
You need to pick the right Graus de aço para ferramentas de prensa dobradeira for good results in metal forming. The steel grade you choose changes how long your tools work, how exact your bends are, and how much you pay for new tools. Some steel grades are very hard and do not wear out fast. Other steel grades are tougher or more stable. What you pick can really change your work each day.
Principais conclusões
- Picking the right press brake tooling steel grade matters. It changes how long tools last, how accurate they are, and how much they cost. Harder steel grades like T10 and Cr12MoV do not wear out fast. This means you do not have to replace them often. Tougher grades like 42CrMo work well for heavy jobs. They stop cracks and bending from happening. Carbon tool steels like T8, T10, and T12 are good for light or medium bending jobs. Alloy tool steels, like 42CrMo, are very tough. They also resist wearing out in hard jobs. High-carbon high-chromium steels like Cr12MoV are great for jobs that need lots of work. They do not wear out easily. Always think about the type and thickness of metal before you pick a steel grade for your tooling. Heat treatment makes steel grades work better. It helps them last longer and do their job well.
Press Brake Tooling Steel Grades Overview

Steel Grade Classifications
When you pick press brake tooling steel grades, you have many choices. Each grade has its own special features to help you. Carbon tool steels like T8, T10, and T12 are very hard and keep sharp edges. Alloy tool steels, such as 42CrMo and chromium molybdenum, are strong and tough. High-carbon, high-chromium steels like Cr12MoV and D2 do not wear out fast. Some advanced jobs use high-speed steel and carbide tooling. These materials work well at high speeds and stay strong when hot.
Here is a table that lists some common press brake tooling steel grades and their main features:
| Grau de aço | Propriedades principais | Formulários |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium Molybdenum | Very strong, does not rust easily | Used for heavy-duty bending |
| T8 and T10 | Very hard, edges last a long time | Used for precise work |
| 42CrMo | Tough and hard at the same time | Used for high-stress jobs |
| Cr12MoV | Does not wear out and is tough | Used for precision tooling |
You can look at this table to compare press brake tooling steel grades and see which ones work best for you.
Why Steel Grade Matters
The steel grade you pick changes how your press brake tooling works. If you choose the right press brake tooling steel grades, your tools last longer and work better. Harder grades like T10 and Cr12MoV do not wear out fast, so you do not need to replace them often. Tougher grades like 42CrMo can handle lots of pressure and use. You will see fewer cracks and less bending in your tools. When you match the steel grade to your job, you save money and get better bends.
Think about what you need for your job. If you bend thick plates or use strong presses, you need press brake tooling steel grades that are strong and tough. If you bend thin sheets or need fine bends, you want grades that are very hard and have sharp edges. Picking the right steel grade helps you avoid stopping work and keeps your job running smoothly.
Tip: Always check the steel grade before you buy new press brake tooling. The right steel grade makes your job easier and your results better.
Carbon Tool Steels for Press Brake Dies

Carbon tool steels play a big role in press brake dies. You see these steels in many shops because they offer high hardness and good wear resistance. You can use them for bending, shaping, and forming metal sheets. Let’s look at the main types: T8, T10, and T12.
T8, T10, and T12 Properties
T8 Steel
T8 steel gives you a balance between hardness and toughness. You find T8 in dies that need to keep their shape but do not face heavy impact. The chemical composition includes about 0.75-0.85% carbon, 0.17-0.37% silicon, and 0.17-0.37% manganese. After heat treatment, T8 steel reaches a hardness of 58-63 HRC. You use T8 for light to medium-duty bending operations. These dies work well for simple shapes and thin sheets.
T10 Steel
T10 steel stands out for its higher carbon content. You get about 0.95-1.04% carbon, 0.17-0.37% silicon, and 0.17-0.37% manganese. After heat treatment, T10 dies reach a hardness of 60-65 HRC. You choose T10 when you need more wear resistance and sharper edges. These dies work best for precision jobs and thin sheet metal. T10 is popular because it balances toughness and wear resistance. You can use T10 dies for repeated bending without losing accuracy.
- T10 is commonly used for bending machine tooling.
- T10 offers moderate toughness and high wear resistance.
- After heat treatment, T10 can achieve a hardness exceeding 60 HRC.
- T10 dies are cost-effective for many shops.
