavori più difficili, utilizzare il DLC sul carburo di tungsteno. Per i lavori più morbidi, utilizzare il TiN sull'acciaio rapido. - Mantenere le lame correttamente
Per preservare le prestazioni dei rivestimenti, pulire, oliare e conservare le lame nel modo corretto. - Considera soluzioni personalizzate
Se devi svolgere un lavoro particolare, chiedi al produttore della lama rivestimenti o forme di lama personalizzate.
La scelta del rivestimento giusto e la cura nella realizzazione delle lame ne garantiscono l'affilatura e il buon funzionamento, anche nei punti più difficili.
Domande frequenti
- Qual è il fattore più importante quando si abbina il materiale della lama all'applicazione?
La cosa più importante è cosa si sta tagliando, ad esempio quanto è duro, ruvido o bagnato. - In che modo il tipo di bordo influisce sulla durata della lama?
La giusta forma del bordo fa sì che la lama duri più a lungo e che effettui tagli migliori, così non dovrai più fare troppe riparazioni. - I rivestimenti possono davvero fare la differenza nelle prestazioni delle pale?
Sì. Il rivestimento giusto può far durare le lame fino a metà del tempo, tagliare in modo più fluido ed evitare che si attacchino o arrugginiscano.
Costo vs. prestazioni

Scegliere la lama giusta non è solo una questione di prezzo. Bisogna pensare a quanto si paga ora e a quanto si risparmia in futuro. Alcuni guardano solo il prezzo. Ma il costo reale dipende dalla frequenza con cui si cambiano le lame, da quanto tempo le macchine si fermano e da quante riparazioni sono necessarie. La lama migliore dipende dal lavoro, da cosa si sta tagliando e da dove si lavora.
Confronto degli investimenti materiali
Ogni materiale della lama ha il suo costo e la sua efficacia:
- Acciaio ad alto tenore di carbonio: Questa lama costa meno all'inizio. Ma si consuma velocemente. Dovrai acquistare spesso lame nuove, il che a lungo andare costerà di più.
- Acciaio inossidabile: Questa lama costa di più al momento dell'acquisto. Non arrugginisce e funziona bene in ambienti umidi o esposti a sostanze chimiche. Dura più a lungo, quindi risparmi denaro in seguito.
- Acciaio legato: Queste lame costano di più all'inizio. Durano più a lungo e aiutano le macchine a funzionare senza fermarsi. Sono ideali per le fabbriche con un elevato traffico.
- Lame in Ceramica: Queste lame sono quelle che costano di più all'inizio. Non necessitano quasi mai di riparazioni e durano a lungo. Se hai bisogno di un lavoro accurato e veloce, sono la scelta migliore a lungo termine.
Tabella costi-benefici dei materiali
| Materiale della lama | Costo iniziale | Frequenza di sostituzione | Esigenze di manutenzione | Valore a lungo termine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acciaio ad alto tenore di carbonio | Basso | Alto | Alto | Basso |
| Acciaio inossidabile | Medio | Medio | Basso | Medio-Alto |
| Acciaio legato | Alto | Basso | Basso | Alto |
| Ceramica | Molto alto | Molto basso | Molto basso | Più alto |
Suggerimento: spendere di più all'inizio può significare meno cambi di lama, meno fermi macchina e costi totali inferiori in seguito.
