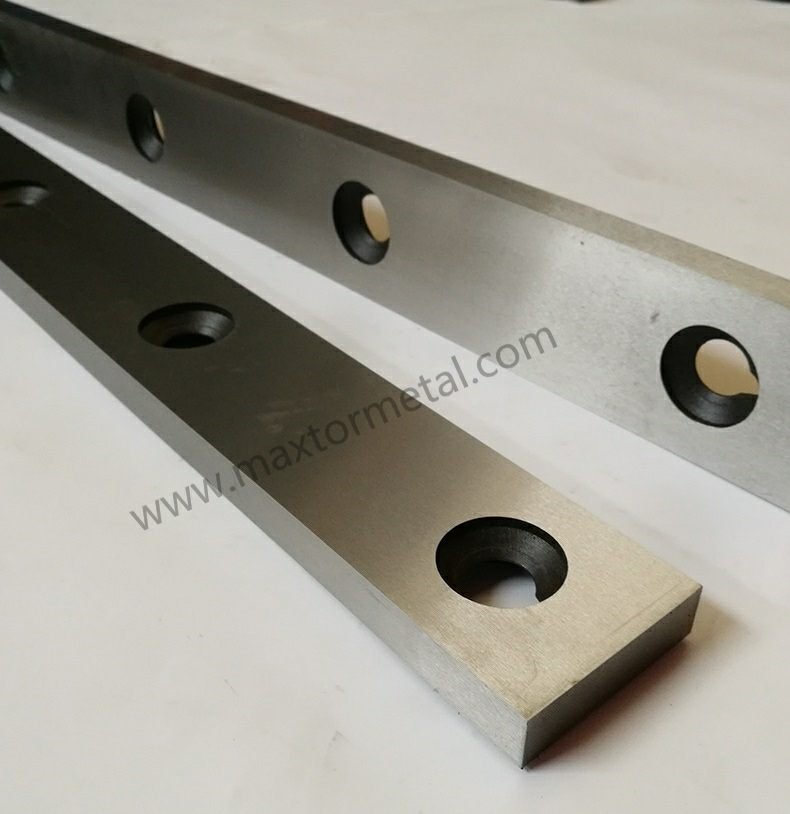

When you pick Lames de cisaille pour acier inoxydable, you face special problems. Stainless steel gets hard fast and wears out tools. Galling and strong metal make cutting hard. You may see too much burring, blade wear, and bent material.
- Hard to machine
- Burring from blades that are not sharp
- Material bends from using wrong pressure
Good blade material and exact shape help stop bite and tear. Metal Industrial uses new ways to make blades that give clean, steady cuts.
Principaux points à retenir
- Pick shear blades made from strong materials like D2 or high-speed steel. These materials help blades last longer and work better.
- Make sure blade materials are hard but also tough. This helps blades stay sharp and not break easily.
- Use special heat treatments to make blades harder and tougher. This helps blades last longer and cut better.
- Keep blades clean and use oil to stop them from sticking. This helps blades cut smoothly, especially with stainless steel.
- Set the blade clearance at 7.5% of the material thickness. This helps you get good cuts and makes blades last longer.
- Check and sharpen blades often to keep them working well. This stops rough or uneven cuts from happening.
- Follow industry rules and advice when picking blades. This helps you choose the right blade for your cutting job.
- Think about custom blades for special jobs. Custom blades can help you cut better and meet your needs.