T12 Steel
T12 steel has the highest carbon content among these grades. You get about 1.15-1.24% carbon, 0.17-0.37% silicon, and 0.17-0.37% manganese. After heat treatment, T12 dies reach a hardness of 62-66 HRC. You use T12 when you need maximum hardness and wear resistance. These dies work best for fine blanking and forming thin materials. T12 dies do not handle heavy impact loads well, but they last a long time in low-impact jobs.
Here is a table that compares the main properties of these carbon tool steels:
| Tipo de aço | Dureza (HRC) | Resistência ao desgaste | Dureza | Typical Use in Dies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T8 | 58-63 | Moderado | Moderado | Light/medium-duty |
| T10 | 60-65 | Alto | Moderado | Precision/thin sheet |
| T12 | 62-66 | Muito alto | Baixo | Fine blanking |
Vantagens e Limitações
You get several advantages when you use carbon tool steels for press brake dies:
- High hardness lets dies keep their shape and edge.
- Good wear resistance means dies last longer.
- Cost-effective for many bending jobs.
- Easy to machine and heat treat.
You should know some limitations too:
- T8, T10, and T12 dies do not handle high impact loads as well as alloy steels.
- T10 dies have poor heat resistance, with a maximum working temperature of 250°C.
- T12 dies work best in low-impact jobs.
Tip: You should match the steel grade to your job. If you need dies for light or medium-duty bending, T8 works well. For precision and repeated bending, T10 gives you better wear resistance. If you need maximum hardness for fine blanking, T12 is the right choice.
You may also see high carbon and high chromium tool steel used for dies that need even more wear resistance. These steels offer extra hardness and longer life, especially in demanding jobs.
You can improve your results by picking the right carbon tool steel for your dies. You get better bends, longer tool life, and fewer problems during production.
Alloy Tool Steels in Press Brake Tooling

Alloy tool steels are a strong choice for press brake tooling. Many shops use these steels for tough and careful jobs. The most used alloy tool steel for press brake dies is 42CrMo, also called chromoly steel. This steel grade mixes strength, toughness, and wear resistance. These features help your tools last longer and work better.
42CrMo and Chromoly Features
Composição química
You can see why 42CrMo is good by looking at what it is made of. The main parts in 42CrMo are carbon, chromium, and molybdenum. These parts help the steel stay hard and tough.
| Element | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.38–0.45 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0.90–1.20 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.15–0.30 |
This mix gives you great hardenability, more toughness, and very good wear resistance. The steel grade also has manganese and silicon. These add even more strength and keep the steel stable.
Propriedades Mecânicas
When you use 42CrMo in press brake tooling, you get strong and stiff tools. This steel grade can handle heavy loads and lots of use. You also get great wear resistance, so your dies last longer. The steel grade stands up to high heat and does not change shape easily. Your tools keep their shape, even in hard jobs.
| Propriedade | 42CrMo | Carbon Tool Steels |
|---|---|---|
| Rigidity and Strength | High rigidity and strength | Moderate rigidity and strength |
| Resistência ao desgaste | Excellent wear resistance | Boa resistência ao desgaste |
| Resistência à temperatura | Resistência a altas temperaturas | Limited temperature resistance |
| Deformation Resistance | High deformation resistance | Lower deformation resistance |
| Dureza | Resistência superior | Moderate toughness |
| Microstructure Stability | High microstructure stability | Variable microstructure stability |
You can see that 42CrMo is better than carbon tool steels in most ways. This makes it a top pick for hard press brake tooling jobs.
Heat Treatment Characteristics
Heat treatment is very important for how 42CrMo works. You can use high-frequency quenching or full heat treatment to make the steel stronger and harder to wear out. Good heat treatment, like tempering, gives your dies both strength and flexibility. The final hardness depends on how you heat, cool, and time the process. Dies that get full heat treatment cost more, but they last longer and work better.
Tip: Always check if your press brake tooling steel grades have been heat treated. Good heat treatment means your tools work better and last longer.
Typical Advantages
You get many good things when you use chromoly steels like 42CrMo for your press brake tooling:
- Very durable and does not rust easily
- Strong enough for heavy jobs
- Lasts a long time, even in tough places
- Easy to weld for special shapes and repairs
- Can take hits without breaking during stamping
- Molybdenum helps it work well in high heat
- Hard enough for cutting and forming tools
Chromoly steel gives you tools that last a long time and work well.
