You want every lame personnalisée in your facility to be completely safe. Using food grade steel is essential for ensuring that food industrial blades are safe to come into contact with food. Food safety standards like NSF and FDA require stainless steel blades to have a smooth surface that is easy to clean and resistant to rust. Choosing the wrong materials can allow bacteria to hide or contaminate food. Selecting the right steel helps protect both your products and your customers.
Principaux points à retenir
- Pick the right food grade steel type. The 200 series is good if you want to save money. The 300 series does not rust easily. The 400 series stays sharp and lasts longer.
- Use blades that have smooth and shiny surfaces. This stops bacteria from growing. It also makes cleaning much easier.
- Choose steels like 304 or 316 because they do not rust. These steels keep blades safe and clean. They also last a long time in wet or sour foods.
- Make sure blades follow FDA and NSF safety rules. Keep the right papers to protect your business and your customers.
- Take care of blades by cleaning them gently. Dry them fast and sharpen them often. This helps blades last longer and saves you money.
1. Food Grade Steel Types

When picking a blade for food processing, you should know which food grade steel type fits your needs. Each stainless steel series has its own benefits for safety, cleanliness, and how well it works. Here are the most common types used in industrial blades.
SAE 200 Series
Le 200 series stainless steels are a cheaper choice for food processing. These steels use manganese instead of some nickel. This makes them cost less, but they do not fight rust as well.
Acier inoxydable 201
- Description: 201 stainless steel fights rust and is tough. It costs less than other grades. But it does not last as long in rough places.
- Applications: 201 is used in light-duty food processing blades and utensils. It is good when you want to save money and do not need the strongest blade.
Acier inoxydable 202
- Description: 202 stainless steel is like 201 but fights rust a bit better. It is still cheaper than higher grades.
- Applications: 202 is used for parts that do not touch food much and for cheap blades. It is best where there is not much risk of rust.
Conseil: If you need a blade for simple food prep and want to spend less, the 200 series is a good pick. But remember, it may not last long in wet or sour places.
SAE 300 Series
The 300 series is the main choice for food grade steel. These grades have more nickel, so they fight rust and last longer.
Acier inoxydable 304
- Description: 304 stainless steel is the most used food grade steel. It does not rust or stain and can handle many cleaning chemicals. Its smooth surface is easy to clean and stops bacteria from growing.
- Applications: 304 is used in many food processing blades, slicers, mixers, and storage tanks. It works well in most food places.
Acier inoxydable 316
- Description: 316 stainless steel has molybdenum, which helps it fight salty and sour things even better. This makes it great for hard food processing jobs.
- Applications: 316 is best for blades that cut seafood, dairy, or sour foods. It can handle tough cleaning and salty or sour places.
Note: Both 304 and 316 stainless steels do not react with food. They keep your food’s taste, smell, and color the same.
SAE 400 Series
The 400 series is harder and keeps its edge longer. These steels are best when you need a sharp blade that lasts.
Acier inoxydable 420
- Description: 420 stainless steel has more carbon, so it is hard and stays sharp. It fights rust from food and water, but not as well as the 300 series.
- Applications: 420 is used in cutting blades, knives, and tools that need to stay sharp. It is often picked for kitchen tools and heavy-duty food processing.
440 Stainless Steel
- Description: 440 stainless steel is the hardest and most wear-resistant food grade steel. It still fights rust, but not as much as 304 or 316.
- Applications: 440 is used for high-performance industrial blades and special cutting tools. It is best when you need a blade to stay sharp for a long time.
Saviez-vous? The 400 series can be heat-treated to make it even stronger. This is why it is great for pro knives and cutting tools.