Shear Blades for Stainless Steel: Key Performance Factors
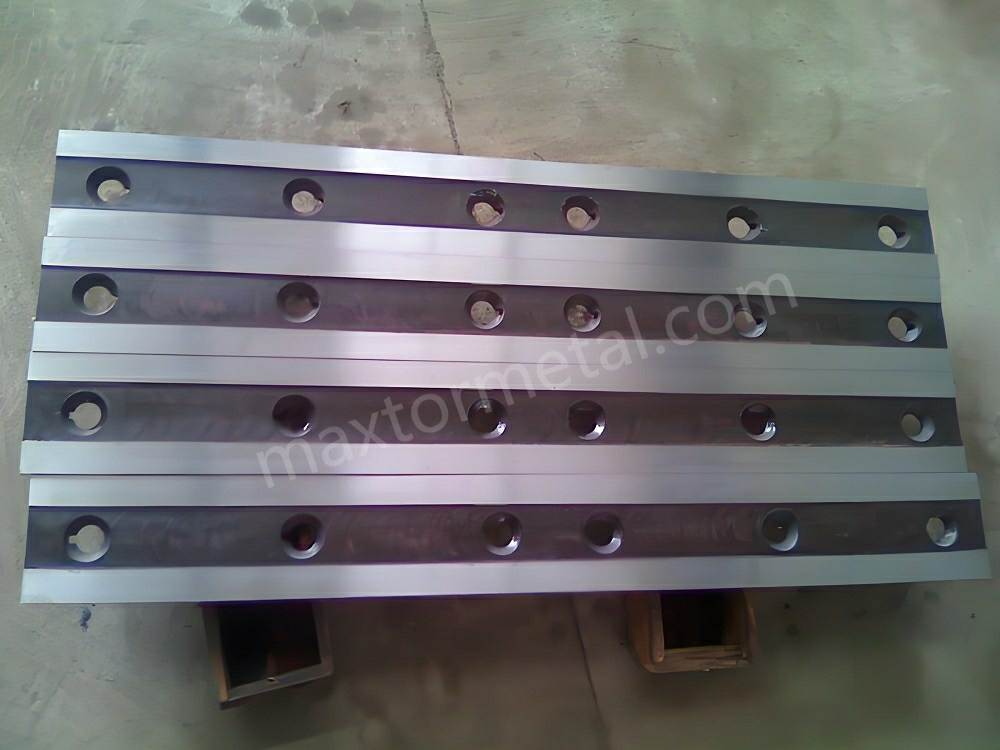

When you pick shear blades for stainless steel, some things matter a lot. These things help you get clean cuts. They also help you use your blades longer and stop downtime. Let’s look at what is most important.
Hardness, Toughness, and Wear Resistance
Balancing Blade Properties
You want blades that stay sharp and last long. Hardness keeps the blade edge sharp and stops wear. Toughness helps the blade take hits without breaking. If a blade is too hard, it can chip. If it is too tough, it may not stay sharp. You need to find the right mix.
- Hardness keeps the blade sharp for more time.
- Toughness stops the blade from breaking when used a lot.
- The right mix means the blade works well and lasts longer.
Impact of Advanced Heat Treatment
Advanced heat treatment helps a lot. This process changes how the steel acts. It helps the blade get the best hardness and toughness. At Nanjing Metal Industrial, blades get special heat treatment. This makes shear blades for stainless steel work better and last longer. You can ask for custom heat treatment if you need it.
Corrosion Resistance and Metallurgy
Stainless Steel’s Unique Challenges
Stainless steel is hard to cut. It can make blades wear out fast. Galling can happen, which means metal sticks to the blade. You need blades with the right alloying elements. Chromium, nickel, and vanadium help blades fight rust and damage.
| Propriété | Description |
|---|---|
| Alloying Elements | Chromium, nickel, and vanadium make blades stronger and fight rust. |
| Résistance aux chocs | Alloy steel takes hits and keeps the blade in good shape. |
| Résistance à la corrosion | These things help blades last longer, even in tough jobs. |
Preventing Galling and Edge Welding
Galling and edge welding can mess up your cuts. You can stop these problems with smooth blades and the right finish. Lubrication helps too. Keep blades clean and use the right oil when cutting. This helps blades move well and stops metal from sticking.
Industry Standards and OEM Recommendations
Capacity Reduction for Stainless Steel
Always follow industry standards when picking shear blades for stainless steel. Experts say D2 steel lasts long and saves money. M2 steel is good for tough jobs. Check the hardness range for your job.
| Type de matériau | Exemples | Hardness Range (HRC) | Domaine d'application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-bonded tool steel | 65, 75 steel, T8, T10 | 57-59 | Low-carbon cold-rolled plates |
| Low-alloy tool steel | 6Crw2sI, Cr5Mo1V, 9CrSi | 58-62 | Stainless steel, medium and thick plates |
| Alloy tool steel | 4Cr5MoSiV1 (H13K), H13 | High temperature resistance | Hot-rolled steel billets, hot shearing |
Conseil: When you cut stainless steel, lower the machine’s rated capacity by 20-30%. This stops blade overload and keeps cuts clean.
Look for blades that are easy to clean and take care of. This helps you follow hygiene rules, like in food factories. Precision matters for fast work. Strong, tough, and rust-fighting steel is needed.