Cenários de Aplicação
Heavy-Duty Applications
You use alloy tool steels like 42CrMo for bending thick plates and using strong presses. These steel grades can take many hits and lots of stress without breaking or changing shape. You get tools you can trust for hard jobs.
- 42CrMo is good for short jobs and sometimes use.
- You get good results without spending too much.
- High-strength alloy steels are good for most bending jobs.
Precision Tooling
If you need very exact bends and the same results every time, you pick 42CrMo. The steel grade’s stable shape and toughness help you make perfect bends. You see fewer mistakes and less stopping in your shop.
Note: Precision dies made from alloy tool steels keep their shape and accuracy, even after many cycles.
Industry Examples
You find alloy tool steels in many fields:
- Automotive: Bending car body panels and frames
- Shipbuilding: Shaping thick plates for hulls and decks
- Construction machinery: Making strong parts
- Large metal fabrication: Making special parts for buildings and machines
You see press brake tooling steel grades like 42CrMo where strength, toughness, and long life are very important.
High-Carbon High-Chromium Steels
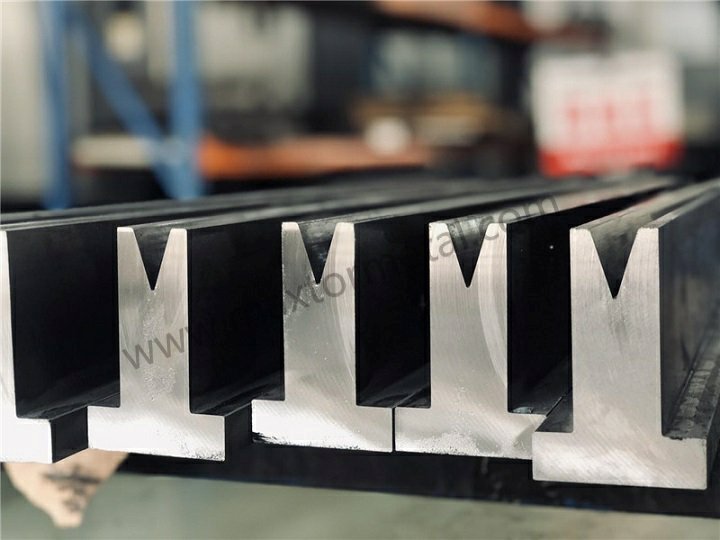

High-carbon high-chromium steels give you a strong option for press brake dies. These steels stand out because they offer excellent wear resistance and high hardness. You often see them in jobs where you need your press brake dies to last a long time and keep their shape. Let’s look at the main grades and what makes them special.
Cr12, Cr12MoV, D2, and Similar Grades
You will find several high-carbon high-chromium steels used in press brake dies. The most common grades are Cr12, Cr12MoV, and D2. Each grade has a unique mix of elements that changes how it works in your shop.