L'impatto dei trattamenti avanzati
Trattamenti speciali per le lame possono influire sul costo e sulla durata delle stesse. Il trattamento criogenico ne è un esempio. Aumenta la durata delle lame e ne rallenta l'usura. La tabella seguente mostra la differenza:
| Aspetto | Trattamento termico regolare | Trattato criogenicamente |
|---|---|---|
| Resistenza all'usura (cicli) | 1,000 | 2,500 |
| Durata media della vita (mesi) | 6 | 12 |
| Tasso di usura (mm³/ora) | 0.15 | 0.05 |
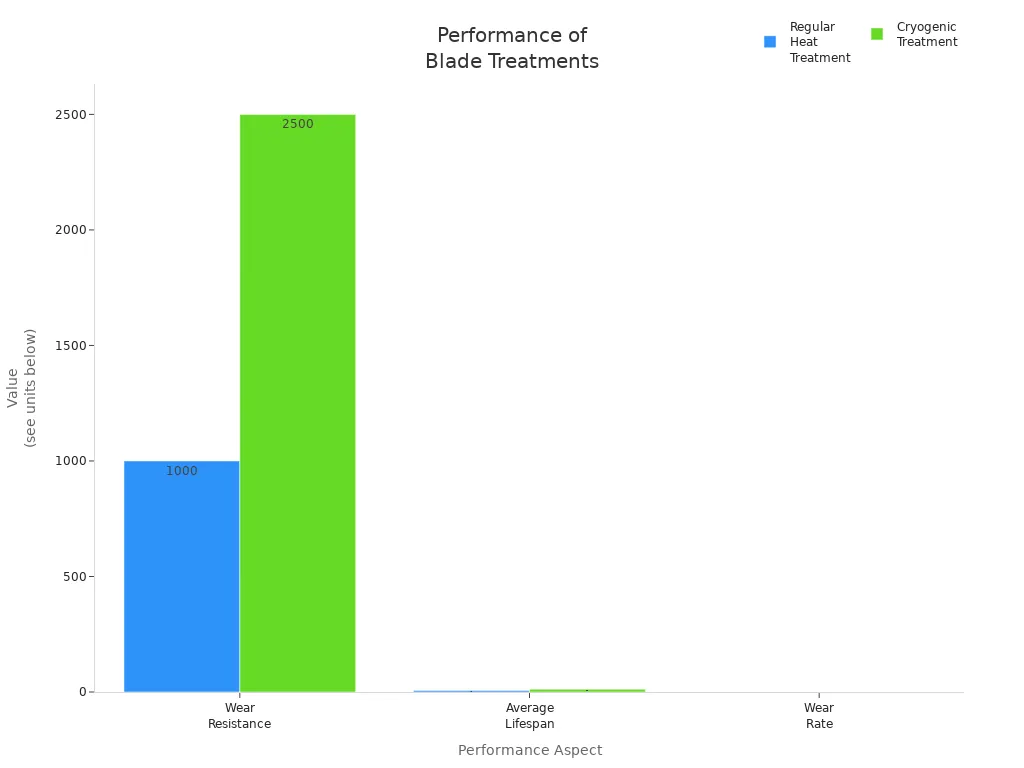
Il trattamento criogenico può raddoppiare la durata delle lame. Inoltre, ne rallenta l'usura. Questo può ridurre i costi totali fino a 30%. Saranno necessarie meno lame nuove e meno riparazioni, quindi sarà possibile produrre più prodotti e ridurre gli sprechi.
Errori da evitare
- Considerare solo il prezzo più basso può rivelarsi costoso in seguito.
- Non considerare l'area di lavoro (ad esempio, bagnata, con sostanze chimiche o sabbia) può causare una rapida usura delle lame.
- Il mancato utilizzo di rivestimenti o trattamenti speciali può comportare maggiori tempi di fermo e maggiori sprechi.
Suggerimenti per massimizzare il valore
- Scegli il materiale della lama più adatto al tuo lavoro e alla tua area di lavoro.
- Acquista rivestimenti o trattamenti che aiutino la tua fabbrica.
- Tieni traccia della durata delle lame e di quando sostituirle. Questo ti aiuterà a trovare modi per risparmiare denaro.
Perché la competenza del produttore è importante
Un buon produttore di lame può aiutarti a scegliere la lama migliore. Nanchino Metal è un produttore leader con 20 anni di esperienza. Il suo team realizza lame personalizzate per molti lavori. Offre servizi di lame personalizzate per aiutarti a ottenere il massimo dal tuo investimento.
Per consigli o per parlare delle tue esigenze, contatta i tecnici commerciali di Nanjing Metal con questo collegamento di contatto.