Key Performance Factors Table
Here is a quick look at the most important things for shear blades for stainless steel:
| Performance Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition du matériau | The right materials, like alloy tool steels and carbide, make blades last and cut better. |
| Découpe de précision | Accurate blades give tight cuts and clean edges. |
| Efficacité opérationnelle | Good blades cut downtime and can boost work by up to 30%. |
| Rentabilité | Good blades save money by cutting waste and fixing less. |
| Pratiques d'entretien | Sharpen and oil blades often to keep them working well. |
If you want expert help or need a special blade, Nanjing Metal Industrial has many choices and strong quality checks. You can ask for help with your needs anytime.
Blade Materials: Comparison and Selection
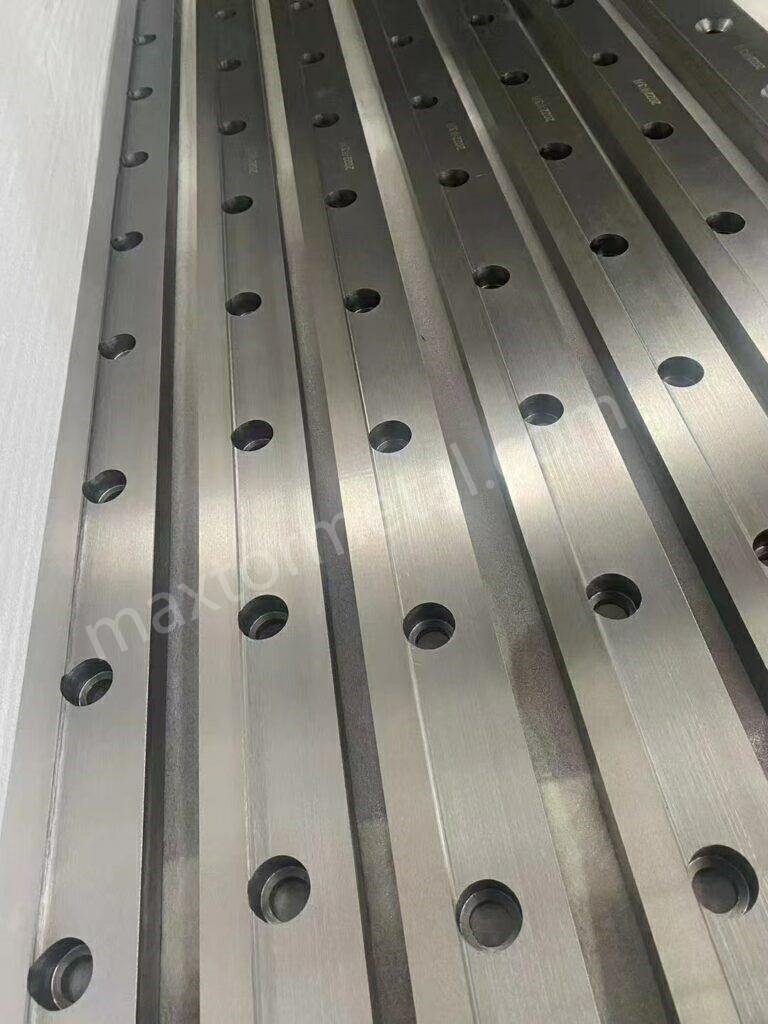

Picking the right blade material helps you get clean cuts on stainless steel. You should think about hardness, toughness, résistance à l'usure, and cost. Each material has its own strengths for cutting.
Tool Steels (D2, HCHC, A8 Mod)
High Chromium and Carbon Content
Tool steels like D2, HCHC, and A8 Mod have lots of chromium and carbon. These elements help blades stay sharp and not wear out fast. Blades last longer and keep their edge after many cuts.
Here is a table that shows how popular tool steels compare:
| Acier à outils | Dureté (HRC) | Résistance à l'usure | Dureté | Usinabilité | Meilleures utilisations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2 | 60-62 | Bien | Better | Easier | Punches, dies, industrial knives |
| D3 | Up to 64 | Excellent | More brittle | Requires advanced techniques | Shearing blades, wire-drawing dies |
| A8 | 60 | Haut | Bien | More challenging | Cutting tools, dies |
Conseil: D2 tool steel gives a good mix of hardness and toughness. You can use it for many jobs in factories.