Comparison Table: Stainless Steel Series for Food Processing Blades
| SAE Series | Structure | Propriétés clés | Applications typiques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Série 200 | Austenitic | Cheaper, okay at fighting rust | Light-duty blades, utensils, budget food processing |
| Série 300 | Austenitic | Great at fighting rust, easy to clean | General-purpose blades, slicers, mixing equipment |
| Série 400 | Martensitic/Ferritic | Very hard, keeps edge, okay at fighting rust | Cutting blades, knives, special tools |
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
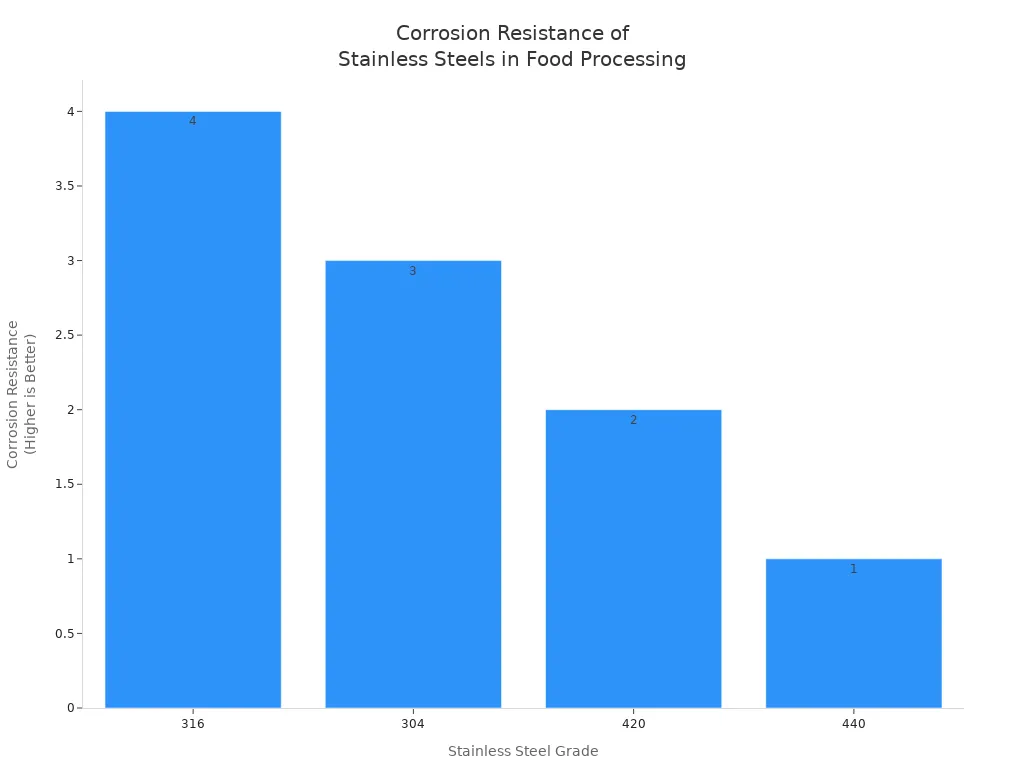
- 316 stainless steel is best at fighting rust, especially in salty or sour places.
- 304 stainless steel gives strong protection for most food processing.
- 420 and 440 stainless steels are very hard but do not fight rust as well.
Why Choose a Trusted Manufacturer?
When you pick a blade for food processing, you want it to be safe and reliable. Nanjing Metal, also called Maxtor Metal, is a trusted food blade maker. With 20 years of work, Nanjing Metal has a skilled team for design and making blades. The company makes custom industrial blades and is known for quality and safety.
Conseil: Always pick a maker with lots of experience in food grade steel blades. This helps make sure your blades meet strict rules for cleanliness and how well they work.
2. Contamination Prevention
To keep food processing blades safe, you need the right material and finish. Germs can spread fast if they find places to hide on your tools. You should pick blades that stop germs from sticking and growing. Acier de Qualité Alimentaire helps stop contamination by using special surface treatments and safe, non-toxic materials.
Smooth Surface Finish
UN smooth blade surface helps keep bacteria away. Polished blades make it hard for germs and food bits to stick.
Surface Treatment Techniques
There are many ways to make a blade’s surface smooth and easy to clean:
- Mechanical polishing takes away scratches and grooves. This makes the blade flat.
- Electropolishing uses electricity to smooth out tiny bumps. It gives the blade a shiny, non-stick finish.
- Alloying with copper or silver can help fight bacteria.
- Laser irradiation, etching, and plasma treatments change the surface. These methods make it harder for bacteria to live there.
- Antimicrobial coatings like PTFE or titanium dioxide make a very smooth, water-repellent layer.
- Hydrophilic polymer coatings, such as polyethylene glycol, help keep bacteria and proteins away.
- Composite coatings, like nickel-graphene oxide, give both antibacterial and anti-corrosive benefits.
Conseil: Electropolishing is a top pick in the food industry. It makes blades easier to clean and helps them resist rust.