Segue abaixo uma tabela que mostra as principais diferenças:
| Grau de aço | Carbon Content | Elementos de liga | Dureza | Resistência ao desgaste | Dureza (HRC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
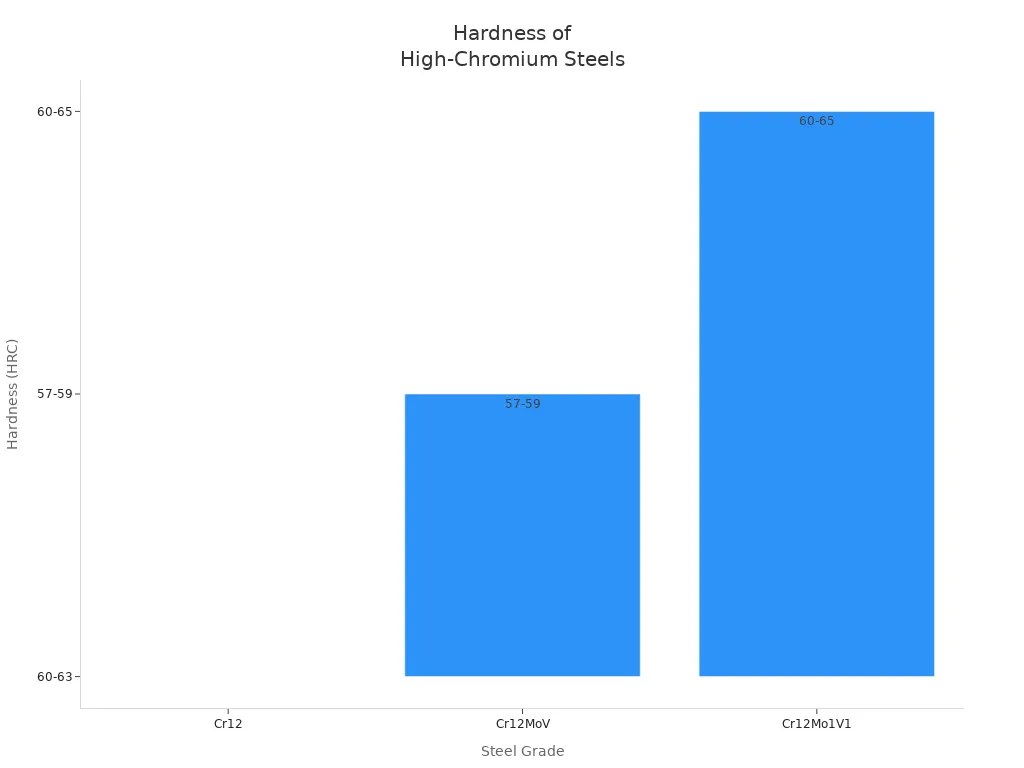
| Cr12 | Mais alto | Nenhum | Poor | Alto | 60-63 |
| Cr12MoV | Mais baixo | Mo, V | Bom | Better than Cr12 | 57-59 (after tempering) |
| Cr12Mo1V1 | Higher than Cr12MoV | Higher Mo, V | Better than Cr12MoV | Melhor | 60-65 (after treatment) |
You can see that Cr12 has high carbon but no extra alloying elements. This gives you high hardness but low toughness. Cr12MoV adds molybdenum and vanadium. These elements improve toughness and wear resistance. Cr12Mo1V1 takes it further with even more molybdenum and vanadium. This grade gives you the best wear resistance and toughness for press brake dies.
Here is a chart that compares the hardness of these grades:
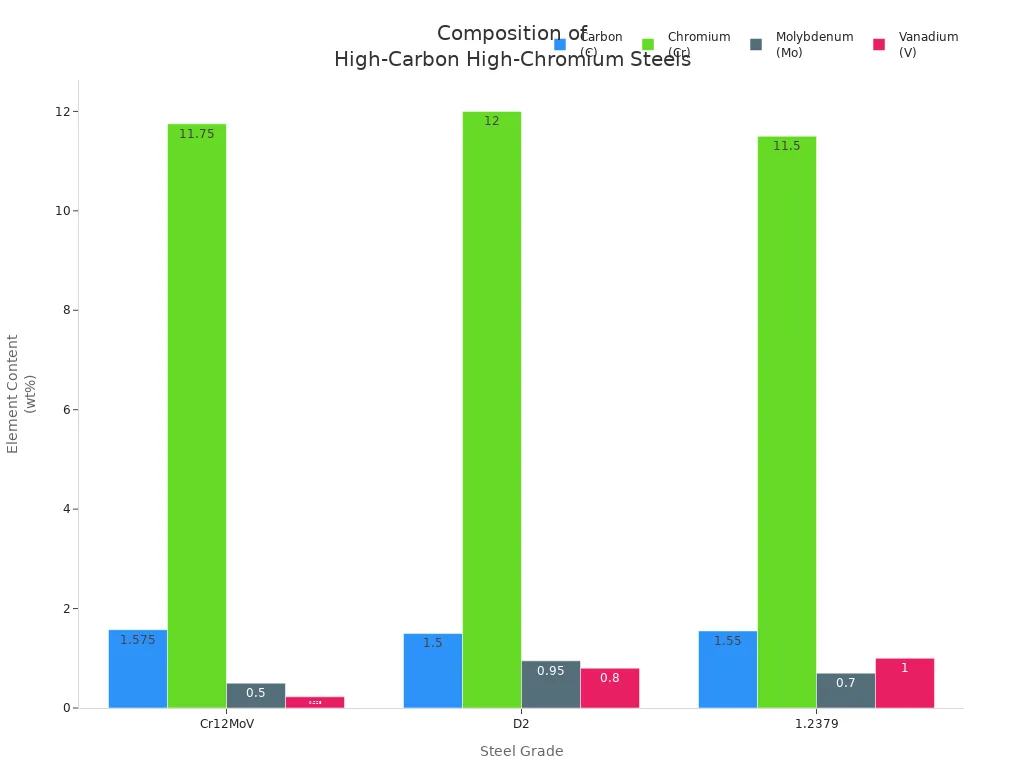
You also see D2 and 1.2379 used in press brake dies. These grades have a similar mix of carbon, chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium. The table below shows their composition:
| Nota | C | Cr | Mo | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr12MoV | 1.45-1.7 | 11-12.5 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.15-0.3 |
| D2 | 1.4-1.6 | 11-13 | 0.7-1.2 | 0.5-1.1 |
| 1.2379 | 1.5-1.6 | 11-12 | 0.6-0.8 | 0.9-1.1 |
You get more wear resistance as you add more chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium. These elements help your press brake dies last longer and resist cracking.