Suitability for Stainless Steel
Blades must handle tough stainless steel. D2 and A8 Mod tool steels have high wear resistance and keep their edge. These steels stay sharp for a long time. You will not need to change blades as often.
- High wear resistance and hardness help cut stainless steel with less blade wear.
- Good toughness and strength mean blades do not break easily.
- Sharp edges last longer, so you do not need to fix them often.
A8 tool steel is good for cutting tools and dies. It is strong and gives precise cuts. It can be harder to machine, but it works well for tough jobs.
High-Speed Steels and Carbide
Performance in Demanding Applications
High-speed steel (HSS) and carbide blades work well for hard jobs. These blades last longer and make cleaner cuts. HSS blades are good for softer metals like stainless steel and aluminum. Tungsten carbide blades are best for tough, long jobs.
| Type de lame | Résistance à l'usure | Lifespan Compared to HSS | Avantages | Inconvénients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acier à haute vitesse | 5,000 cuts on low-carbon steel | N / A | Good impact resistance, cost-effective | Lower wear resistance on harder materials |
| Carbure de tungstène | High wear resistance | Approximately 3 times longer | Extreme hardness, suitable for high-intensity cutting | Prone to chipping under heavy impact |
- HSS blades are good for stainless steel and can take hits.
- Tungsten carbide blades last longer and do hard jobs, but they may chip if hit hard.
Cost vs. Longevity
You should think about how much blades cost and how long they last. HSS blades cost about twice as much as regular steel blades. They last 2-3 times longer and can make 4,000-6,000 cuts before sharpening. Carbide blades cost 3-4 times more than HSS blades. They last 3-5 times longer and can make over 20,000 cuts before you need to fix them.
| Type de lame | Comparaison des coûts | Longevity Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| HSS | 2x Standard Steel | 2-3x Standard Steel, 4,000-6,000 cuts per sharpening |
| Carbure | 3-4x HSS | 3-5x HSS, over 20,000 cuts before service |
Note: Carbide blades last the longest, but they cost more. HSS blades give a good balance of price and how well they work.
Customization and Quality Control
Metal Industrial’s Custom Blade Options
Sometimes you need blades with special sizes or shapes. Metal Industrial can make custom blades for you. You can pick materials like D2 tool steel, H13 hot-work steel, or tungsten carbide. These blades are made with exact sizes and advanced CNC grinding for sharp cuts. Custom blades can have different lengths, thicknesses, edge shapes, and hardness. Special coatings help blades resist heat and rust.
| Option de personnalisation | Description |
|---|---|
| Matériaux de première qualité | High-grade D2 tool steel, H13 hot-work steel, and tungsten carbide for durability and wear resistance. |
| Ingénierie de précision | Exacting tolerances and advanced CNC grinding for optimal cutting precision. |
| Custom Design Options | Tailored solutions with custom lengths, thicknesses, edge geometries, and hardness levels. |
| Heat & Corrosion Resistance | Specialized treatments and coatings for resistance to high temperatures and chemical degradation. |
| Durabilité améliorée | Advanced manufacturing techniques ensure blades withstand high-impact applications. |
| Entretien facile | Designed for simple sharpening, reducing downtime and operational costs. |
| Application-Specific Designs | Optimized for various materials including stainless steel, enhancing cutting performance. |
Quality Control Processes
You want blades that work the same way every time. Nanjing Metal Industrial uses strict checks to make sure you get good shear blades for stainless steel. The company uses special tools to check the back gage for accuracy within ±0.005″. Machine settings like blade speed, hold-down pressure, and shear angle are set for each job. After cutting, the team checks blade edges for burrs or damage.
| Fréquence d'inspection | Tâches | Points clés |
|---|---|---|
| Tous les jours | Clean blades, check for visible wear, lubricate | Look for dullness, chips, cracks, and rust |
| Hebdomadaire | Inspect alignment, check blade clearance, review cut quality | Measure blade thickness and check for straightness |
| Mensuel | Full blade maintenance check, including calibration and detailed inspection | Inspect mounting bolts for tightness |
You can expect advanced tools like calibration probes, laser scanners, and sensors for high accuracy. These steps help blades last longer and cut better.
Conseil: Custom blades and strict checks help you get the best results when cutting stainless steel.