Impact on Bacterial Adhesion
A polished, non-porous blade gives germs fewer places to hide. Removing tiny cracks and rough spots keeps bacteria from settling in. This makes cleaning faster and better. Studies show smooth finishes lower the risk of germs because bacteria cannot stick or form biofilms. You also protect food from metal pieces and other dangers that come from rough or damaged blades.
Non-Toxic Composition
You also need to know what metals are in your blades. Acier de Qualité Alimentaire uses a special mix of metals to keep food safe.
Food Grade vs. Regular Steel Composition
Acier de Qualité Alimentaire has lots of chromium and nickel. These make a layer that stops rust and keeps germs away. Regular steel may have more bad metals or impurities. These can get into food, especially with sour or salty foods. Groups like the FDA and NSF have strict rules for what metals can be used in food tools. They say food contact materials cannot have too much of any dangerous metal.
Examples of Restricted Elements
Here is a table that shows which toxic elements are not allowed in Acier de Qualité Alimentaire:
| Type de matériau | Toxic Elements Restricted | Relevant Regulations and Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Acier inoxydable | Lead, Cadmium, Mercury, Arsenic | FDA CPG 7117.05, NSF/ANSI 51-2012 |
| Steel, Cast Iron, Plating | Lead, Cadmium, Mercury, Arsenic (dissolution limits) | CMAFDA CPG 7117.05 (AOAC 973.32) |
The FDA and NSF use sensitive tests to check for these metals. They make sure blades do not let harmful substances get into food.
Choisir Acier de Qualité Alimentaire helps you follow these safety rules. You lower the risk of foodborne illness and keep customers safe from toxic metals. The right steel also keeps blades strong and easy to clean.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is very important in food processing. Blades are always around water, acids, cleaners, and salty foods. These tough things can cause rust and damage if you use the wrong steel. Picking the right steel keeps your tools safe, clean, and lasting longer.
Importance in Food Processing
Food Safety and Hygiene
Corrosion makes blades rough and rusty. These spots can trap food and germs. Cleaning gets harder when blades are damaged. Rust can get into your food and change how it tastes or looks. Using corrosion-resistant blades keeps food safe from these problems. Stainless steel has a chromium oxide layer that protects it. This layer fixes itself if scratched. It keeps the blade smooth and stops germs from hiding. Your blades do not react with food, so food stays fresh and safe.
- Corrosion resistance keeps your tools strong and clean.
- Smooth blades are easier to wash and sanitize.
- You follow food safety rules because blades do not add bad stuff to food.
Conseil: Check your cleaning steps. Do not use rough scrubbers or hot chlorine cleaners. These can hurt the blade’s protective layer.
Blade Longevity and Cost Efficiency
Rust and corrosion make blades wear out faster. When a blade rusts, you need to buy a new one sooner. This costs more money and time. Corrosion-resistant blades last longer, so you save money. They also stay sharp, so you do not sharpen them as much.
- Stainless steel blades do not rust in wet or sour places.
- You buy fewer new blades each year.
- Longer blade life means you spend less on fixing or replacing them.
Maintenance and Downtime Reduction
When you fix or change a blade, work stops. Corrosion-resistant blades help you avoid these stops. You spend less time fixing and more time working. Cleaning and storing blades right makes them last even longer.
- Buy good, corrosion-resistant blades to need less fixing.
- Make a plan to check blades often and catch problems early.
- Store blades the right way to stop surprise breaks.
Note: Corrosion-resistant blades help you keep working and avoid losing time.
Resistant Grades
You can pick from many corrosion-resistant blades. Each type is good for different jobs.
Acier inoxydable 304
304 stainless steel is the most used for food blades. It has at least 18% chromium and 8% nickel. This mix helps it fight many acids and cleaners. You can use 304 blades for cutting, mixing, and general food work. The smooth surface is easy to clean and stops germs from sticking.
Acier inoxydable 316
316 stainless steel is even better at fighting rust. It has molybdenum, which helps against salty and harsh chemicals. If you cut salty or sour foods, 316 is best. It handles tough cleaning and keeps blades in good shape.
Acier inoxydable 420
420 stainless steel is hard and fights rust well. You see it in sharp tools that get cleaned a lot. It does not fight rust as well as the 300 series, but it works for knives and blades that need to stay sharp.