Domande frequenti
In che modo il materiale della lama influisce sul costo totale di proprietà?
Il materiale delle lame cambia la frequenza con cui è necessario sostituirle e il tempo di fermo macchina. Le lame più dure costano di più all'inizio, ma fanno risparmiare denaro in seguito.
Il trattamento criogenico vale il costo aggiuntivo?
Sì. Il trattamento criogenico può far durare le lame il doppio del tempo e farle usurare meno, così da risparmiare sulle nuove lame e sulle riparazioni.
Quando un'azienda dovrebbe scegliere le lame in ceramica?
Le lame in ceramica sono ideali per lavori rapidi e accurati, in cui si desidera che durino a lungo e non richiedano molte riparazioni.
La scelta del materiale, dello stile del filo e del rivestimento giusti cambia l'efficacia dei coltelli circolari industriali. Quando le aziende abbinare la durezza della lama e tipo di filo in base a ciò che devono tagliare, le lame durano più a lungo e funzionano meglio. Questo significa meno cambi di lama e più lavoro svolto.
| Fattore | Come aiuta la lama |
|---|---|
| Materiale | Fa durare le lame e previene la ruggine |
| Stile del bordo | Aiuta a realizzare tagli puliti e si adatta al lavoro |
| Rivestimento | Le lame durano più a lungo e necessitano di meno riparazioni |
Per ottenere i migliori risultati, le persone dovrebbero:
- Informare i fornitori di tutto ciò di cui hanno bisogno e di eventuali problemi di taglio.
- Provate le lame campione prima di acquistarne una grande quantità.
- Chiedi aiuto agli esperti per realizzare lame speciali per i lavori più difficili.
Domande frequenti
Qual è il miglior materiale per lame circolari industriali per il taglio di pellicole multistrato?
Le lame in carburo di tungsteno o in acciaio rapido con un bordo affilato e sottile garantiscono tagli più puliti nei film multistrato. Questi materiali non si usurano rapidamente e mantengono il filo tagliente anche quando si taglia rapidamente.
Il rivestimento TiCN può durare più a lungo del TiN nel taglio ad alta velocità?
Sì. I rivestimenti TiCN sono più duri e resistono meglio all'usura rispetto al TiN. Questo significa che sono ideali per lavori di taglio rapidi in cui si desidera che le lame durino più a lungo.
In che modo lo stile del bordo influisce sulle prestazioni di taglio?
Lo stile del filo determina l'efficacia del taglio e la precisione del taglio. Un filo a smusso singolo consente tagli molto netti su oggetti sottili. I fili seghettati o dentati sono più adatti per oggetti duri o fibrosi. Aiutano la lama a muoversi più facilmente e rendono i tagli più uniformi.
Quando un'azienda dovrebbe scegliere le lame in ceramica?
Le lame in ceramica sono ideali quando si desidera che rimangano affilate a lungo e non reagiscano con le sostanze chimiche. Sono ideali per lavori igienici, medici e alimentari, dove cambiare spesso le lame è difficile.
Quali sono i principali vantaggi dell'utilizzo di coltelli circolari rivestiti?
Le lame rivestite durano più a lungo, scorrono più fluidamente e non arrugginiscono. Rivestimenti come DLC o TiN impediscono l'accumulo di residui appiccicosi e contribuiscono a una maggiore durata delle lame tra una sostituzione e l'altra. Questo consente di risparmiare denaro e di aumentare la produttività degli operatori.
In che modo i coltelli industriali personalizzati possono migliorare l'efficienza produttiva?
Le lame personalizzate sono realizzate per lavori e materiali speciali. Contribuiscono a ottenere tagli migliori e a ridurre i tempi di fermo macchina.
Vedi anche
Trova le Lame di Granulazione Perfette per le Tue Esigenze di Lavorazione della Plastica
I 10 migliori consigli per far durare più a lungo le lame del tuo rasoio circolare
Cosa sono i coltelli Crush Cut e come funzionano nell'industria
Come scegliere le lame per taglierine circolari giuste per prestazioni durature