Here is a chart that shows the content of these elements:
- Cr12 gives you poor toughness and high brittleness. Carbides do not spread evenly, so you may see cracks.
- Cr12MoV improves toughness and wear resistance. You see fewer cracks and less deformation.
- Cr12Mo1V1 offers the best toughness, wear resistance, and oxidation resistance.
Wear Resistance and Hardness
You want your press brake dies to last as long as possible. High-carbon high-chromium steels help you reach this goal. These steels give you top-level wear resistance. You can use them for jobs where your dies face lots of friction and pressure.
The wear resistance of press brake die depends on the steel’s hardness and the way carbides form inside the metal. Cr12, Cr12MoV, and D2 all form hard carbides. These carbides protect your press brake dies from wearing out. You get less downtime and fewer replacements.
You will notice that Cr12MoV and D2 offer better wear resistance than plain Cr12. The added molybdenum and vanadium help the steel resist cracking and chipping. You can use these grades for high-volume jobs or when you bend abrasive materials.
Tip: If you want the best wear resistance, choose Cr12Mo1V1 or D2 for your press brake dies. These grades keep their edge and shape even after thousands of bends.
You also get high hardness with these steels. Most grades reach 57-65 HRC after heat treatment. This high hardness means your press brake dies cut and form metal with sharp, clean lines. You get precise bends and less tool wear.
High-Speed Steel and Carbide Tooling

When you use press brake tools, you want strong materials. High-speed steel and cemented carbide are both great for hard jobs. These materials help your tools last longer and work better. Each one has special benefits that can help you in your shop.
Benefícios do aço rápido
High-speed steel (HSS) is better than regular tool steels in many ways. You can use HSS for tools that must stay sharp and work fast. This material does not get soft when it gets hot. It keeps its shape even if you bend metal quickly.
Here is a table that shows how high-speed steel and regular tool steels are different:
| Beneficiar | Aço Rápido (HSS) | Traditional Tool Steels |
|---|---|---|
| Retains cutting edge at very high speeds | Sim | Não |
| Withstands heat generated during machining | Sim | Não |
| Superior cutting performance | Sim | Não |
| Long service life in demanding operations | Sim | Não |
You can see that high-speed steel works well even when you use your machines a lot. You get smooth bends and do not have to stop often. The tooling does not wear out fast. HSS saves you money because you do not need new dies all the time.
Tip: Pick high-speed steel if you want your tools to work well in fast or hot jobs.
Cemented Carbide Strengths
Cemented carbide is one of the hardest materials for press brake dies. It is very tough and does not wear out quickly. This means your tools last a long time, even in hard jobs.
Here are some main strengths of cemented carbide:
- Cemented carbide is known for being very hard.
- It does not wear out fast, so it is good for jobs you do often.
- Cemented carbide tooling lasts a long time in press brake work.
Cemented carbide is best when you bend hard or rough materials many times. You do not have to worry about your dies wearing out soon. This material is good for jobs with little impact but lots of wear.