440 Stainless Steel
440 stainless steel is the hardest and wears down the slowest. It still fights rust, so it is good for special and tough blades. If you need a blade to stay sharp for a long time, 440 is a great pick.
| Grade | Caractéristiques principales | Meilleurs cas d'utilisation |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | Excellent corrosion resistance, easy to clean | General food processing, slicers, mixers |
| 316 | Superior resistance to chlorides and acids | Seafood, dairy, acidic food processing |
| 420 | Good hardness, moderate corrosion resistance | Cutting tools, knives |
| 440 | Highest hardness, strong corrosion resistance | High-performance, specialized blades |
Saviez-vous? Electropolishing and chemical passivation can make blades fight rust even better. These treatments fix the chromium oxide layer and make cleaning easier.
4. Regulatory Standards
When you pick blades for food processing, you must follow safety rules. These rules keep your customers and business safe. Food contact materials, like stainless steel blades, must pass national and international standards. If you do not follow these rules, you could get fined or lose your business.
FDA and NSF Compliance
FDA Food Contact Material Regulations
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) makes rules for materials that touch food. You must use approved stainless steel grades like 304, 316, or 430. The FDA says food contact surfaces must be smooth and easy to clean. Surfaces cannot have cracks where bacteria can hide.
Here is a table with the main FDA rules for food contact materials:
| FDA Regulation (21 CFR Part) | Scope and Relevance to Food Contact Materials |
|---|---|
| Part 1 | General rules for food contact substances in materials that hold, make, pack, or move food. |
| Part 174 | Rules for indirect food additives and limits for food contact materials. |
| Part 186 | Lists substances that are Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS). |
| Part 170 | Rules for food additives in materials that touch food. |
| Part 171 | How to ask for approval of food additives. |
| Part 180 | Food additives allowed for a short time. |
| Part 181 | Food ingredients approved before 1958. |
To follow the rules, you must do at least one of these things:
- Use materials listed in Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR)
- Pick materials with GRAS status
- Use materials with a prior approval letter
- Get a Threshold of Regulation (TOR) exemption
- Have a Food Contact Substance Notification (FCN)
You should ask your supplier for a letter of guaranty. This letter shows the blade meets FDA rules for food contact.
NSF/ANSI Standard 51 Certification
NSF/ANSI Standard 51 gives rules for materials in commercial food equipment. Your blades should pass these tests:
- Easy to clean
- Resist rust
- Resist breaking
- Resist scratching
- Resist heat
- Coating stays on
NSF/ANSI 51 covers many materials like stainless steel, aluminum, copper, glass, and wood. The certification checks every step, from applying to yearly plant checks. Only materials that pass all tests are safe for food contact.
Conseil: NSF/ANSI 51 certification shows your blades are safe for food. It is different from NSF/ANSI/CAN 61, which is only for water.
Documentation and Traceability Requirements
You must keep records to show your blades follow all rules. These records include:
- Test results
- Compliance certificates
- Letters of guaranty from suppliers
- Traceability papers for each batch
If you cannot show these papers, you could get fined or have a recall. Good records protect your business and your customers.
International Standards
EU Food Contact Materials Regulation (EC 1935/2004)
If you sell blades in Europe, you must follow Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. This rule says food contact materials cannot change food or make it unsafe. You must use good manufacturing steps and keep full traceability. If you do not follow the rule, your products can be banned or recalled.
| Consequence Type | Estimated Share of Total Cost (%) |
|---|---|
| Business disruption | 33 |
| Revenue loss | 26 |
| Productivity loss | 24 |
| Reputational damage | 10-15 |
| Miscellaneous | 2-7 |
Not following the rules can also cause trade problems and health risks. The money loss can be very high.
ISO 22000 Food Safety Management
ISO 22000 is a global food safety rule. You use it to set up a food safety system. This rule helps you control risks and show your blades are safe for food. Many buyers want ISO 22000 certification before they buy from you.
Other Regional Certifications (e.g., GB 4806 in China)
Other countries have their own rules. For example, China uses GB 4806 for food contact materials. You must check the rules for every country where you sell blades. Meeting local rules helps you avoid recalls and trade problems.
Global Traceability and Compliance Documentation
You need to track every blade from raw material to finished product. Good tracking helps you find and fix problems fast. You should keep:
- Batch numbers
- Supplier certificates
- Test reports
- Shipping records
If you cannot track your products, you may have recalls, lost sales, and hurt your reputation.