Blade Geometry and Cutting Efficiency

Blade geometry is very important for cutting stainless steel. The right shape and settings help you make smooth cuts. They also help your blades last longer. Let’s see what parts of blade geometry matter and how to use them well.
Edge Angles and Profiles
Optimizing for Stainless Steel
You must pick the right edge angle and profile. A sharp angle cuts cleaner but wears out faster. A blunt angle lasts longer but may not cut as well. For stainless steel, you need a balance. Most shops use an edge angle from 20° to 25°. This gives a sharp edge that can handle tough metal.
The blade’s profile is important too. A straight profile works for most sheet and plate cutting. For thicker or harder metal, a curved or beveled edge helps. This spreads the force and lowers stress on the blade.
| Aspect of Blade Geometry | Impact on Cutting Efficiency and Quality |
|---|---|
| Proper blade geometry | Makes smooth cuts and less burrs, so you do not need much extra work. |
| Incorrect blade geometry | Can cause tearing, too much heat, and blades wearing out too soon. |
| High cutting precision | Means less waste and better products, which is important for safety. |
| Material composition | Decides what shapes work best and how long blades last. |
Tip: Always match your blade’s shape to the thickness and type of stainless steel you cut. This helps you get good results and keeps blades working longer.
Blade Clearance and Tolerances
Importance of Tight Clearance
Blade clearance is the small space between the top and bottom blades. You must set this space just right. If it is too wide or too tight, your cuts and blades will have problems.
| Dédouanement (%) | Effet sur la qualité de coupe et la durée de vie de l'outil |
|---|---|
| 7.5 | Best for good cuts and longer blade life |
| >7,5 | Causes burrs and worse cut quality |
| <7,5 | Makes double-shear and wears blades faster |
Set your clearance at 7.5% of the metal’s thickness. This gives the best mix of cut quality and blade life.
Risks of Incorrect Settings
If you do not set the clearance right, you can have problems:
- Cuts may be rough with more burrs and bent metal.
- Blades wear out faster and need to be changed more.
- Machines may use more power and work less well.
- It can be unsafe for workers if blades break.
Check your blade clearance often. Small mistakes can cause big trouble in your shop.
Surface Finish and Lubrication
Preventing Galling and Work Hardening
Stainless steel can stick to blades and cause galling. The metal can also get harder at the cut edge. This makes later cuts harder. You can stop these problems by using the right surface finish and lubrication.
Austenitic stainless steels bend instead of cracking. This can make the metal stick to the blade. Work hardening happens where the blade touches the metal. This makes the surface harder and stickier. The oxide layer on stainless steel can break under pressure. This makes galling more likely.
- High ductility means the metal bends easily when rubbed.
- Work hardening makes the surface harder and stickier.
- The metal’s reactive nature makes it bond more.
You can use these ways to stop galling and work hardening:
| Prevention Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Lubricate if possible | Lubricant makes a layer that stops metal from sticking. |
| Avoid extremely smooth surfaces | Very smooth blades can make galling worse. |
| Increase contact area | Spreads out the force and lowers wear. |
Note: Always keep blades clean and use the right oil for your job. This helps you stop galling and keeps your cuts smooth.
When you use the right blade shape, set the right clearance, and care for your blades, you get the best results. Your shop will also be safer and work better.
Selection Guide: Choosing Shear Blades for Stainless Steel
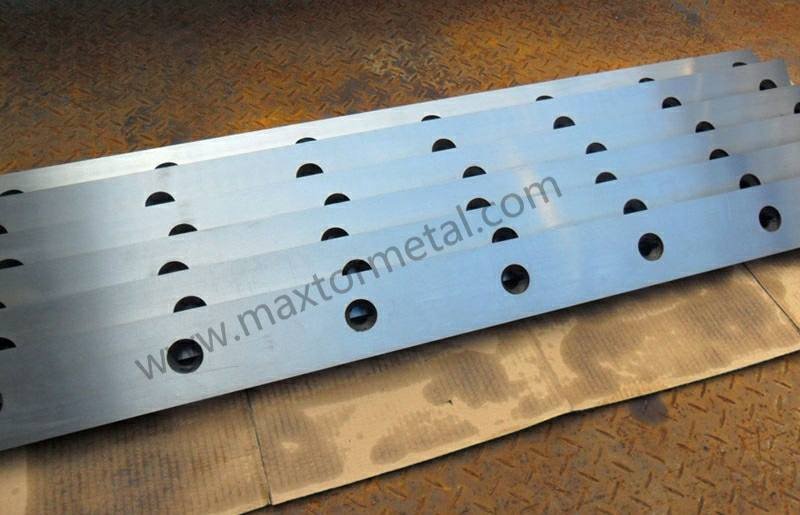

Picking the right shear blade for stainless steel is important. It helps you get clean cuts and makes blades last longer. You also spend less time fixing or changing blades. Think about the blade’s material, shape, and how you will use it. Follow these steps to make the best choice for your work.