Here is a table that compares high-speed steel and cemented carbide for press brake dies:
| Material | Custo | Dureza | Resistência ao desgaste | Dureza |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aço de alta velocidade | Mais baixo | Moderado | Moderado | Bom |
| Carboneto Cimentado | Mais alto | Superior | Excelente | Moderado |
You can see that cemented carbide costs more, but it is harder and lasts longer. High-speed steel is not as hard, but it is tough and costs less. You should choose the material that fits your job and your budget.
Note: Cemented carbide is best for jobs you do often and when you want your tools to last a long time.
When you pick strong materials like high-speed steel or cemented carbide, your tools work better. You do not have to change tools as much. Your shop runs better and you get more value from your press brake tools.
Selecting Press Brake Tooling Steel Grades

Principais fatores de seleção
There are many things to think about when picking press brake tooling. The right steel grade helps you do a better job and saves money. First, think about what kind of metal you want to bend. Mild steel is easy to bend and works with most dies. If you use high-strength alloy or stainless steel, you need stronger tooling that can handle more force and last longer.
The thickness of the metal is very important. Thin sheets need tooling with sharp edges and high hardness. Thick plates need dies that are tough and do not bend easily. How many parts you make also matters. If you make lots of parts, pick tooling that lasts a long time and keeps its shape. You want your dies to stay the same size and shape after many bends.
You should also check your press brake machine. Manual machines work best with lighter metals. Hydraulic and CNC machines can bend thicker plates and make more shapes. Make sure your tooling matches what your machine can do.
Here are some simple tips to help you choose:
- Check what kind of metal and how thick it is before picking a steel grade.
- Think about how many bends you will make each day.
- Make sure your tooling fits your press brake’s power and design.
- Look for steel grades that keep their shape and are tough.
- Think about how much the tooling costs and how long it will last.
Tip: If you need special shapes or blades, you can look at Lâminas Personalizadas made just for your needs.
Matching Grade to Application
You can pick the right steel grade by looking at hardness, wear resistance, and how many bends you need. Each steel grade is best for certain jobs. Use this table to compare some common choices for press brake tooling:
| Material | Dureza (HRC) | Bending Cycles | Melhor para |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aço ferramenta (D2) | 58-62 | 50,000-100,000 | General fabrication |
| Carboneto | 85-92 | 500,000+ | Produção de alto volume |
| Aço temperado | 50-55 | 30,000-60,000 | Budget-conscious shops |
| Tool Steel (A2) | 56-60 | 40,000-80,000 | Precision bending |
| Powdered Metal | 60-64 | 150,000-300,000 | Specialty alloys |
Carbide tooling lasts the longest and is good for making lots of parts. D2 tool steel is a good choice for most jobs. Hardened steel is cheaper and works for shops that do not make as many parts. A2 tool steel is great for jobs that need very exact bends. Powdered metal is best for special metals and unique jobs.
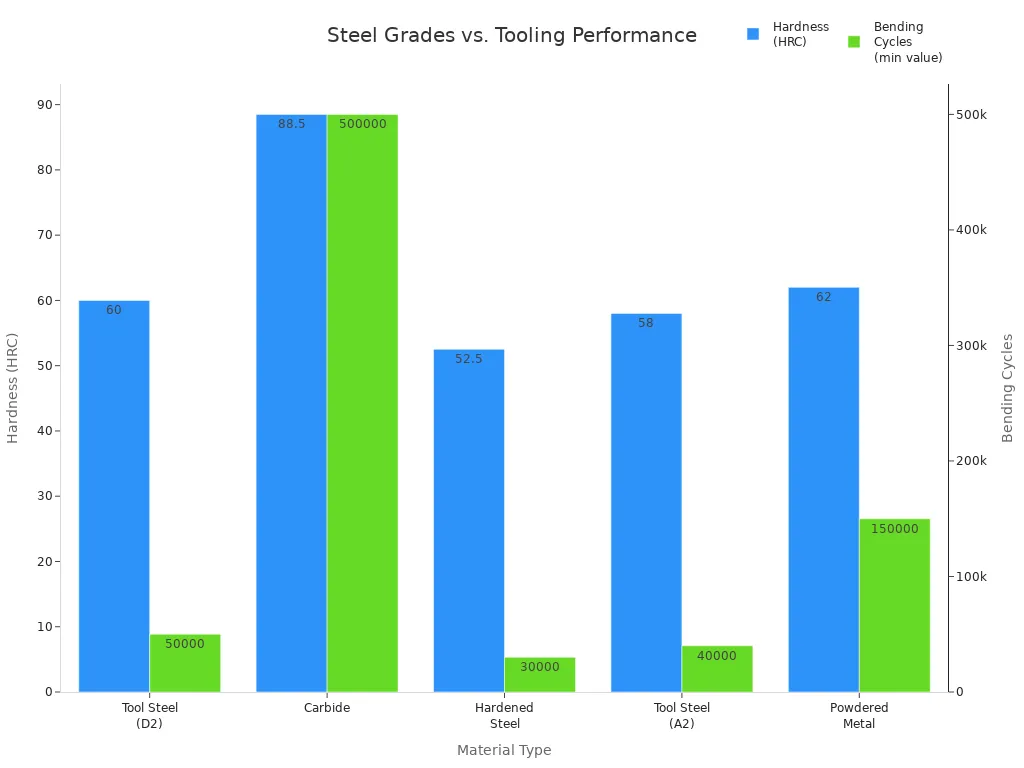