5. Easy Maintenance
It is important to keep your blades clean and working well. This helps keep food safe and your work running smoothly. In food processing, you need tools that are easy to clean, do not stain, and last a long time. Acier de Qualité Alimentaire blades make caring for them simple and dependable.
Cleaning and Hygiene
Smooth, Non-Porous Surfaces
You want blades that do not hold onto food or germs. Acier de Qualité Alimentaire has a smooth surface that does not let things soak in. This means bacteria and dirt cannot hide. Cleaning is fast and easy. You lower the chance of spreading germs. A shiny finish, like electropolishing, makes cleaning even easier. You can wipe off dirt and clean the blade with little effort.
Resistance to Staining and Odors
Stainless steel does not stain or keep bad smells. You do not have to worry about food smells or colors staying on your blades. This keeps your tools fresh and safe every time you use them. The smooth surface also means strong cleaners will not hurt the blade or leave smells behind.
Common Cleaning Methods
Here are steps to keep your blades clean and safe:
- Rinse the blade to get rid of loose food.
- Wash with a special soap to remove fats and proteins.
- Rinse again to wash away any soap left.
- Sanitize with a safe chemical or hot water (about 170°F for 30 seconds).
Conseil: Always use safe cleaners and do not use rough chemicals that can scratch the blade. Smooth finishes, like a No. 4 ground finish, help you clean faster and better.
Reduced Downtime for Sanitation
Blades that are easy to clean save you time. You can get back to work quickly. Smooth surfaces do not need hard scrubbing. This means less work and your line keeps moving.
Durability in Use
Corrosion and Wear Resistance
Acier de Qualité Alimentaire stands up to water, acids, and cleaners. You do not have to worry about rust or holes. This keeps your blades sharp and safe for longer. The material also does not wear down fast from daily use and cleaning.
Durée de vie prolongée de la lame
Strong blades last longer and save you money. You do not have to buy new ones as often. Factories that use good blades have less downtime and spend less.
| Blade Management Strategy | Cost per Blade | Annual Cost (300 Blades) | Économies annuelles |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Blades | $300 | $90,000 | N / A |
| Regrinding | $120 | $36,000 | $54,000 |
Sharpening and caring for blades can make them last two or three times longer. This cuts down on waste and helps you work better.
Lower Replacement Frequency
When you use Acier de Qualité Alimentaire blades, you do not need to change them often. This means you spend less money on new blades. You stop work less for repairs. Your blades cut well every time.
Maintenance Best Practices
You can keep your blades sharp and safe by doing these things:
- Use wooden or plastic boards, not glass or steel.
- Cut gently and let the blade do the work.
- Do not scrape food with the blade edge. Use the back instead.
- Wash blades by hand with warm water and mild soap. Do not soak or use dishwashers.
- Dry blades right after washing to stop rust.
- Store blades in a block, on a strip, or in a case.
- Sharpen blades often with a rod or stone.
- Check blades for damage or rust.
- Follow the maker’s care and replacement tips.
Note: Cleaning and storing blades the right way helps you avoid damage like rust, bending, or dullness.
You have learned the basics for picking safer blades in food processing. Keep these five important points in mind:
- Precision cutting helps keep your products good.
- Corrosion resistance stops rust and damage from food acids.
- Easy maintenance makes cleaning simple and saves time.
- Strong, hard blades last longer when used a lot.
- Customization helps your work go faster and fit your needs.
Choosing certified food grade steel keeps things safe and follows the rules. For expert help, trust Nanjing Metal, a well-known food blade maker with 20 years of experience. Want custom blades? Contact their sales engineers today.
FAQ
What makes food grade steel different from regular steel?
Food grade steel uses a special mix of metals. It resists rust and does not let harmful elements get into your food. You can clean it easily. This keeps your food safe.
How do I know if a blade is safe for food processing?
Look for certifications like FDA or NSF. These show the blade meets strict safety rules. You can also ask your supplier for test results or a letter of guaranty.
Can I use the same blade for cutting meat and vegetables?
You should use separate blades for meat and vegetables. This helps stop germs from spreading. Color-coded handles or labels make it easy to keep blades apart.
Voir aussi
Choisir les meilleures lames de trancheuse à viande selon vos besoins