Adaptation du matériau de la lame à l'application
The blade material you pick depends on how thick and strong the stainless steel is. Each material has its own hardness, wear life, and sharpening needs.
| Matériau | Wear Life | Affûtage | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acier 52100 | Faible | Not sharpened | Specific plastics |
| Acier D2 | Long | Facile | Plastiques, papier |
| Acier M2 | Increased | Facile | Non-woven materials, paper |
| CPM 10V | Haut | Facile | Plastiques multicouches, papiers |
| Incrustation en carbure | Haut | Maintient la netteté | Abrasive materials |
For stainless steel, alloy tool steels and high-speed steels work best. Here are some common types and what they do:
- 6CrW2Si Alloy Tool Steel is good for regular steel and hard stainless-steel plates.
- W6Mo5Cr4V2 High-Speed Tool Steel can handle fast cutting and heavy loads.
- Cr12MoV Die Steel is used for hydraulic shear blades with big cross-sections.
- 9CrSi Alloy Tool Steel gives high wear resistance and does not bend much.
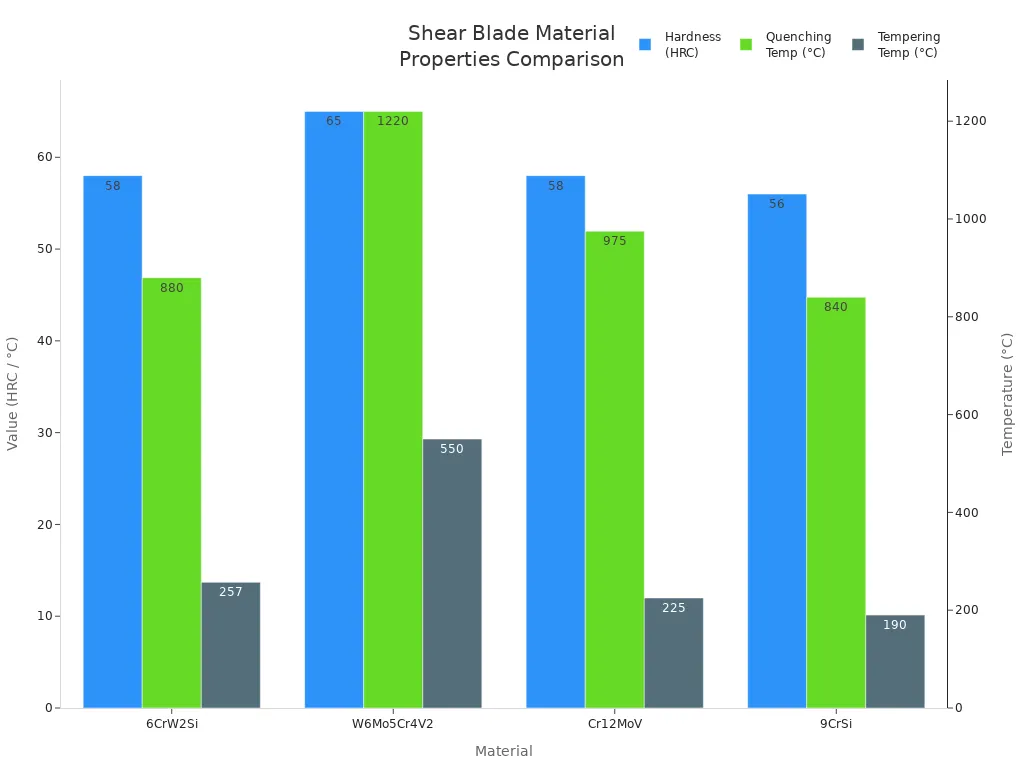
You can also look at how hard these materials are and how they are treated with heat:
| Matériau | Dureté (HRC) | Quenching Temp (°C) | Tempering Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6CrW2Si | 56 ~ 60 | 860 ~ 900 | 285 ~ 229 |
| W6Mo5Cr4V2 | 62 ~ 68 | 1210 ~ 1230 | 540 ~ 560 |
| Cr12MoV | 56 ~ 60 | 950 ~ 1000 | 200 ~ 250 |
| 9CrSi | 55 ~ 58 | 820 ~ 860 | 180 ~ 200 |
Thickness and Grade Considerations
You need to match the blade to the thickness and grade of the stainless steel. Thicker or harder steel needs blades that are tougher and last longer. For thick or strong stainless steel, W6Mo5Cr4V2 high-speed steel is best. For thin sheets, 6CrW2Si or Cr12MoV works well for sharpness and strength.