If you want your dies to keep their shape and last a long time, pick grades like 42CrMo or carbide. These materials do not wear out fast and stay the same after many bends. For sharp edges and clean lines, D2 and A2 tool steels are good picks. If you bend thick plates or strong alloys, use tooling that does not bend or break easily.
Nanjing Metal makes press brake tooling from 42CrMo alloy steel. This steel grade is tough and keeps its shape well. You can also ask for special tooling for unique jobs. If you need blades for special shapes or metals, check the página de lâminas personalizadas Para mais opções.
Always match your steel grade to your job. Think about the metal type, thickness, and how many bends you need. Pick tooling that works with your machine and fits your shop’s needs. When you choose the right press brake tooling, you get better results and your tools last longer.
Note: It is important for your dies to keep their shape and be tough. Make sure your tooling grade fits your job.
You have learned how press brake tooling steel grades affect tool life, accuracy, and cost. Choose T8, T10, or T12 for light jobs. Pick 42CrMo or D2 for heavy-duty or high-volume work. Match the steel grade to your needs for better results.
- Check your metal type and thickness.
- Select tooling that fits your machine and production goals.
- Ask experts for advice if you need help.
Perguntas frequentes
What are the most common press brake tooling steel grades?
You often see T8, T10, 42CrMo, Cr12MoV, D2, and high-speed steel used for press brake tooling. Each steel grade offers different hardness, toughness, and wear resistance.
How do I choose the right press brake tooling steel grade?
You should look at the type of metal, thickness, and how many bends you need. Harder steel grades work best for thin sheets. Tougher grades handle thick plates and heavy-duty jobs.
Why does steel grade affect press brake die life?
Steel grade changes how long your dies last. Harder grades resist wear and keep sharp edges. Tougher grades prevent cracks and bending. The right steel grade helps you avoid frequent replacements.
Can I use the same steel grade for all press brake jobs?
You should not use one steel grade for every job. Each press brake tooling steel grade fits different tasks. Pick a grade that matches your metal type and bending needs.
What is the difference between carbon tool steel and alloy tool steel?
Carbon tool steel gives you high hardness and sharp edges. Alloy tool steel offers more toughness and better wear resistance. Alloy grades like 42CrMo work well for heavy-duty bending.
How does heat treatment improve press brake tooling steel grades?
Heat treatment makes steel harder and tougher. You get better wear resistance and longer tool life. Always check if your press brake tooling steel grades have been heat treated.
Are carbide press brake dies better than steel dies?
Carbide dies last longer and resist wear better than steel dies. You should use carbide for high-volume jobs. Steel dies cost less and work well for general bending tasks.
What industries use different press brake tooling steel grades?
You see press brake tooling steel grades in automotive, shipbuilding, construction, and appliance manufacturing. Each industry picks steel grades based on job needs and metal types.
Veja também
Ferramentas de Prensa Dobradeira Estilo Europeu vs. Americano: Qual É a Certa para Sua Oficina?
Escolhendo a Melhor Ferramenta de Prensa Dobradeira para Aço Inoxidável
Dominando ferramentas de prensa dobradeira: como identificar e consertar desgaste de punção e matriz