Tip: Pick a shear that can cut steel 1.5 to 2 times thicker than what you need. This keeps blades from breaking and helps them last longer.
Geometry Selection for Cut Quality
The shape of your blade changes how good your cuts look. You need to pick the right edge angle and shape for your job.
Desired Finish and Efficiency
- Flat knife edge (90°) is used for most jobs. It gives a strong edge for general cutting.
- Oblique knife edge (82°) gives smoother and more even cuts. It is best for thin plates and makes the cut look better.
Match the edge type to how thick your stainless steel is. An oblique edge helps thin steel look better and have fewer burrs. A flat edge is stronger for thick plates.
Note: Always check if your blades are lined up and spaced right. This helps you get the best cuts and makes blades last longer.
Customization and Procurement
Sometimes you need special blades for certain jobs or machines. Metal Industrial lets you pick from many options to get the blade you need.
Metal Industrial’s Flexible Options
You can choose different materials, sizes, and edge shapes. Here are some tips for picking and ordering blades:
- Pick the right material for your job. AISI L6 is good for tough jobs. AISI D2 is better for sheet metal.
- Choose the blade shape that gives you the cut you want.
- Know the difference between swing beam shears and guillotine shears. Pick the one that fits your machine.
- Think about the types of steel: carbon-bonded, low alloy, and alloy tool steel.
- Ask for lame personnalisée lengths, thicknesses, or edge shapes to fit your machine.
- Ask about special coatings or heat treatments for blades that last longer and fight rust.
| Matériau | Application |
|---|---|
| AISI L6 | Heavy duty shear blades |
| AISI D2 | Sheet metal shear blades |
| A-2 | General use for shear blades |
Tip: Before you put in new blades, turn off the machine and lock it. Clean the blade holders and look for damage. Put in the new blades and check if they line up. Test with scrap metal to make sure the cut is good.
You can trust Metal Industrial’s quality checks and custom blade service. With many choices and expert help, you can make your cutting better and get great results.
Step-by-Step Selection Checklist
- Find out how thick and what grade your stainless steel is.
- Pick the blade material that fits your job and how long you want it to last.
- Choose the edge shape for the finish and speed you want.
- Decide if you need special sizes or coatings.
- Make sure the blade works with your machine.
- Work with a trusted company like Metal Industrial for good blades and help.
If you follow these steps, you will get shear blades for stainless steel that cut well, last long, and work every time.
Maintenance and Optimization

Proper care and handling of shear blades for stainless steel help you get the best results and extend blade life. You can avoid many common problems by following a few simple steps.
Affûtage et manipulation
Techniques for Stainless Steel Blades
You need to keep your shear blades for stainless steel sharp and clean. Regular maintenance stops rust and keeps your cuts smooth. Use the right sharpening angle for your blade type. Always inspect the blade for chips or cracks before and after use. Lubricate moving parts to reduce friction and wear. Check blade alignment often to make sure your cuts stay even.
Here is a table to help you remember the best maintenance actions:
| Maintenance Action | Recommended Interval/Condition |
|---|---|
| Nettoyage régulier | After each use to stop rust and keep cuts sharp. |
| Affûter les lames | When cuts get rough or harder to make. Use the right angle. |
| Inspect for Wear | Look for chips, cracks, or uneven edges every time you clean. |
| Lubrifier les pièces mobiles | After cleaning and before you put blades away. |
| Contrôles d'alignement | Check often to make sure cuts are even and blades wear less. |
| Replace Blades | If you see cracks, big chips, or if the blade gets too thin. |
Conseil: Always use gloves when handling blades. This keeps your hands safe and protects the blade edge.
Dépannage des problèmes courants
Galling, Chipping, and Poor Cuts
You may face some problems when using shear blades for stainless steel. Knowing how to spot and fix these issues helps you keep your blades in top shape.
- Dull Blades: Replace or sharpen blades when you notice rough or uneven cuts.
- Incorrect Blade Gap: Adjust the gap to match the thickness of your stainless steel. This prevents uneven cuts.
- Material Issues: Check the type and grade of stainless steel before cutting. Harder metals need different settings.
- Machine Jamming: Look for misaligned material, lack of lubrication, or hydraulic problems.
- Excessive Noise or Vibration: Tighten loose parts and check for worn blades. Make sure your machine sits on a stable surface.
- Electrical or Control Problems: Inspect controls and power supply. Test safety systems often.
Note: If you see galling or chipping, stop and inspect the blade. Clean and lubricate the blade before you continue.
Maximiser la durée de vie de la lame
Conseils de maintenance préventive
You can make your shear blades for stainless steel last longer with a few easy habits.
- Replace dull blades quickly. This prevents extra pressure on the machine and keeps cuts clean.
- Clean blades after every use. Remove dirt and rust, then apply rust-proof grease to unpainted parts.
- Clean the blade seat and pocket surfaces. This helps the blade fit well and reduces wear.
- Keep the blade edge sharp. Sharpen or replace blades before they get too dull.
- Follow the correct torque when tightening blade fasteners. This stops them from coming loose.
- Keep blades sharp by replacing them often.
- Clean blades to remove dirt and rust.
- Sharpen blades when they become dull.
Conseil: Regular maintenance saves you time and money. Well-cared-for blades cut better and last longer.
By following these steps, you keep your shear blades for stainless steel working at their best. Good maintenance means fewer problems and better results every time you cut.
When picking shear blades for stainless steel, look for strong materials and exact blade shapes. Good manufacturing helps blades work better and last longer. The table below shows how different blade materials help performance:
| Type de matériau | Avantages |
|---|---|
| Acier à outils au carbone | Works well and gives steady quality. |
| Acier à outils allié | Made for special jobs and cuts faster. |
| Heat Treated Blades | Mixes hardness, toughness, and wear resistance for best results. |
To keep blades working well, do these things:
- Clean blades and check them after every use.
- Oil blades often and keep them dry when stored.
- Get blades sharpened by experts.
If you need help, talk to our sales engineers for advice on your job.
FAQ
What makes shear blades for stainless steel different from regular blades?
Shear blades for stainless steel use tougher materials and special edge designs. You get cleaner cuts and longer blade life. These blades resist wear and galling better than regular blades.
How often should you sharpen shear blades for stainless steel?
You should sharpen blades when cuts become rough or uneven. Most shops check blades after every shift. Regular sharpening keeps your cuts smooth and helps blades last longer.
Which material works best for shear blades for stainless steel?
Tool steels like D2 and high-speed steels work best. These materials offer high hardness and wear resistance. Carbide blades last even longer but cost more.
How do you prevent galling when cutting stainless steel?
You can use lubrication and choose blades with the right surface finish. Clean blades often and avoid extremely smooth surfaces. This helps stop metal from sticking to the blade.
What edge angle should you use for cutting stainless steel?
Most experts recommend an edge angle between 20° and 25°. This angle gives you a sharp edge for clean cuts and helps the blade last longer.
Can you use the same shear blades for different grades of stainless steel?
You can use the same blades for many grades, but harder grades need tougher blades. Always check the blade material and adjust settings for each job.
How do you know when to replace shear blades for stainless steel?
Replace blades when you see chips, cracks, or dull edges. If cuts look rough or the blade gets too thin, it is time for a new blade.
What maintenance steps help shear blades for stainless steel last longer?
Clean blades after each use. Lubricate moving parts. Check alignment often. Sharpen blades before they get dull. These steps help you get the best performance and longer blade life.



2 réponses
I will right away grasp your rss as I can not find your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me recognise in order that I may subscribe. Thanks.
Thank you for your support. You can find the subscribe button at the bottom of the webpage. We look forward to receiving your subscription notification!